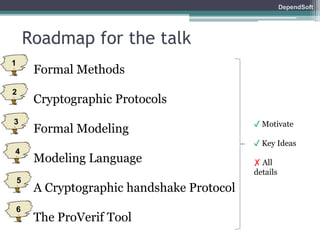
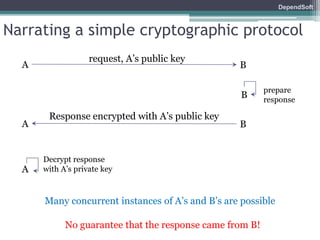
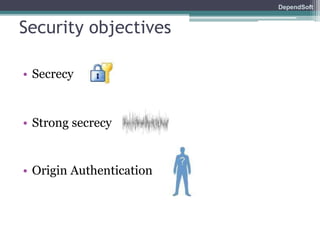
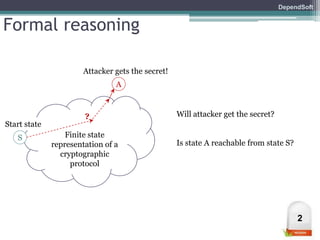
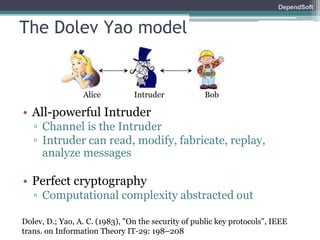
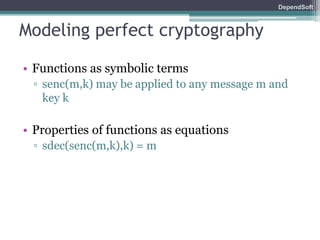
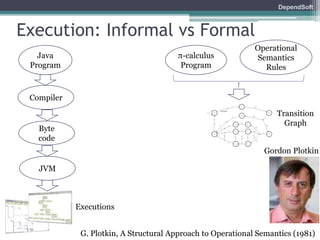
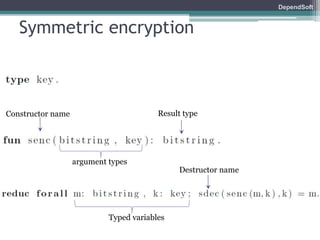
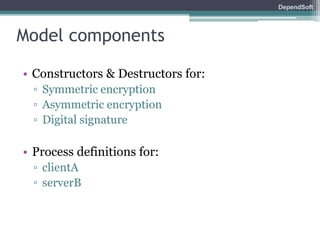
The document discusses formal modeling and analysis of cryptographic protocols. It introduces formal methods, the Dolev-Yao model, pi-calculus as a modeling language, and the ProVerif tool. As an example, a naïve handshake protocol is presented and a man-in-the-middle attack is demonstrated. The talk concludes that formal methods provide rigorous analysis of protocol security properties.