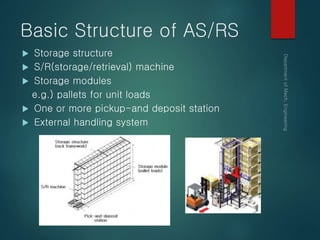
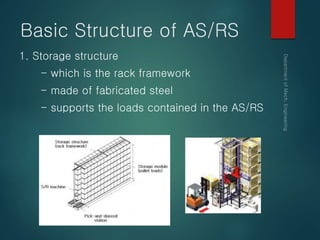
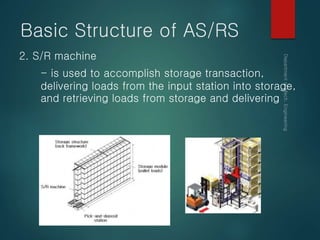
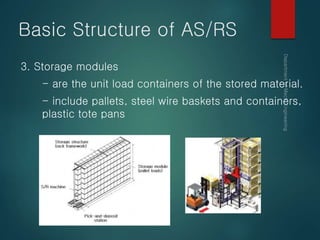
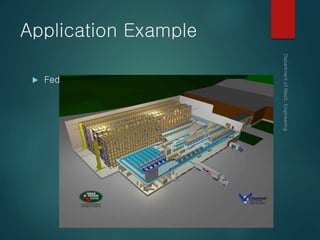
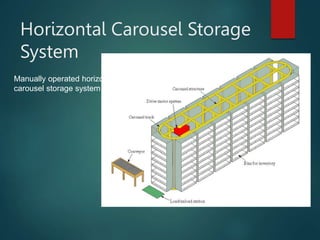
This document provides an overview of automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS). It discusses the problems with conventional storage systems and introduces the concept and basic structure of AS/RS. The structure includes storage racks, storage/retrieval machines, storage modules, pick-and-deposit stations, and external handling systems. It also covers AS/RS control using computers and positioning methods. Benefits include improved efficiency, accuracy, space usage, and costs. Design considerations include structural dimensions and load capacities. Carousel storage systems operate items on continuous conveyors and are used for storage, transport, and work-in-process applications.