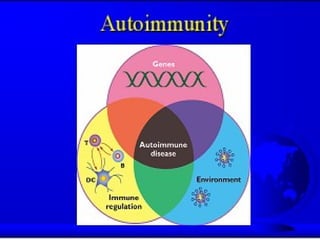
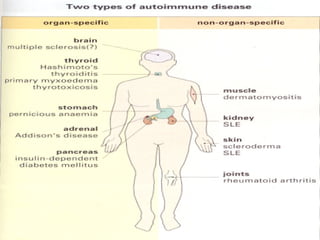
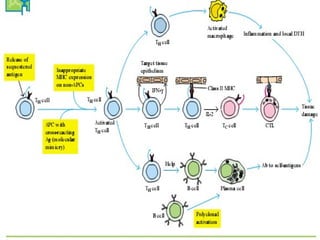
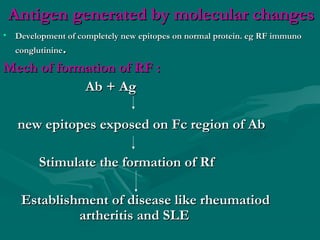
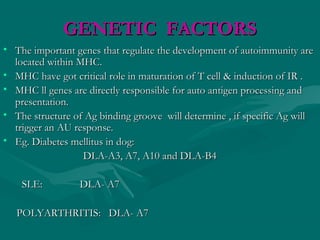
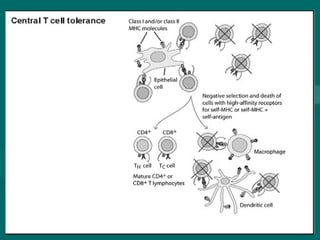
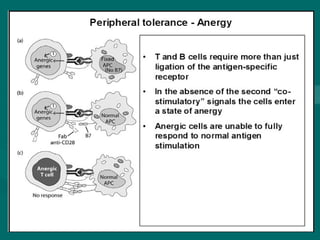
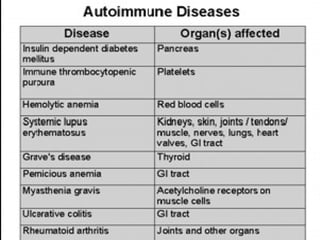
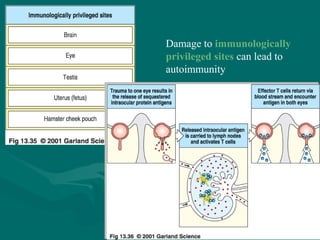
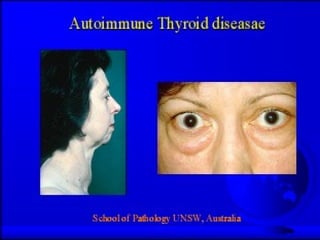
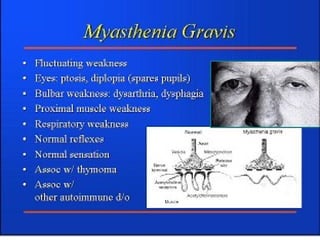
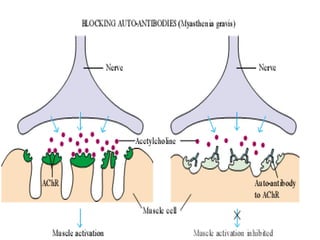
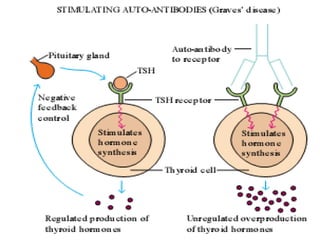
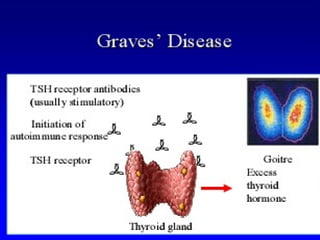
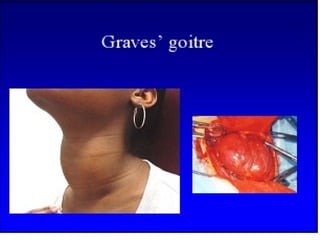
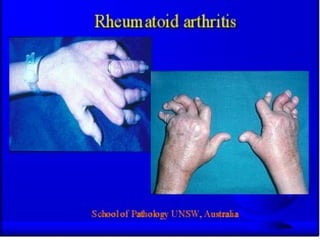
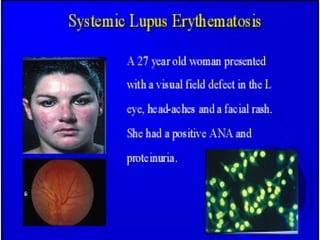
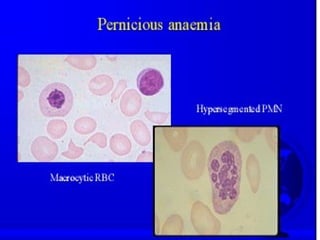
Autoimmunity is caused by a failure of self/non-self discrimination in the immune system. More than 40 human diseases are known to have an autoimmune origin, affecting 5-7% of adults, with women being affected more often than men. Left-handed individuals also seem to be more susceptible to autoimmune diseases than right-handed individuals, though the reasons for this are unclear. Common autoimmune diseases include rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, Graves' disease, and myasthenia gravis. Potential causes of autoimmunity include the release of sequestered antigens, molecular mimicry between self and foreign antigens, genetic factors, and infections that dysregulate the immune response. Treatment options aim to suppress the immune