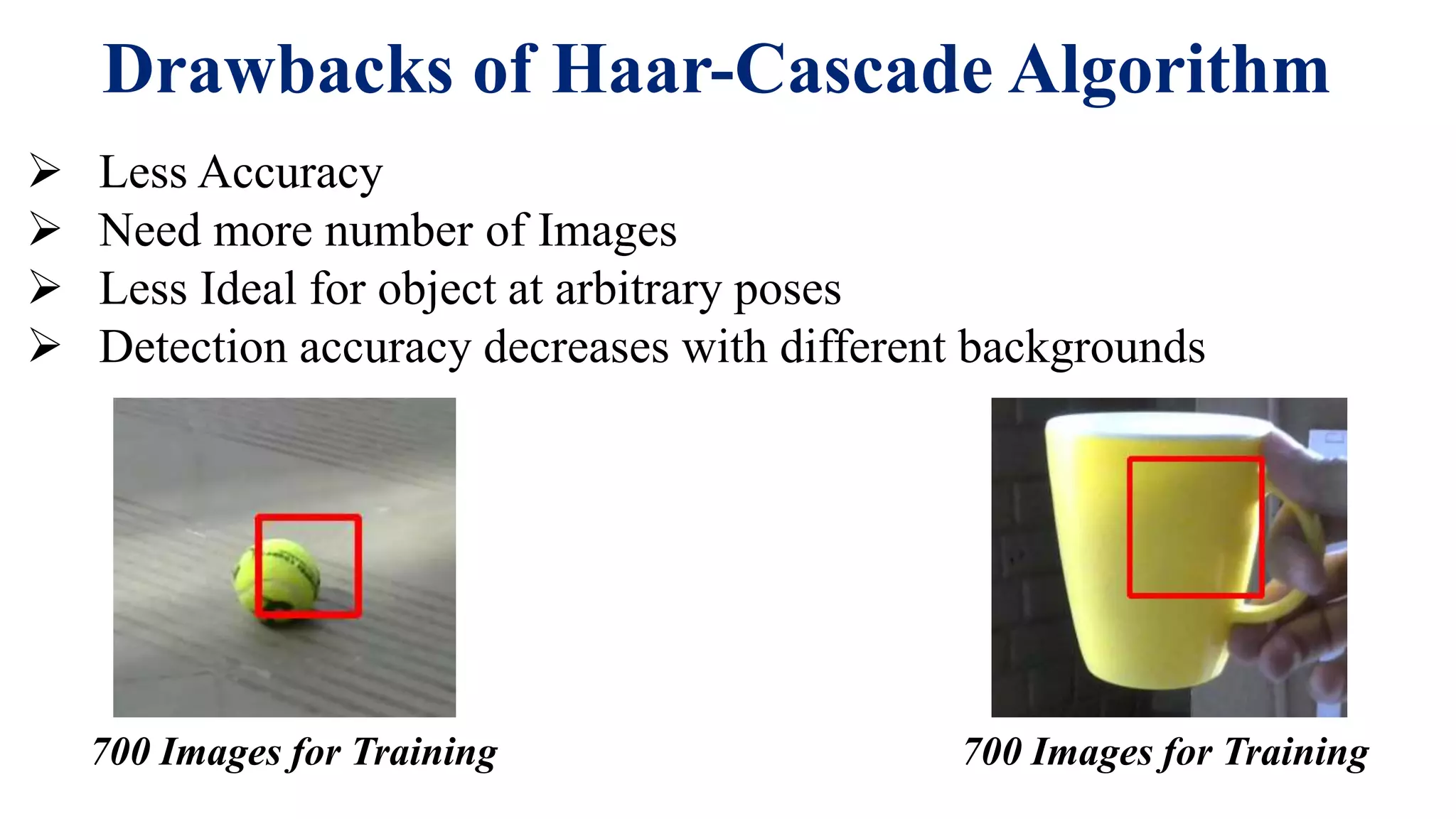
The document discusses the design of an auto-assistance system aimed at helping visually impaired individuals navigate independently, addressing the limitations of current tools like blind sticks and wheelchairs. It details the methodology using YOLO (You Only Look Once) for effective object detection, showcasing its advantages over traditional algorithms like Haar Cascade in terms of accuracy and real-time performance. The findings indicate that while Haar Cascade is faster on CPU, YOLO provides better accuracy for detecting multiple objects, thereby enhancing the independence of visually impaired users.