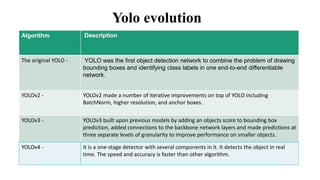
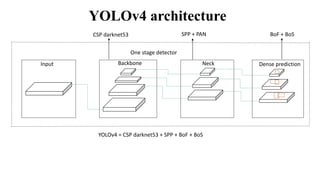
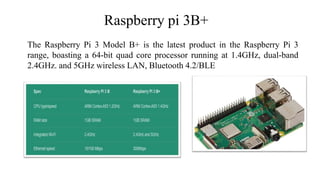
The document presents a major project on real-time object recognition designed to assist visually impaired individuals, utilizing the YOLO algorithm for object detection and audio output. It outlines the methodology, hardware requirements, and the advantages of the proposed system, which aims to enhance independence for blind users by providing fast and accurate object recognition. The project is based on a thorough literature review and aims to improve existing solutions for real-time assistance for the visually impaired.


![Introduction
The World Health Organization (WHO) had a survey over around 7889 million people.
The statistics showed that among the population under consideration while survey, 253
millions were visually impaired.[4]
There are many visually impaired people facing many problems in our society.
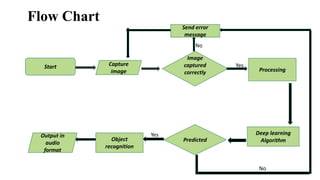
The device developed can detect the objects in the user's surroundings.
This is a model has been proposed which makes the visually impaired people detect
objects in his surroundings. The output of the system is in audio form that can be easily
understandable for a blind user.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-copy-240507182430-91fcab5e/85/ppt-Copy-for-projects-will-help-you-further-3-320.jpg)

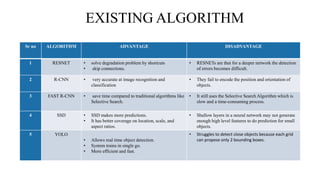
![Literature review
1. “The authors in(Seema et al ) suggested using a smart system that guides a
blind person in 2016[1]”
• The system detects the obstacles that could not be detected by his/her cane.
However, the proposed system was designed to protect the blind from the area
near to his/her head.
Problem statement - The buzzer and vibrator were used and employed as output
modes to a user. This is useful for obstacles detection only at a head level without
recognizing the type of obstacles.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-copy-240507182430-91fcab5e/85/ppt-Copy-for-projects-will-help-you-further-5-320.jpg)
![Contd.
2. “A modification of several systems used in visual recognition was proposed
in 2014.[2]”
• The authors used fast-feature pyramids and provided findings on general object
detection systems. The results showed that the proposed scheme can be strictly
used for wide-spectrum images.
Problem statement - It does not succeed for narrow-spectrum images. Hence,
their work cannot be used as efficient general objects detection.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-copy-240507182430-91fcab5e/85/ppt-Copy-for-projects-will-help-you-further-6-320.jpg)
![Contd.
3. “In (Nazli Mohajeri et al, 2011) the authors suggested a two-camera
system to capture photos”.[3]
• However, the proposed system was only tested under three conditions and for
three objects. Specific obstacles that have distances from cameras of about 70 cm
were detected.
Problem statement - The results showed some range of error. Blind helping
systems need to cover more cases with efficient and satisfied results.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-copy-240507182430-91fcab5e/85/ppt-Copy-for-projects-will-help-you-further-7-320.jpg)