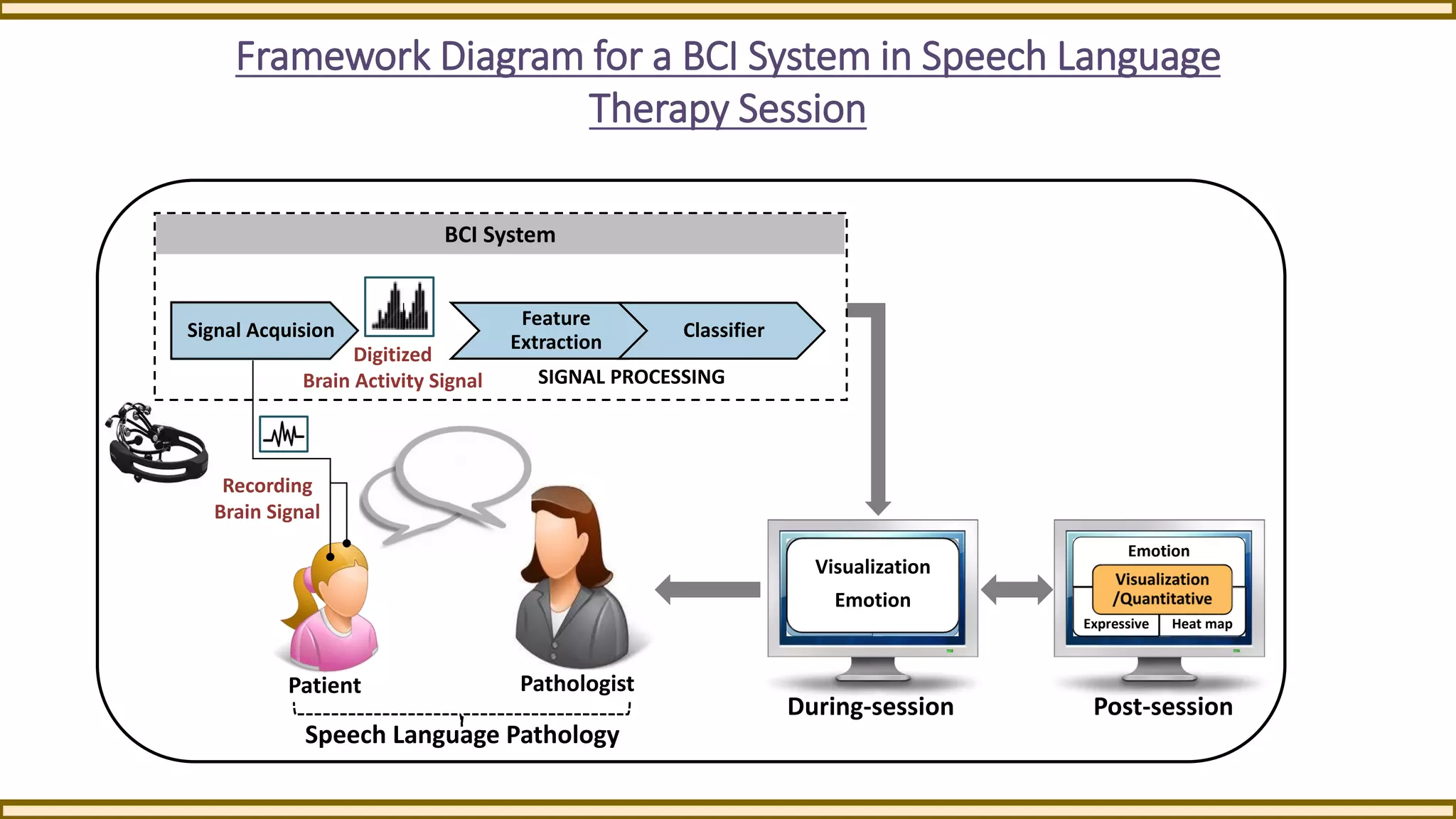
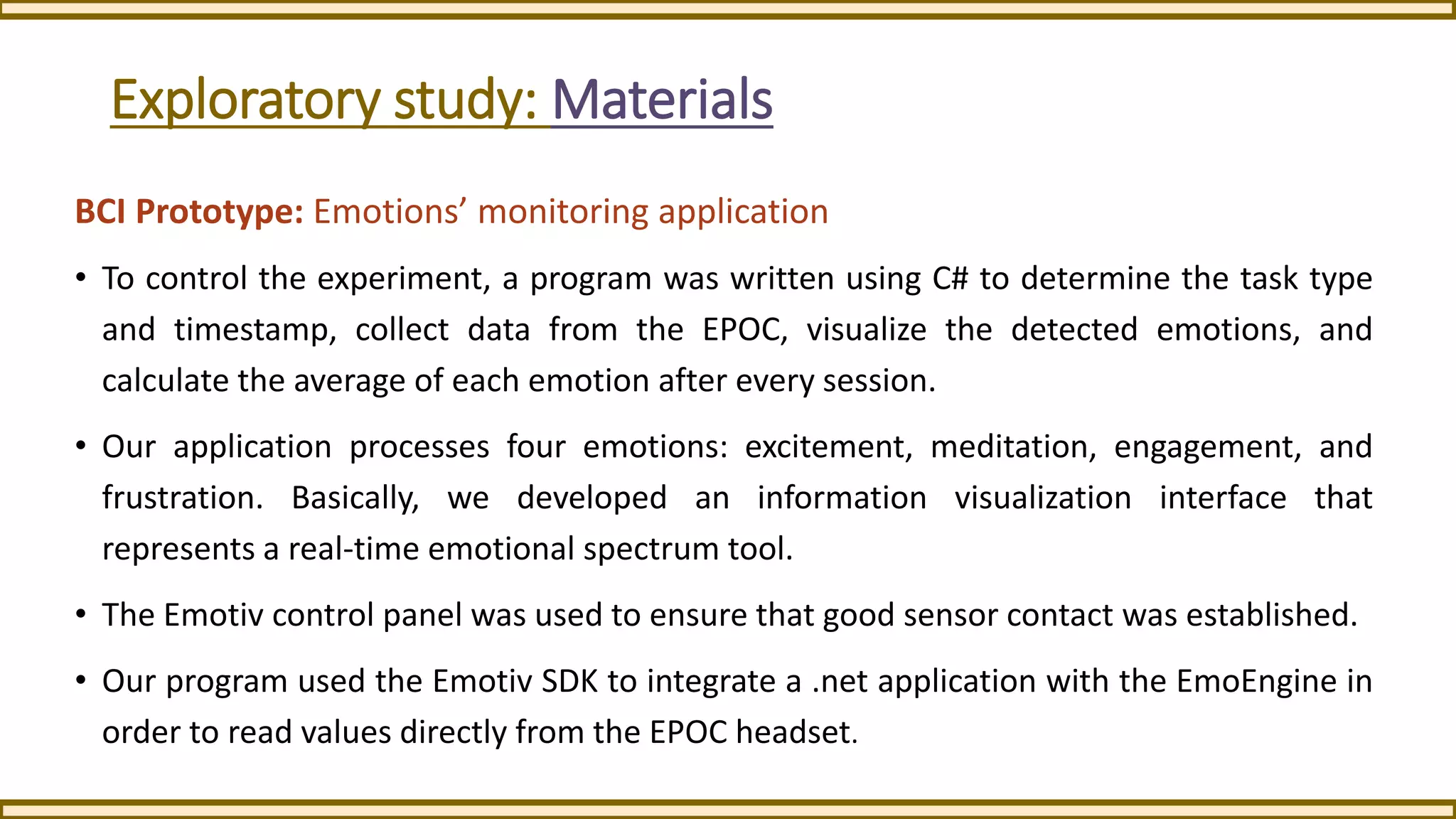
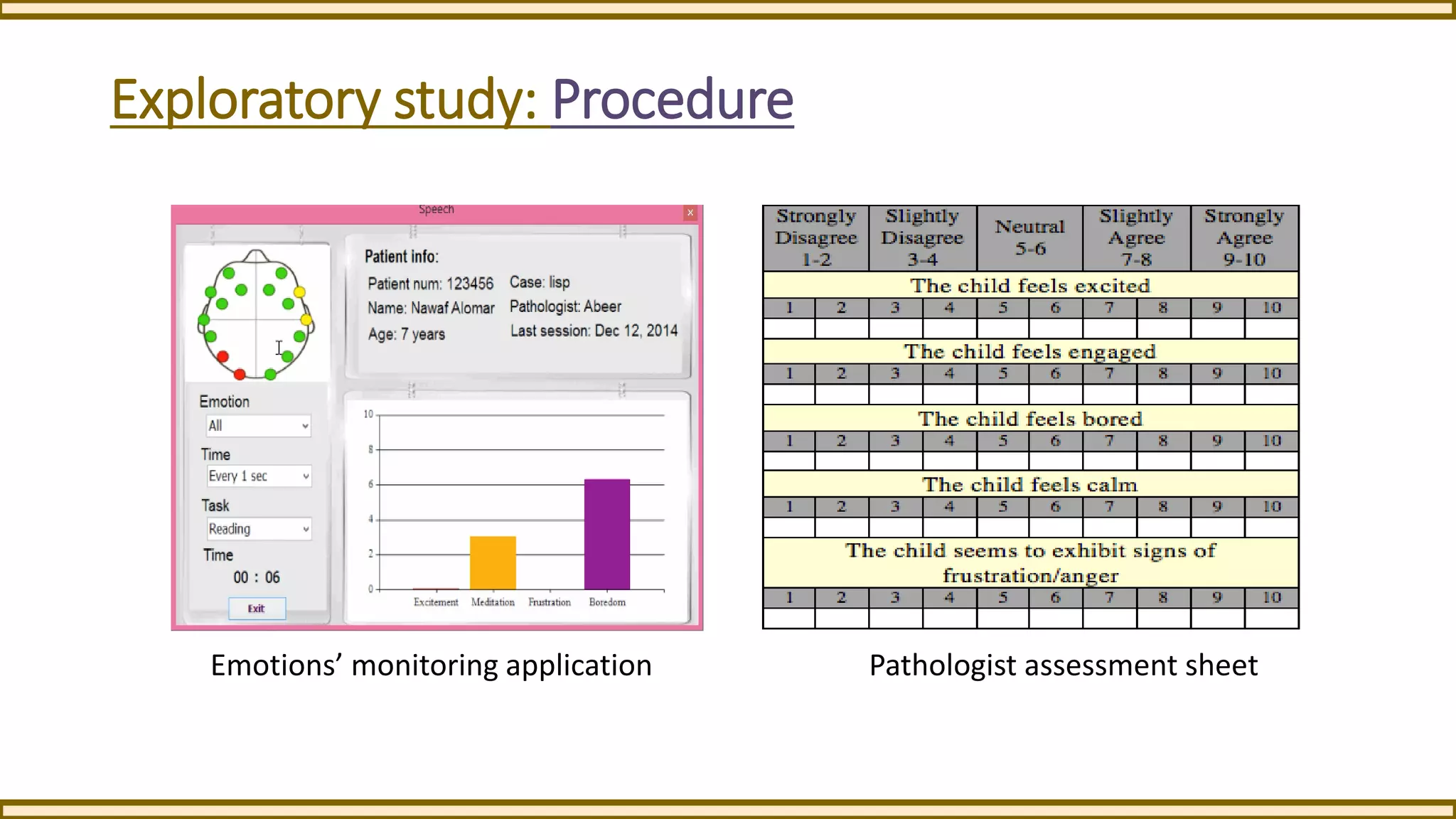
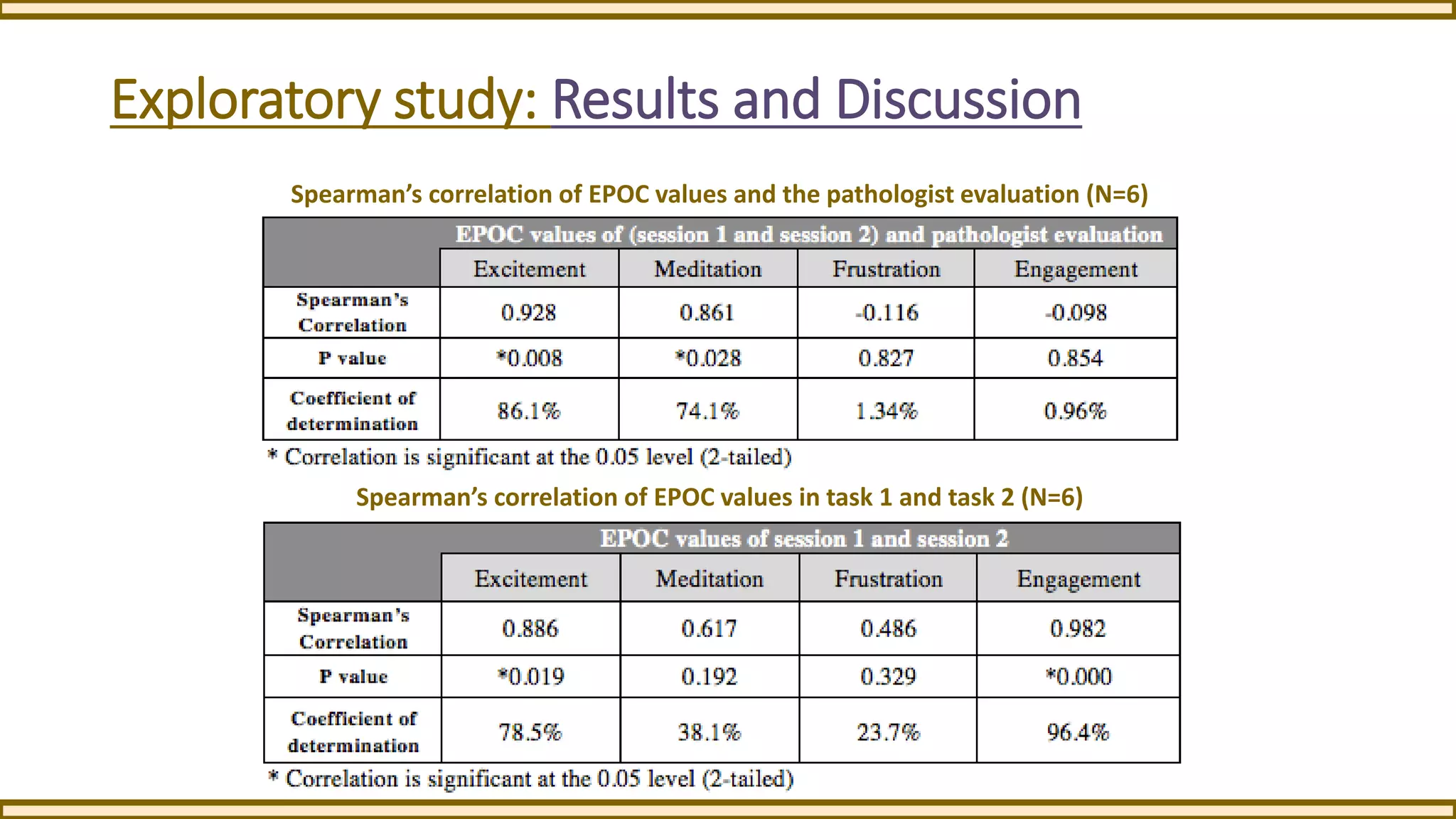
This exploratory study investigates the application of an EEG-based brain-computer interface (BCI) in speech-language rehabilitation, aiming to enhance therapy sessions by monitoring brain activity. The study outlines the potential benefits and challenges of using non-invasive EEG technology in a clinical setting, highlighting its ability to provide insights into cognitive and emotional states during therapy. Preliminary findings suggest that this framework could improve the assessment and treatment of speech and language disorders.