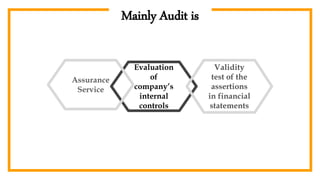
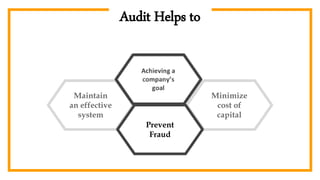
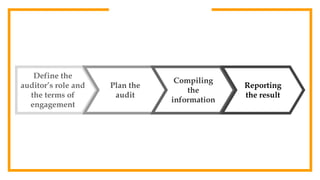
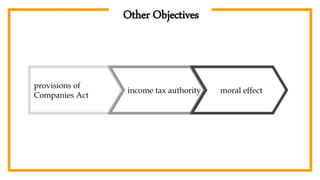
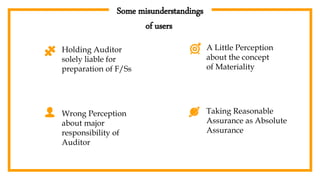
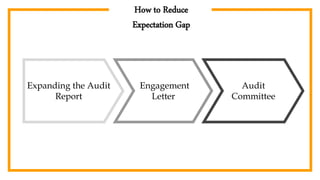
The document provides an overview of auditing, detailing its historical context, objectives, and processes. It stresses the importance of auditors in ensuring accurate financial statements and preventing fraud, along with their responsibilities under the Companies Act of 1994. Additionally, it discusses the concept of the 'expectation gap' between users' perceptions and auditors' responsibilities, and the essential components of an audit report.