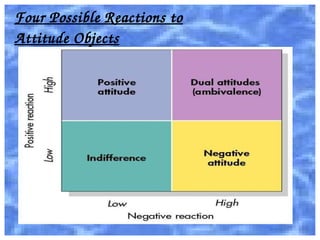
This document discusses attitude development and theories of attitude change. It defines an attitude as a positive or negative view of a person, place, thing or event. Attitudes have three components - cognitive beliefs, affective feelings, and behavioral reactions. Two major theories of attitude change are cognitive dissonance theory, which posits that people seek consistency between attitudes and behaviors, and self-perception theory, where attitudes form after behaviors to make sense of them. Attitudes alone do not strongly predict behaviors but can influence intentions and behaviors when important, specific, accessible, and socially reinforced with experience.