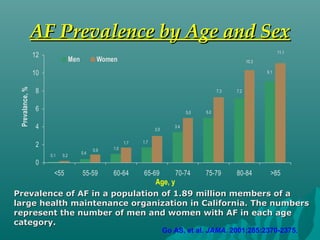
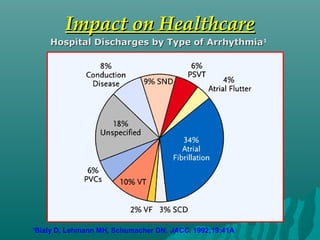
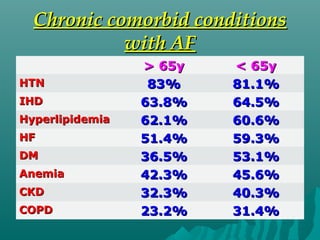
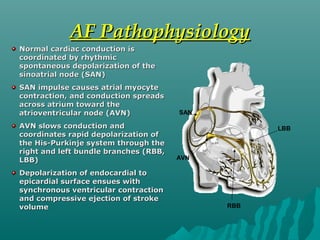
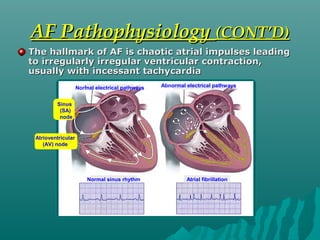
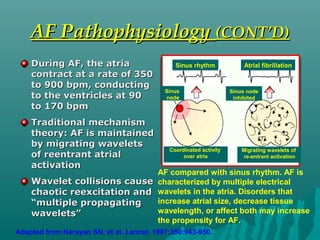
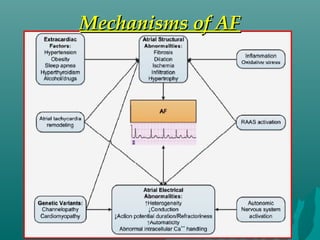
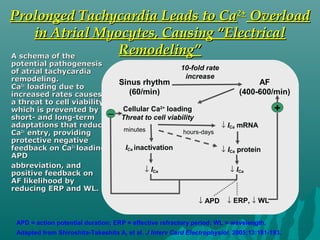
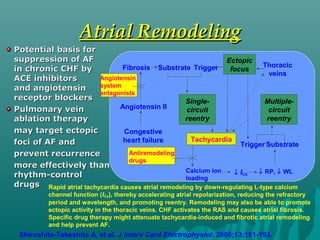
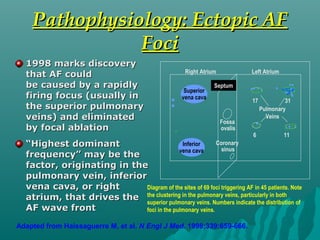
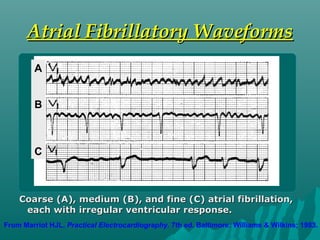
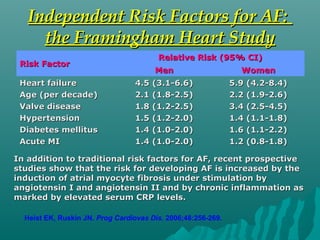
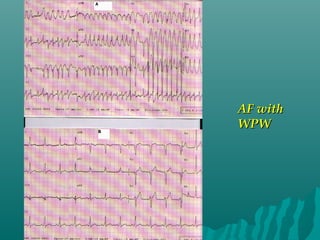
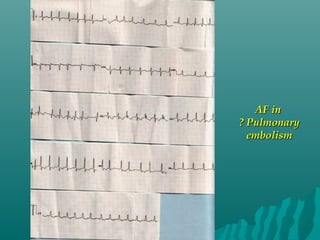
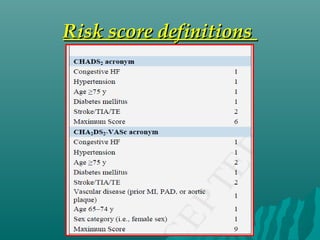
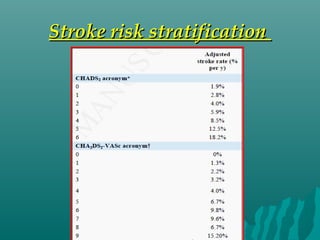
1. Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an irregular heartbeat that can lead to blood clots, stroke, heart failure, and other complications. It is the most common arrhythmia and its prevalence increases with age.
2. AF occurs due to uncoordinated electrical signals in the atria that cause rapid and irregular beating. Risk factors include heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, sleep apnea, and thyroid problems.
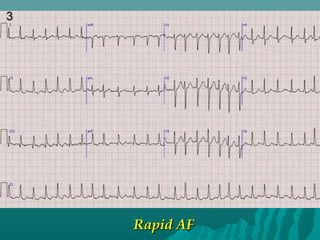
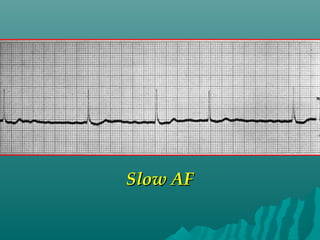
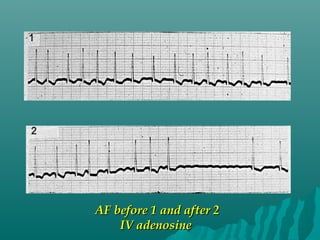
3. Diagnosis involves an electrocardiogram to detect the irregular rhythm. Treatment depends on symptoms and includes rate or rhythm control medications, lifestyle changes, and sometimes procedures like ablation to restore normal rhythm.