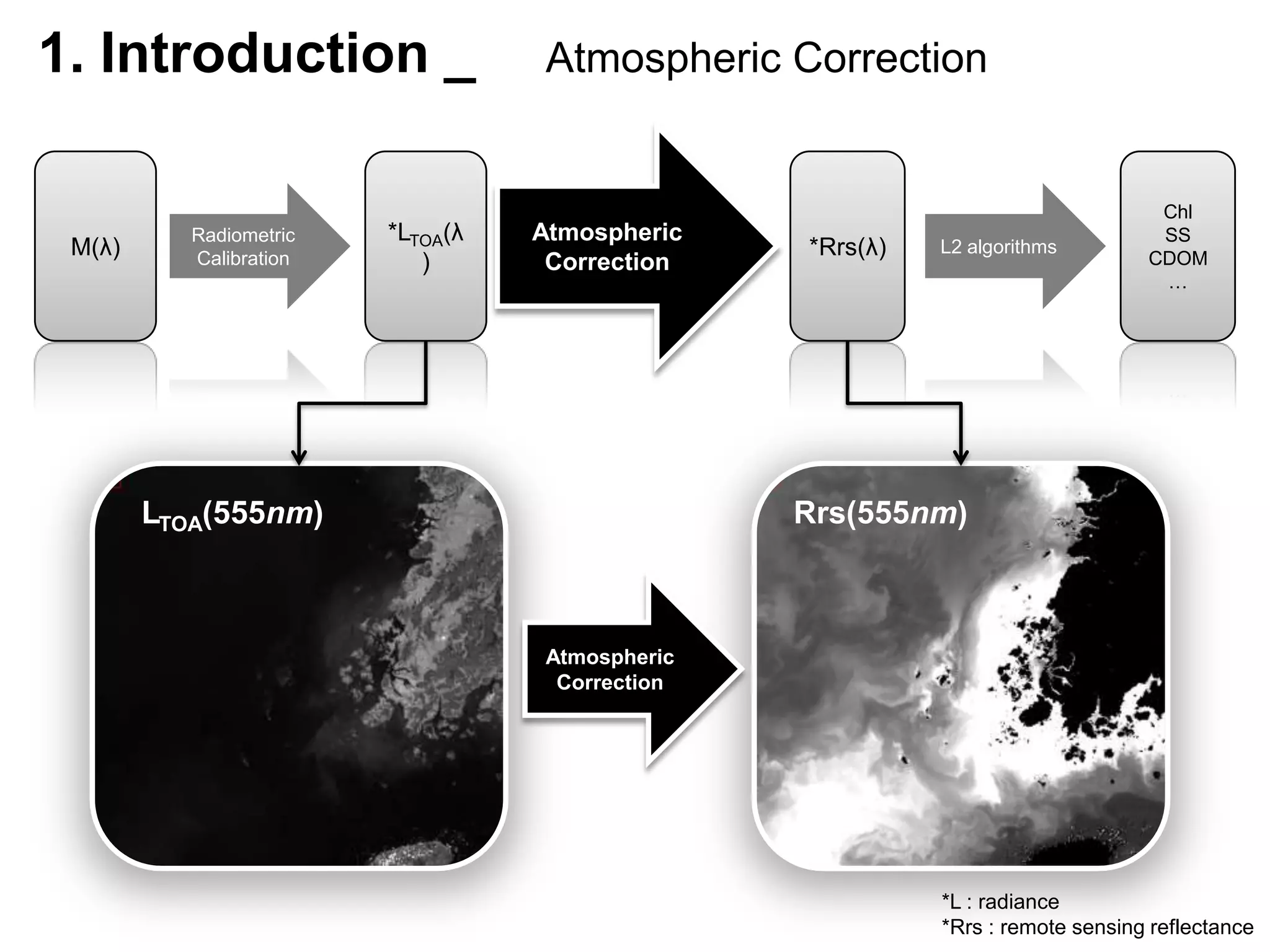
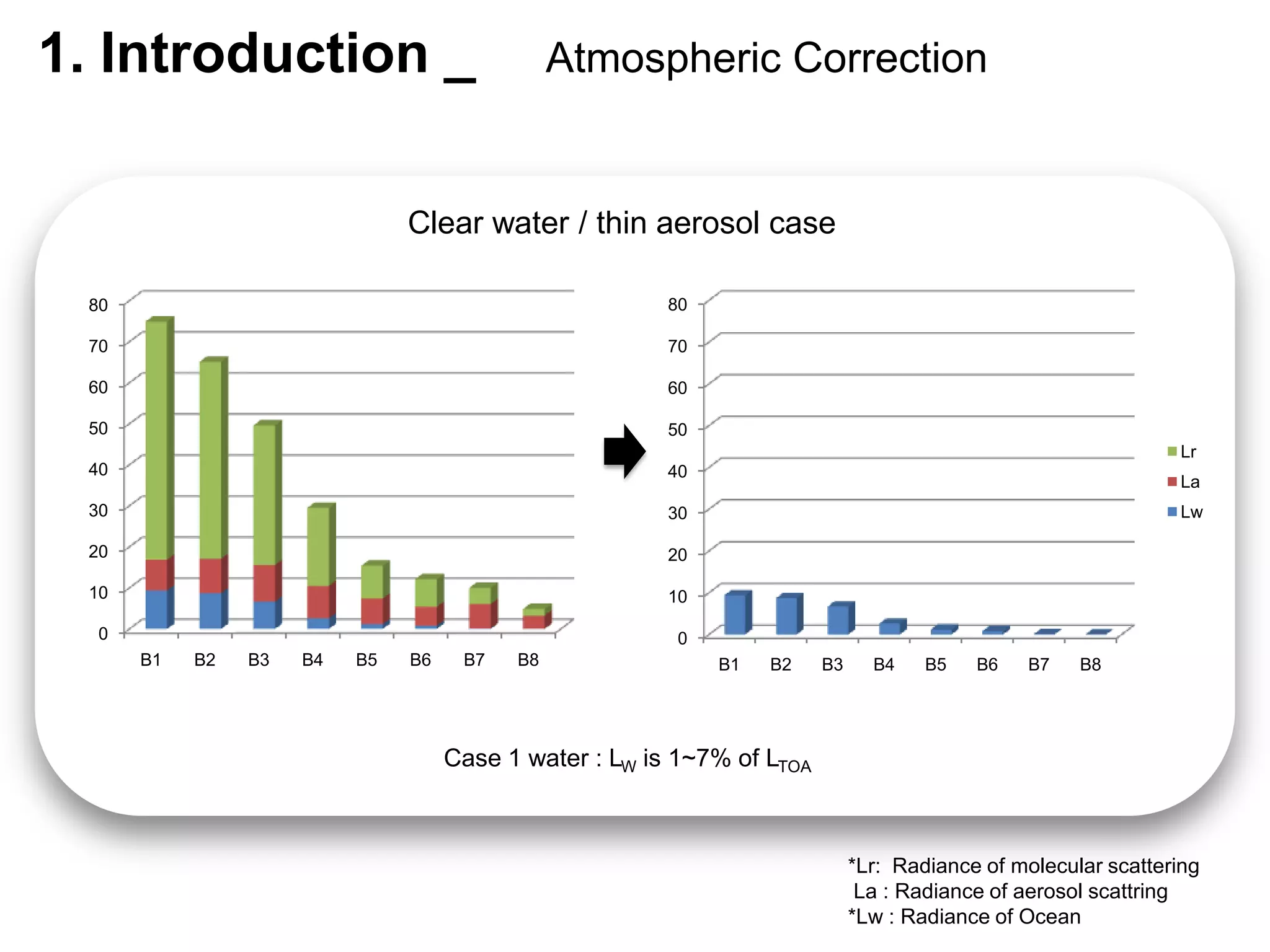
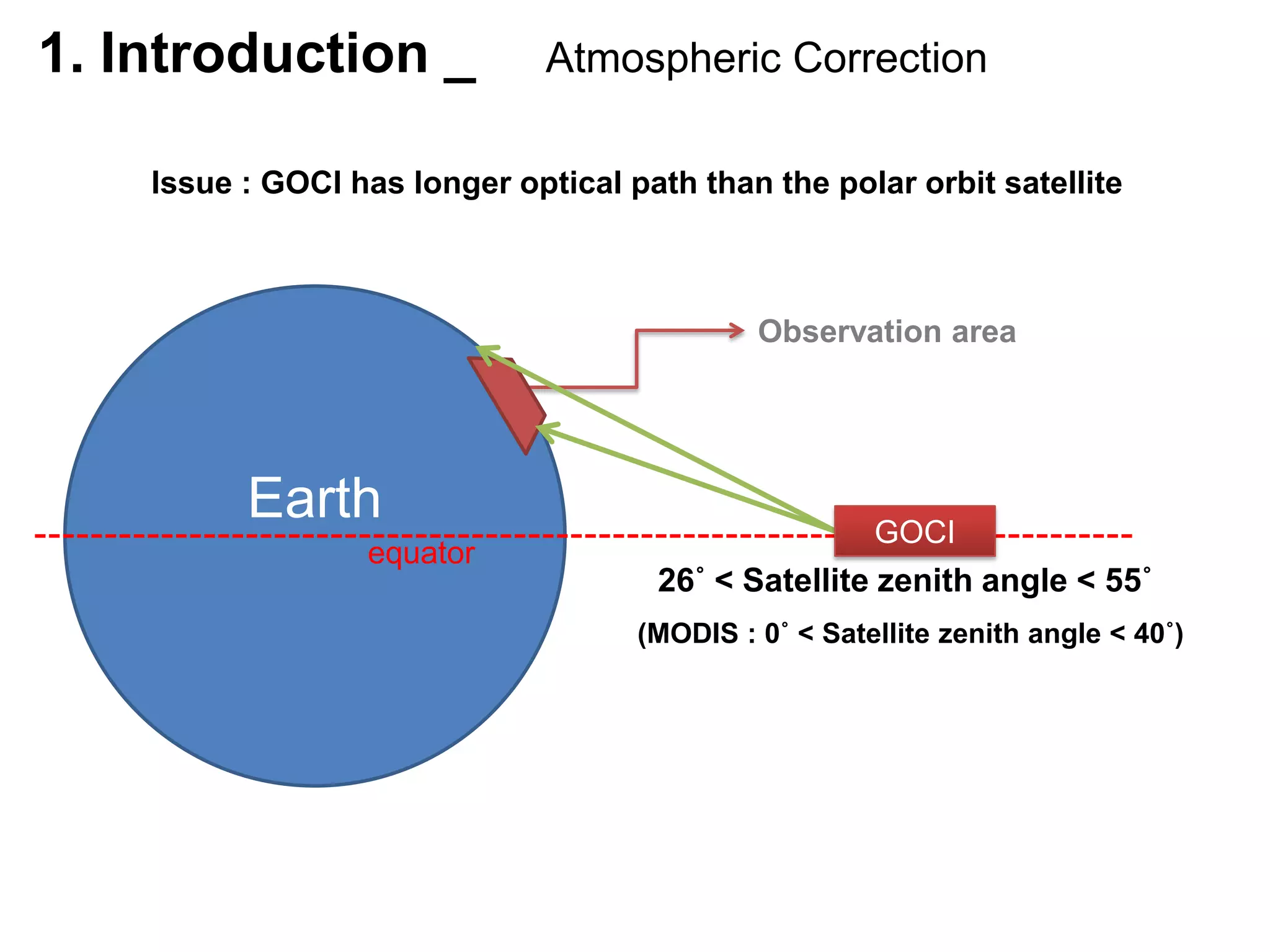
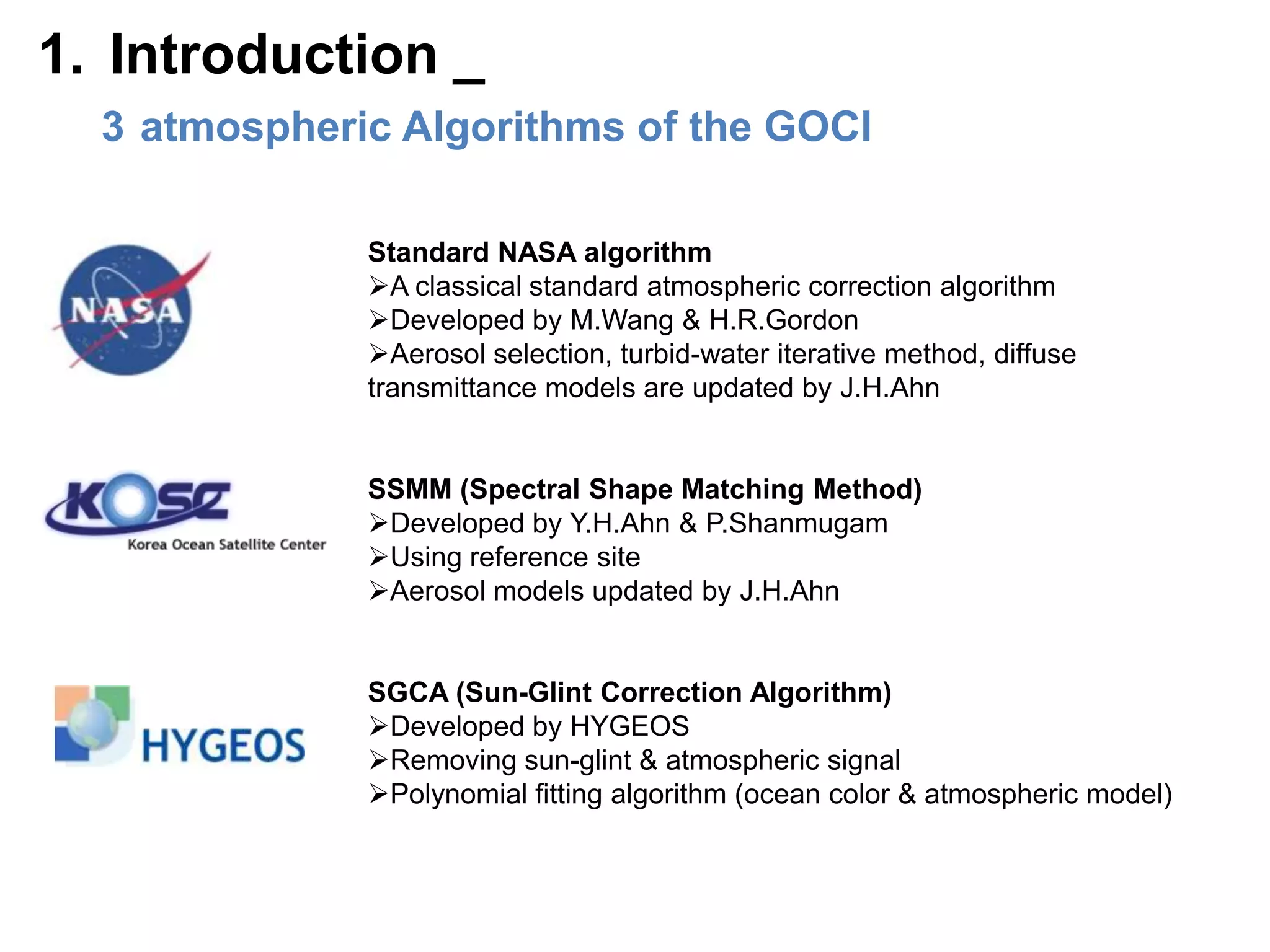
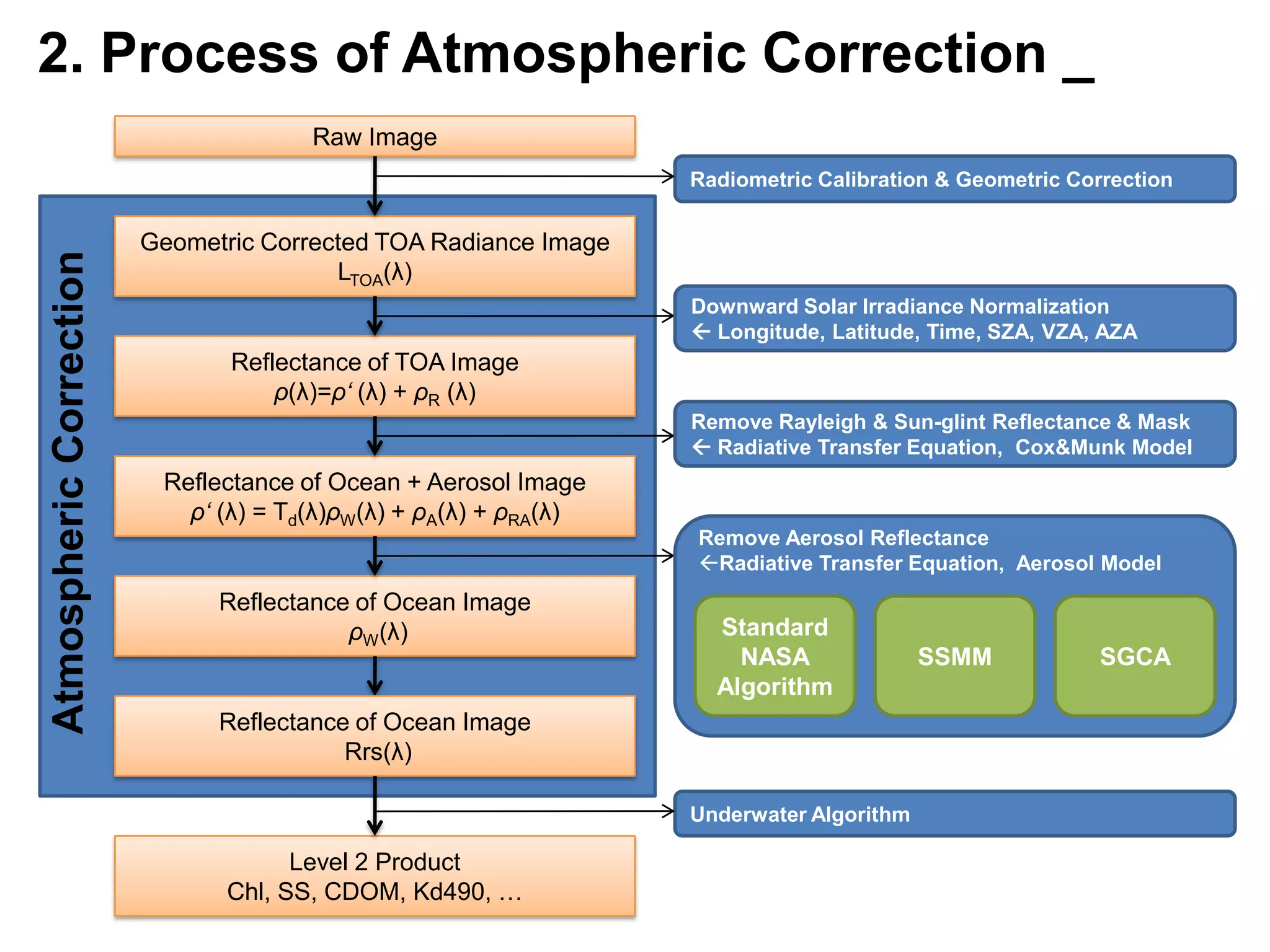
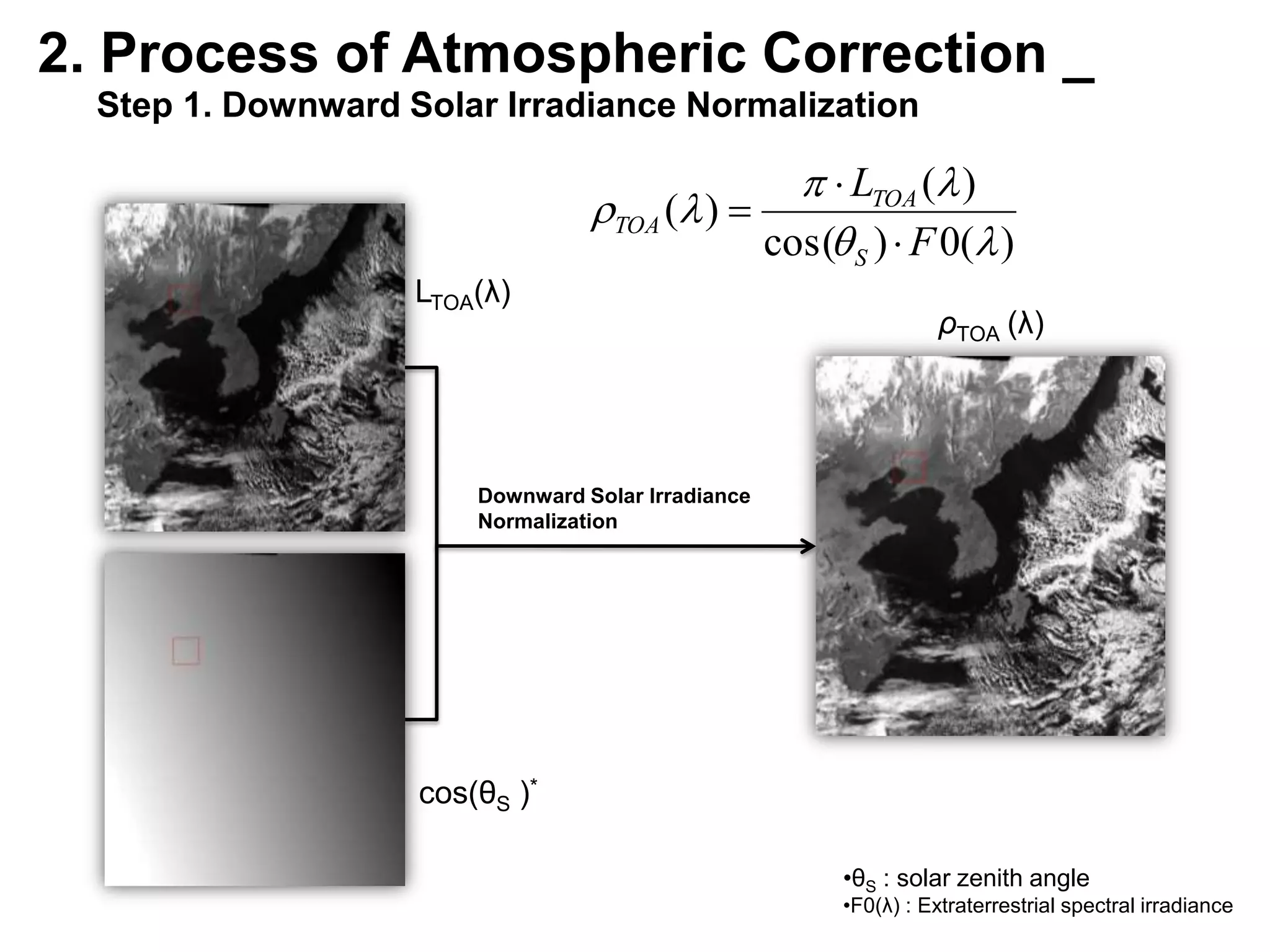
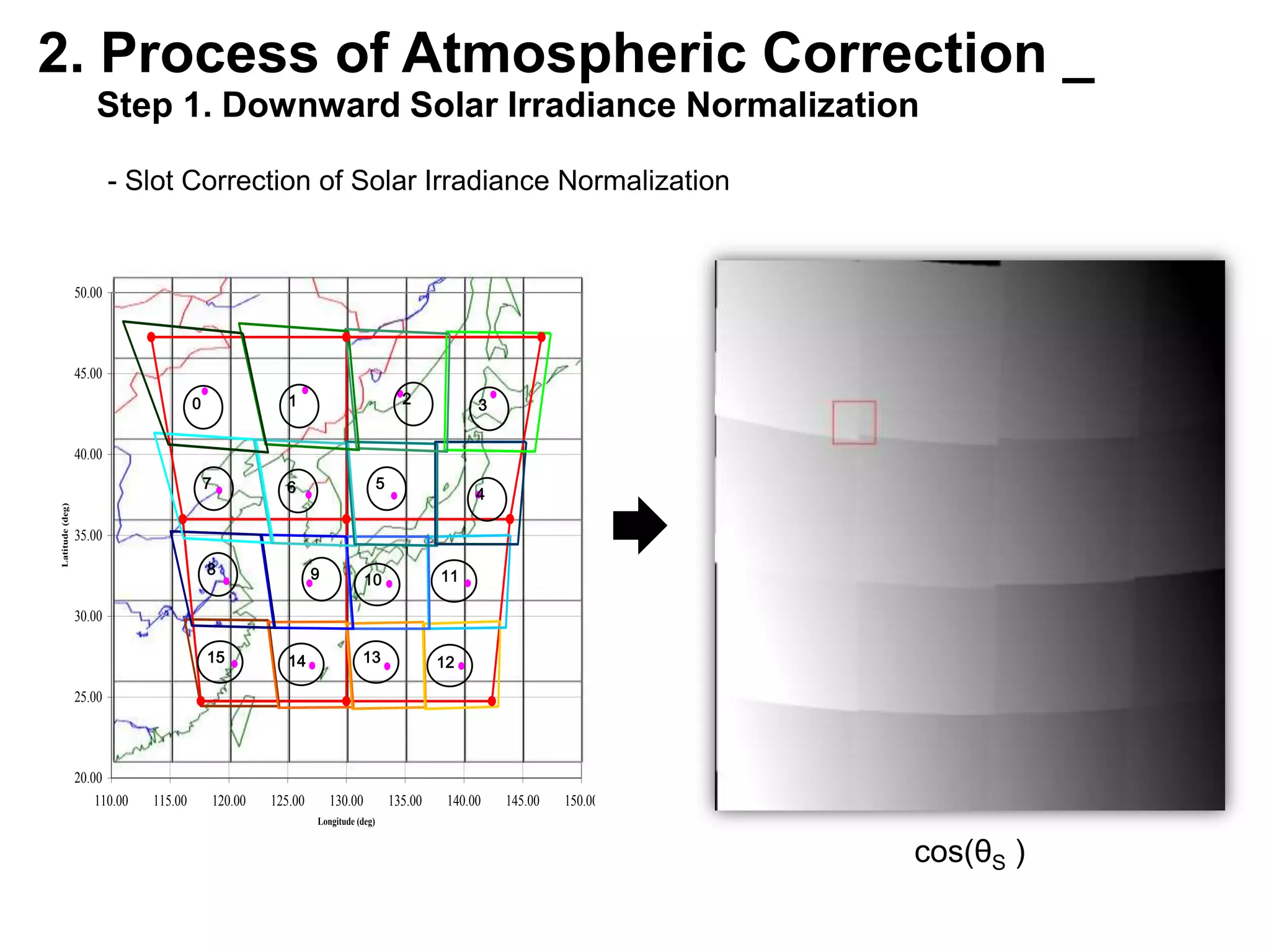
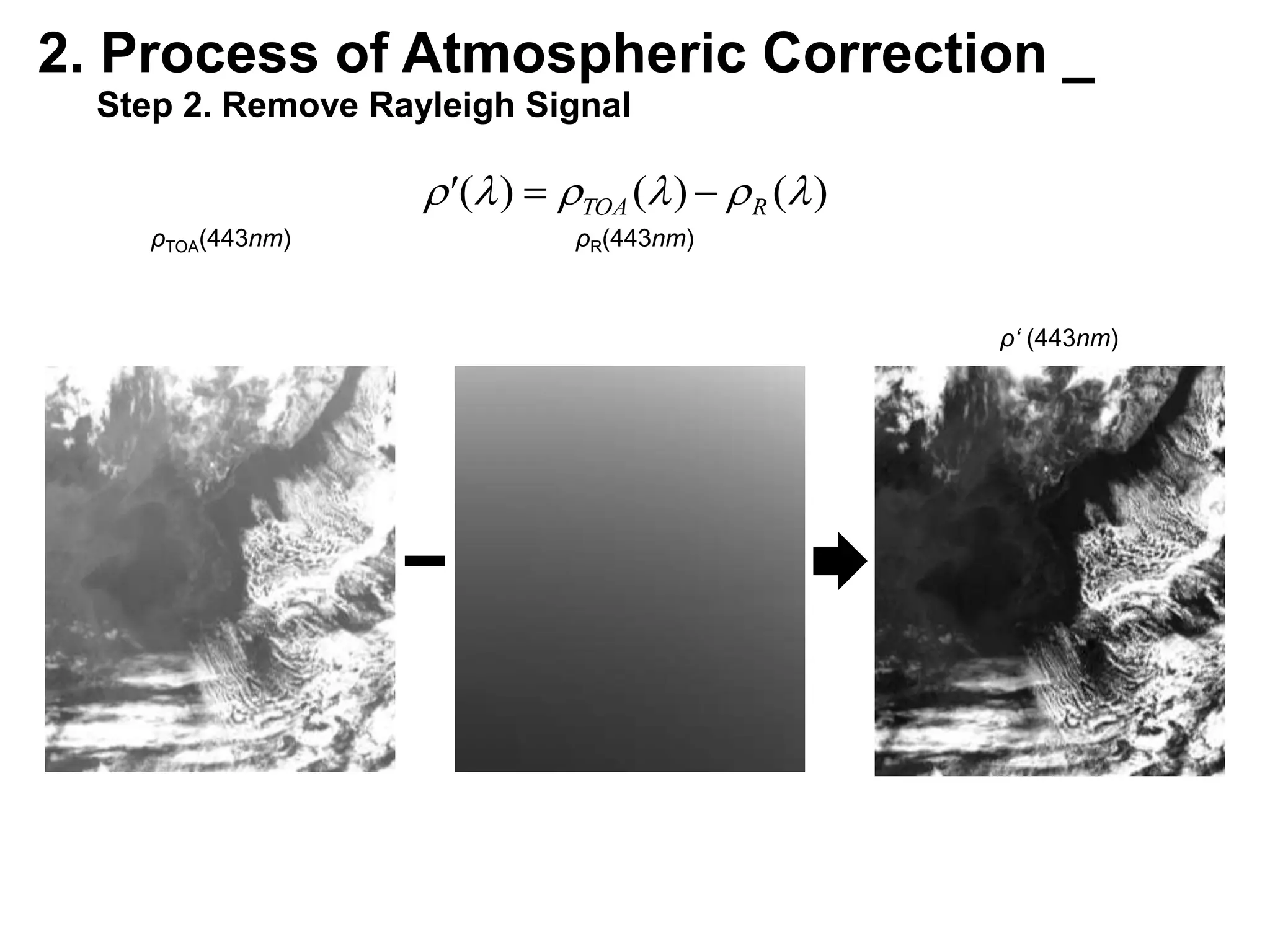
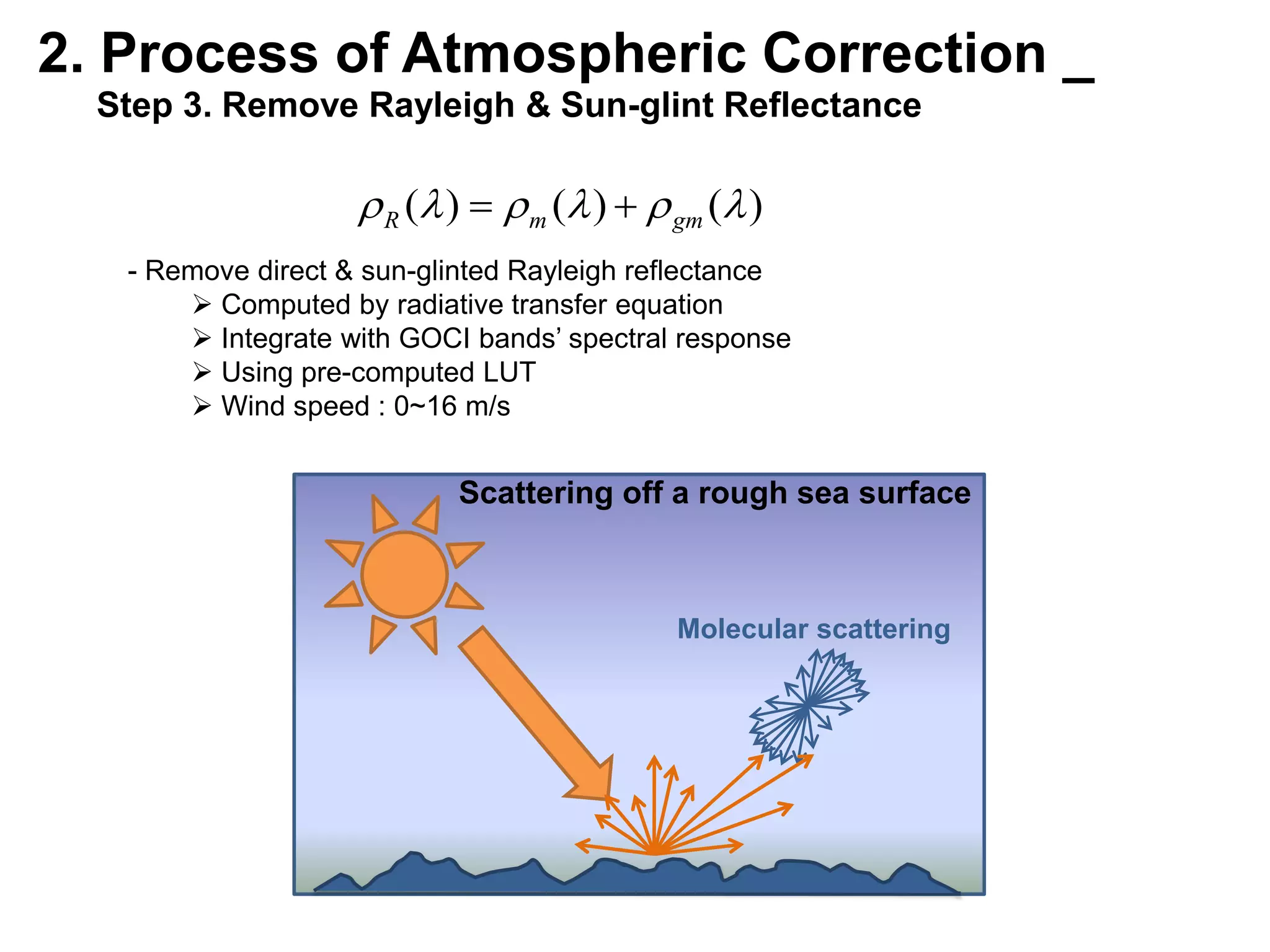
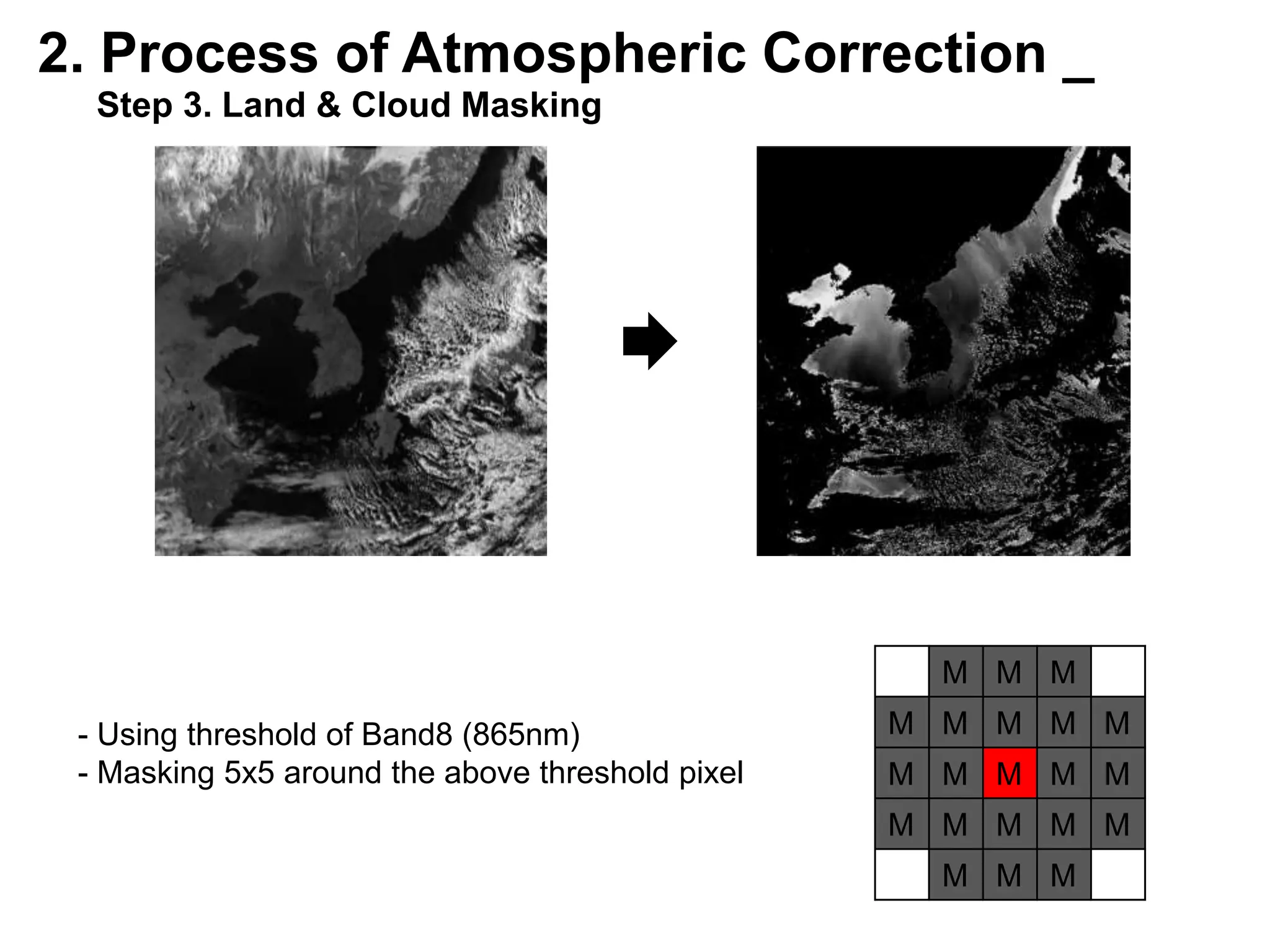
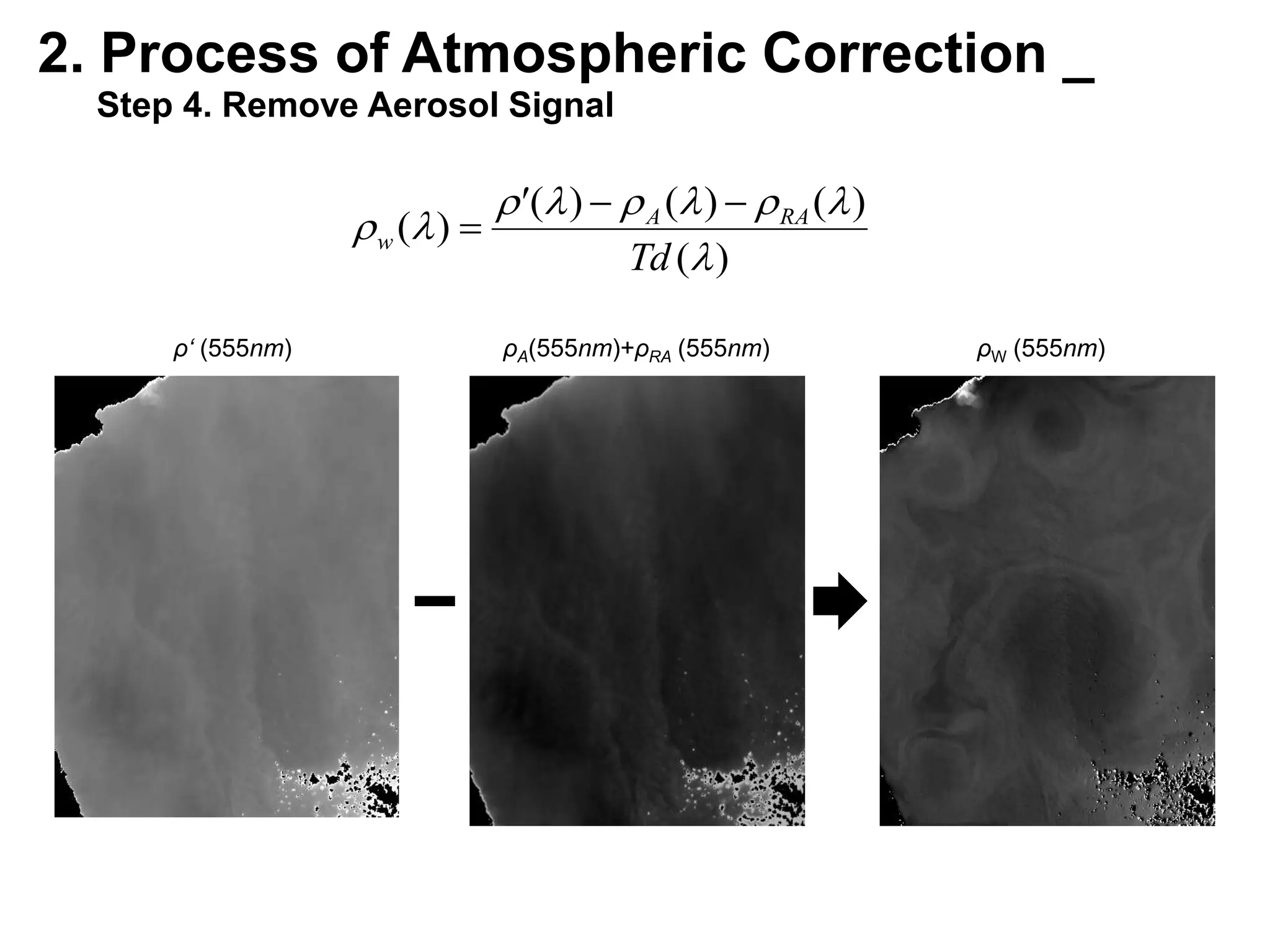
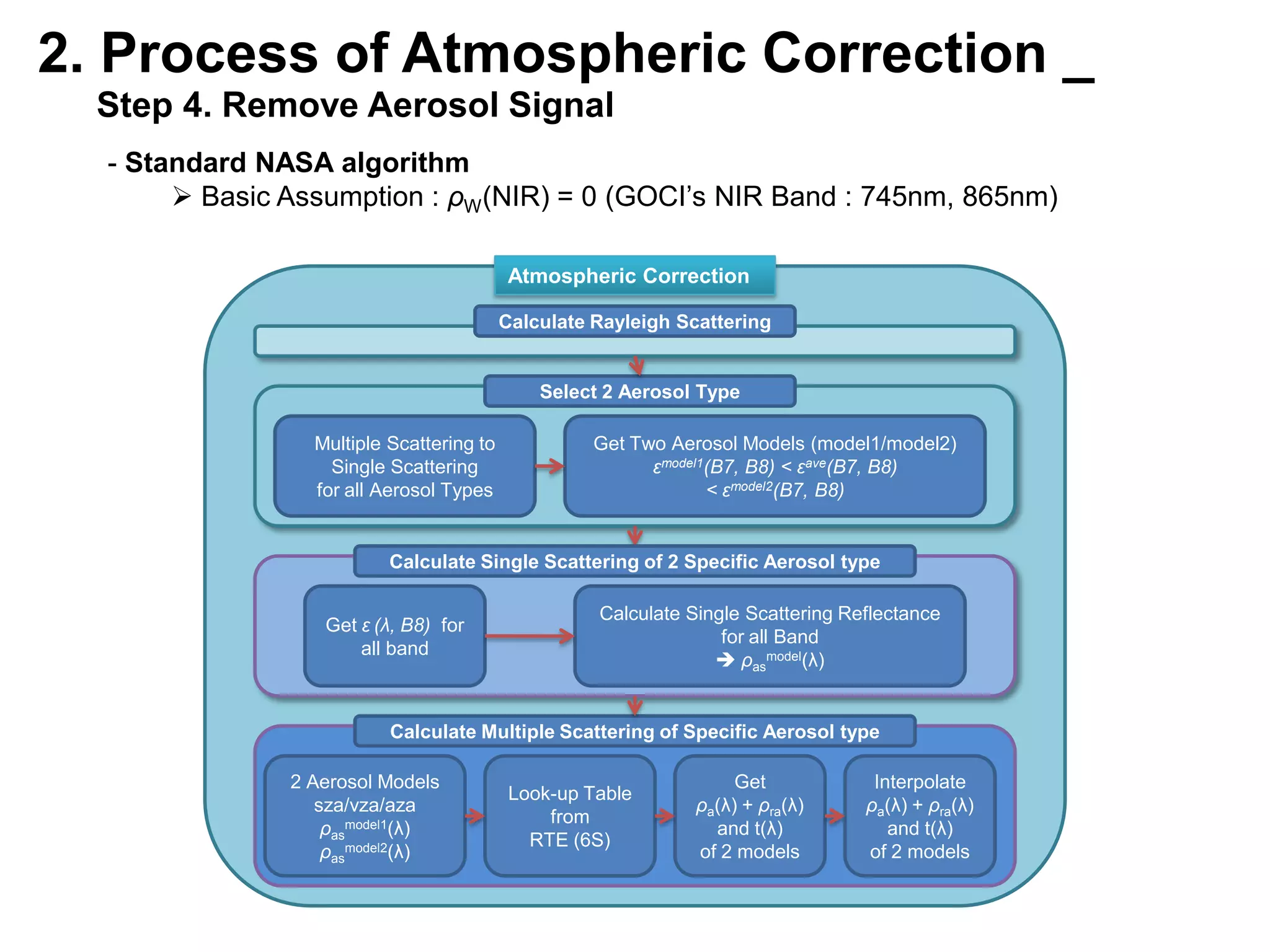
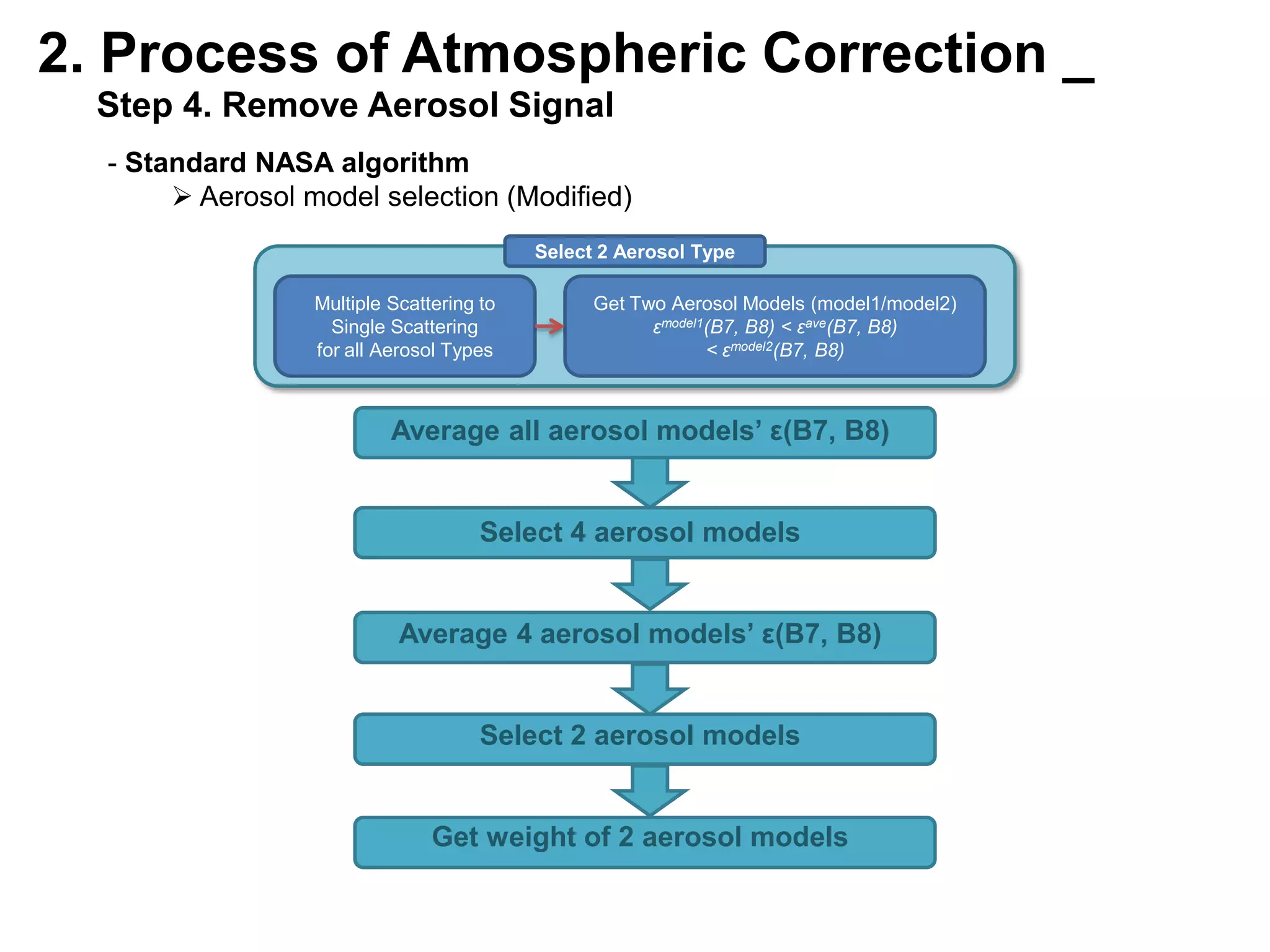
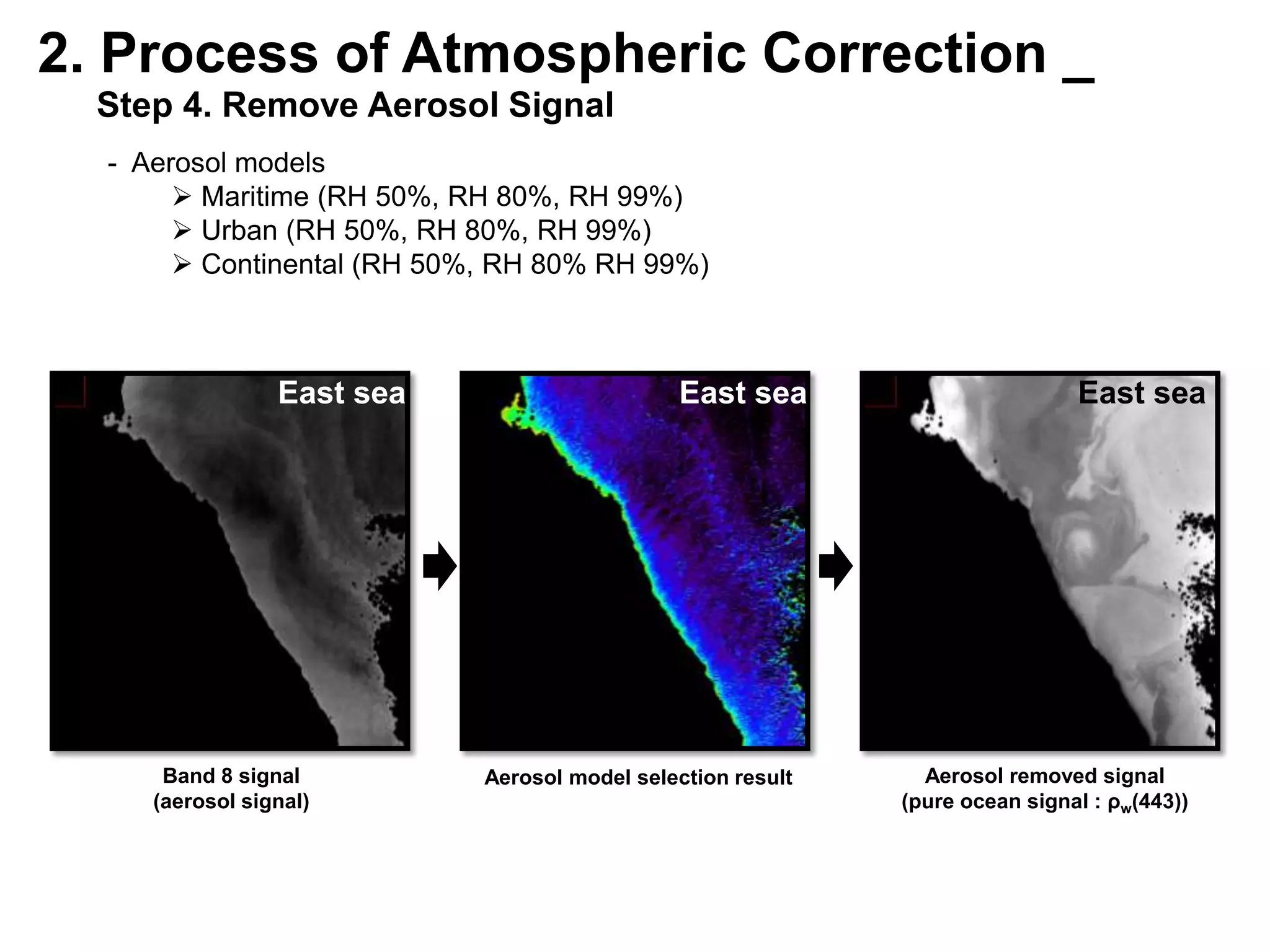
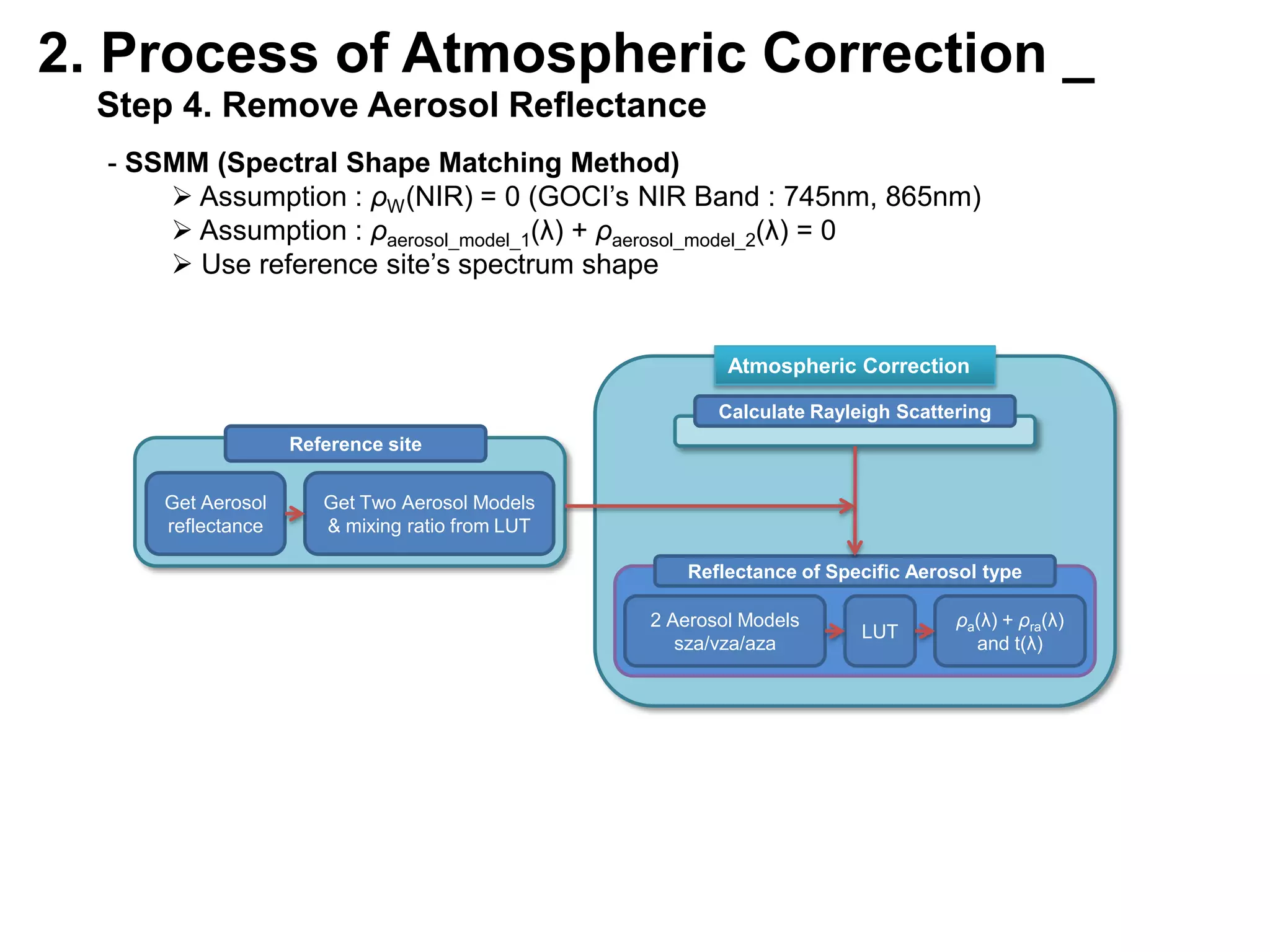
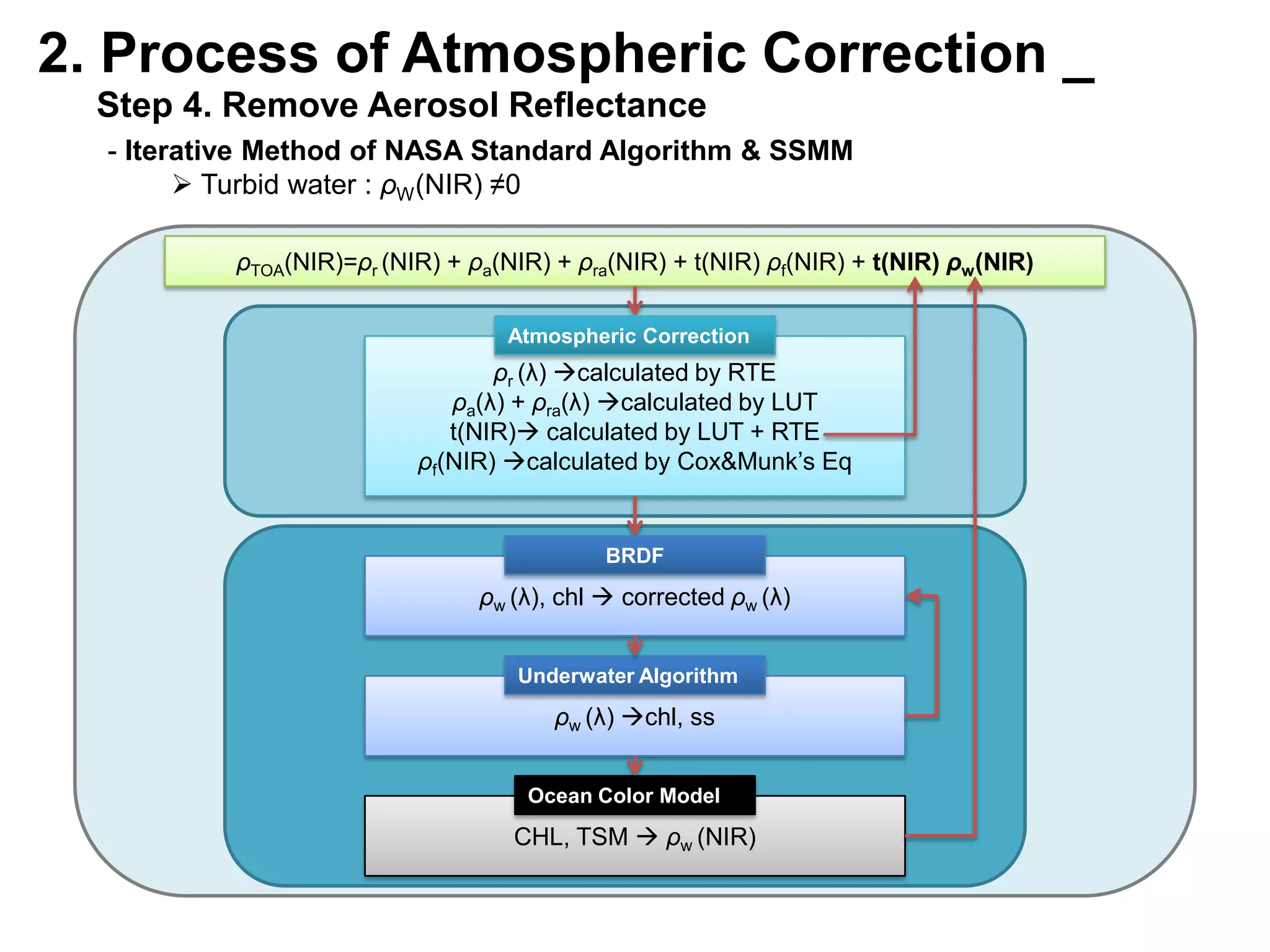
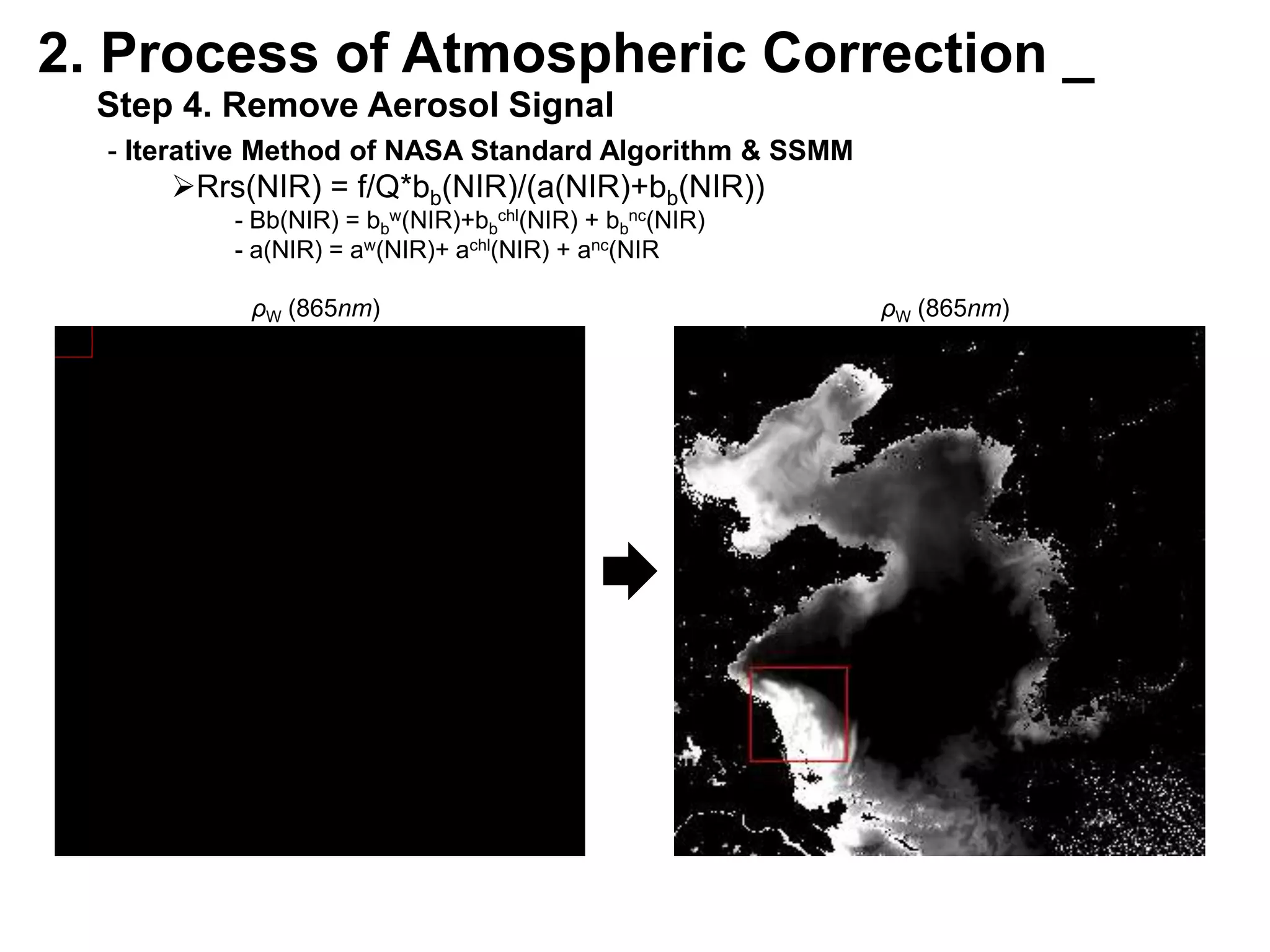
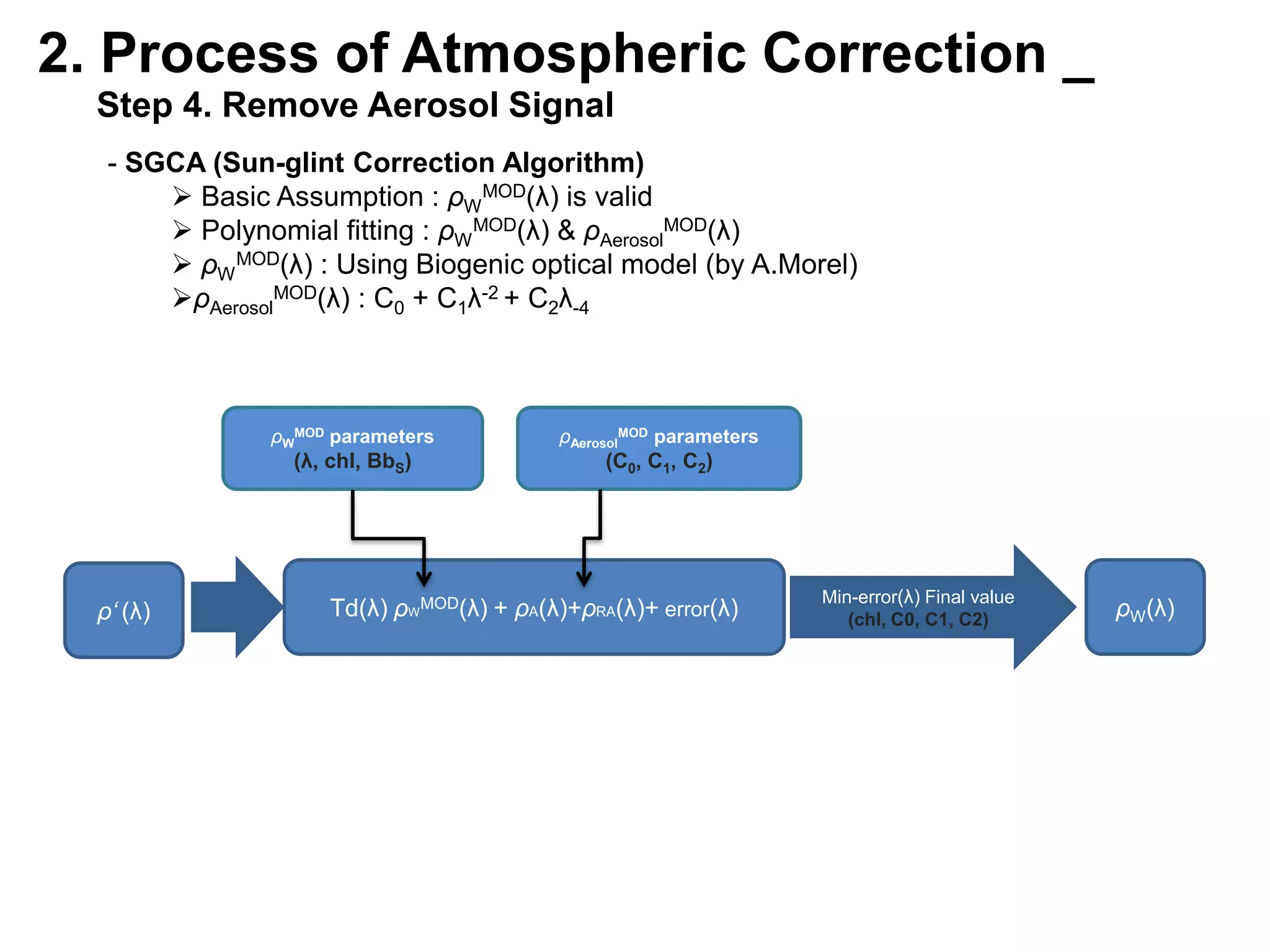
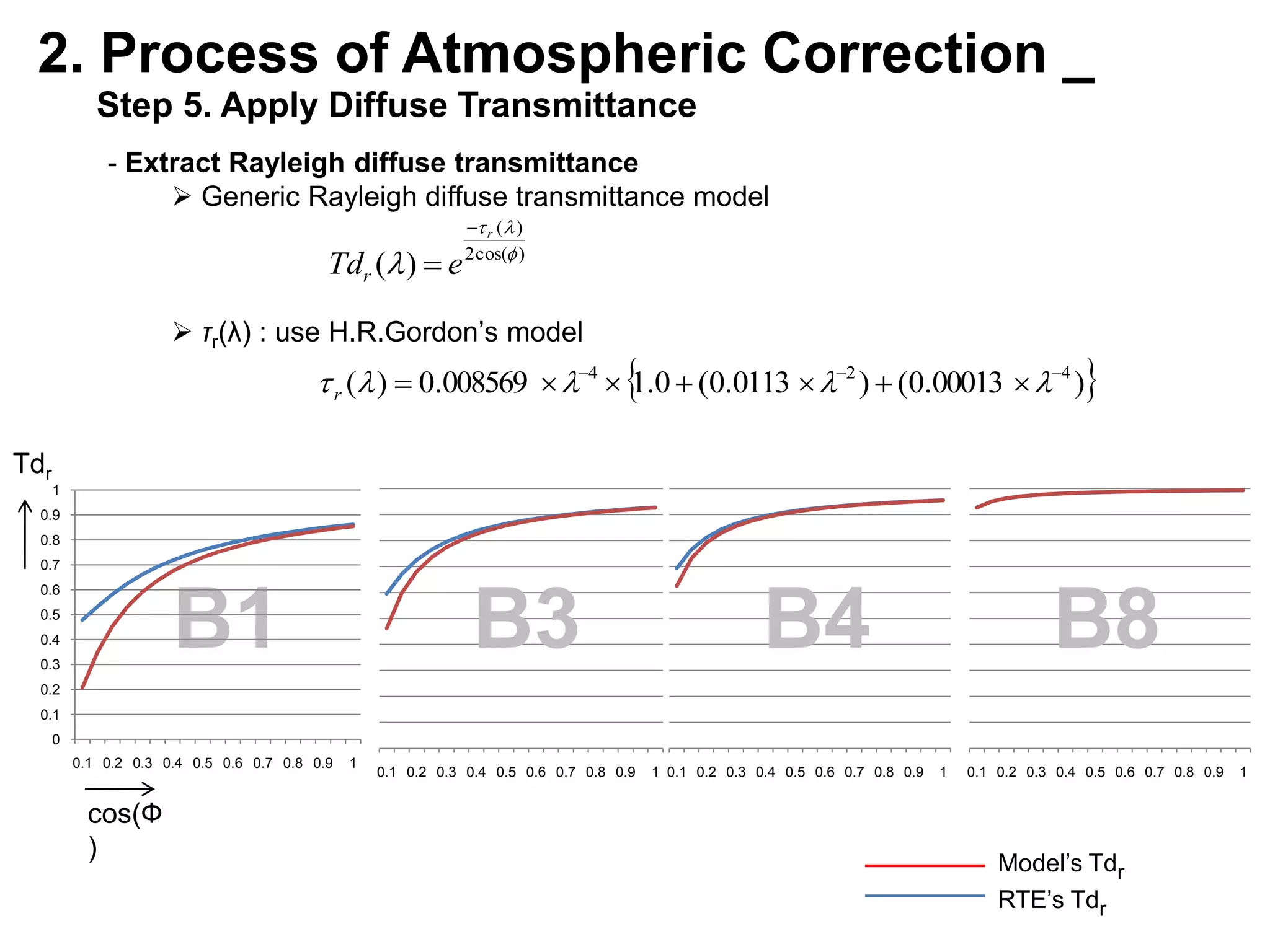
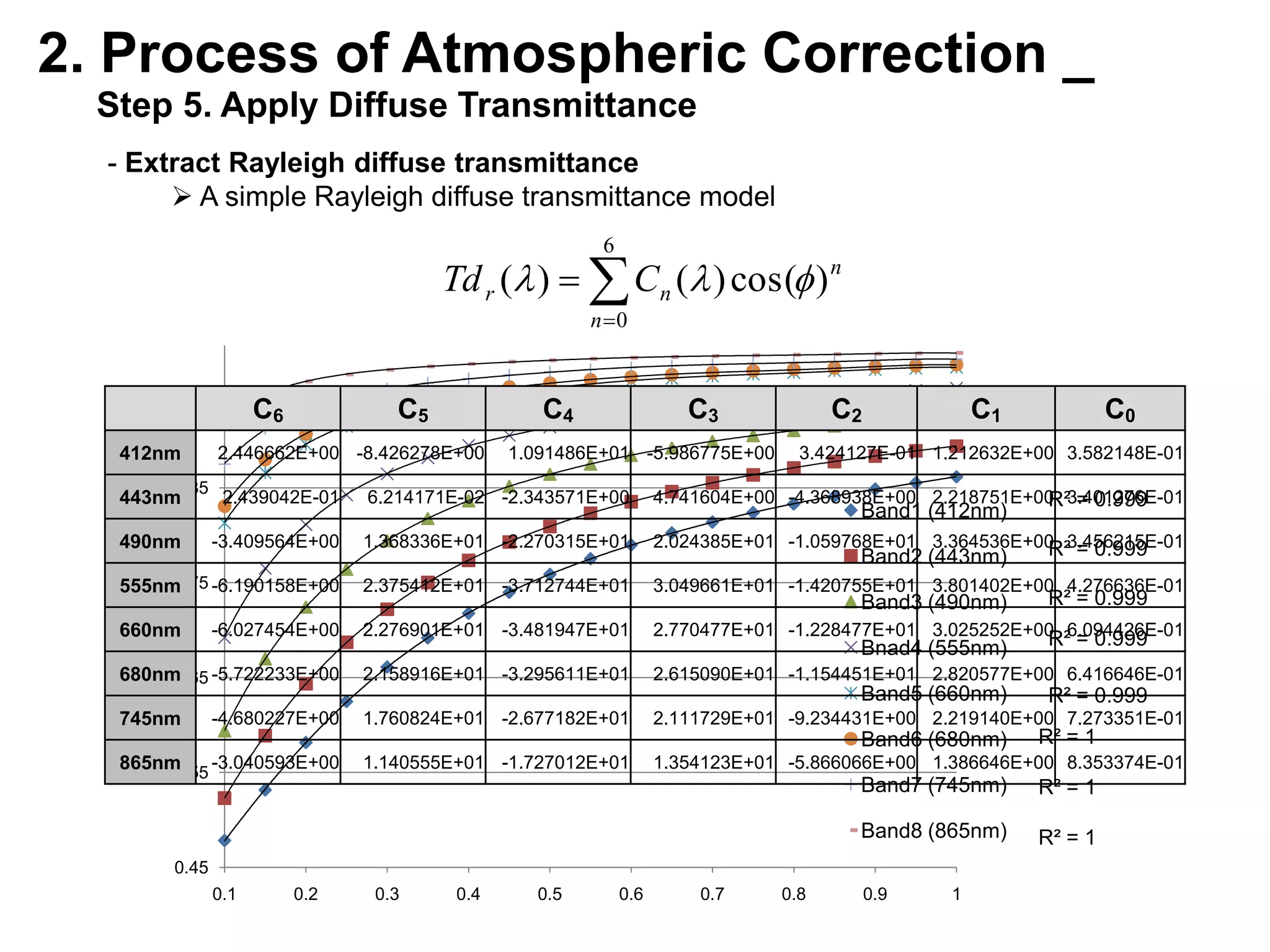
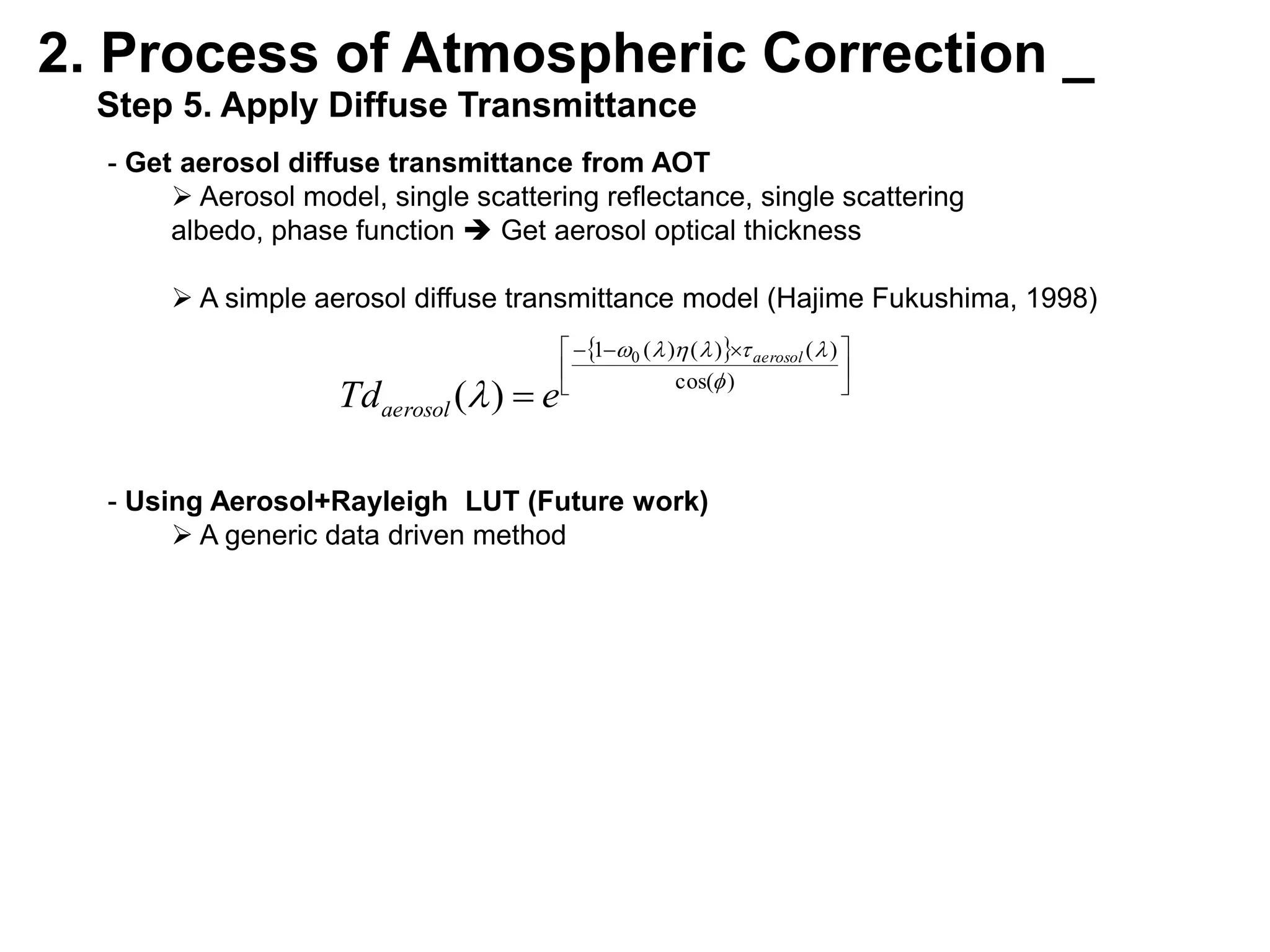
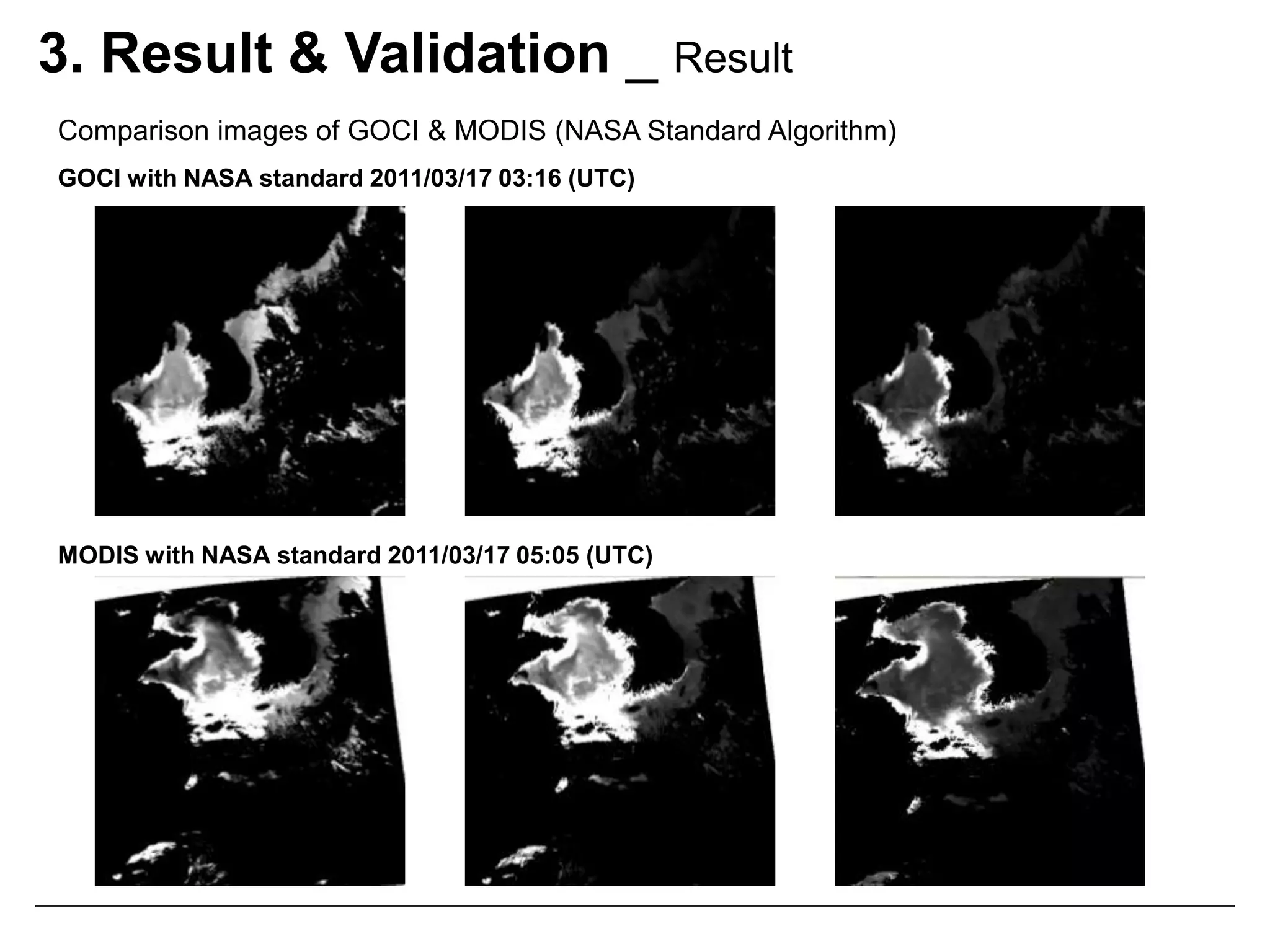
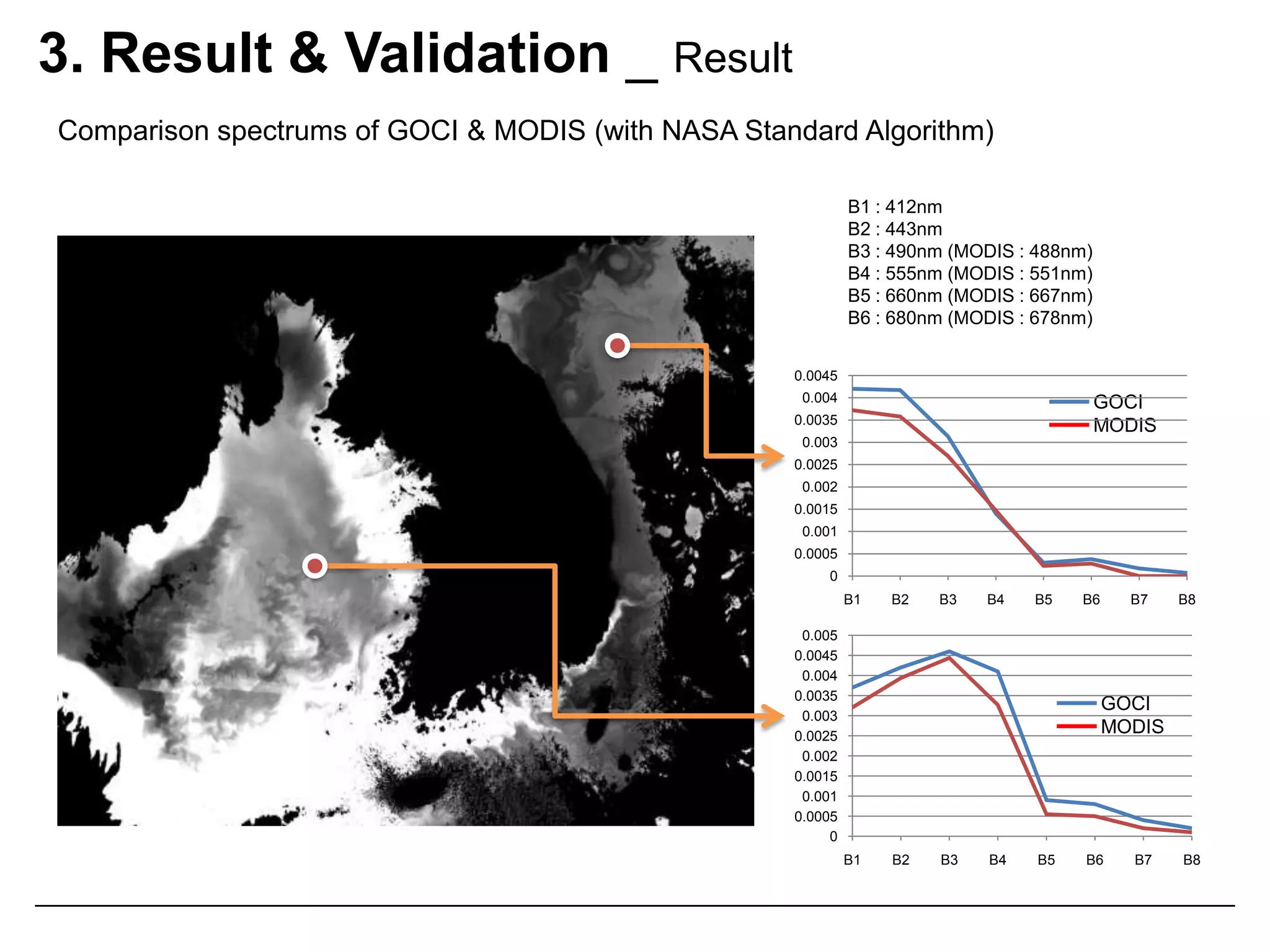
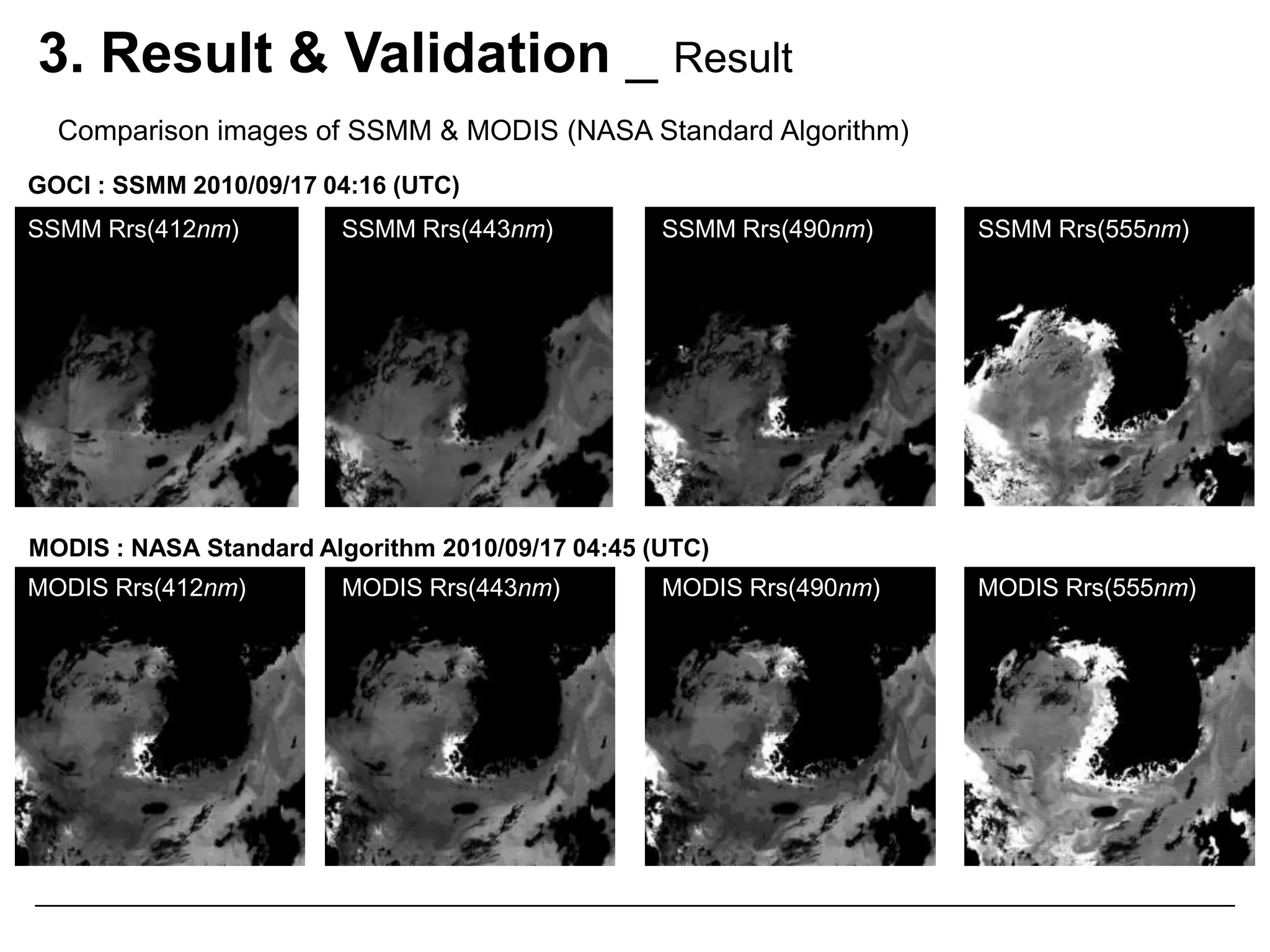
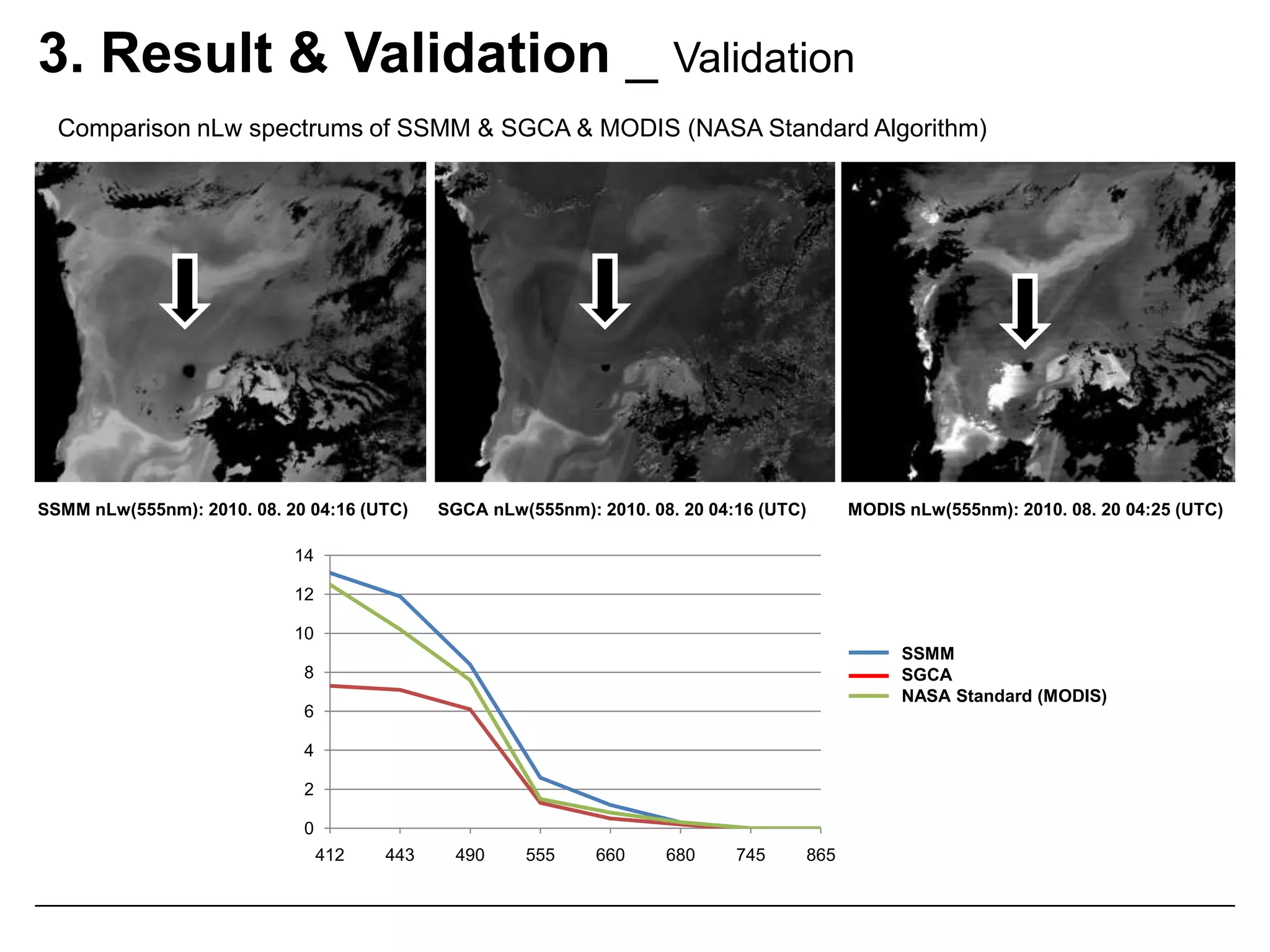
This document describes three atmospheric correction algorithms for the Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI): the Standard NASA algorithm, the Spectral Shape Matching Method (SSMM), and the Sun-Glint Correction Algorithm (SGCA). It outlines the processing steps for each algorithm, including radiometric calibration, removal of Rayleigh and aerosol scattering, and derivation of remote sensing reflectance. Validation results show SSMM and SGCA provide reasonable matches to NASA standard processing of MODIS data, though all three GOCI algorithms could be improved by updating aerosol and ocean models. The document concludes the algorithms capture the essential ocean color measurement but would benefit from further refinement.