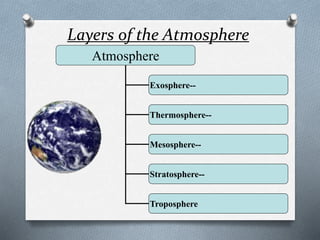
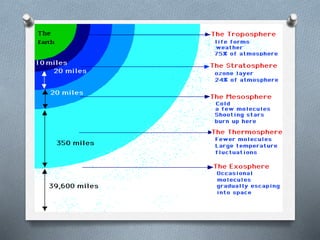
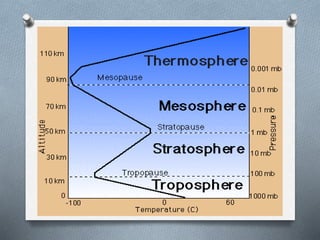
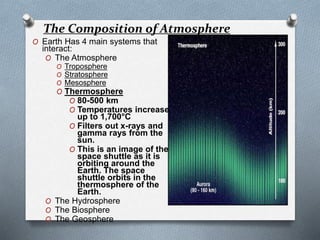
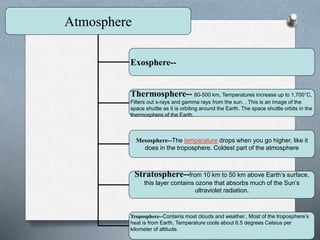
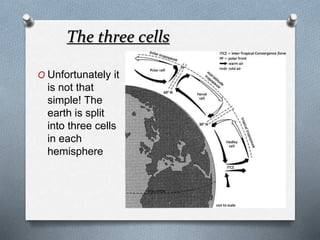
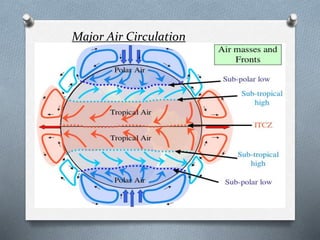
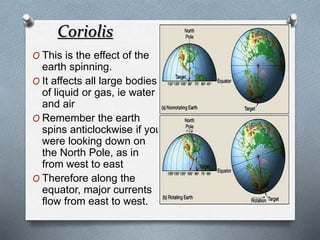
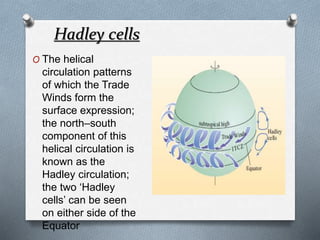
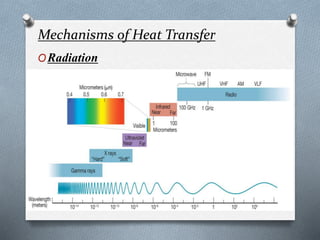
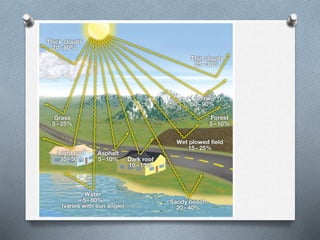
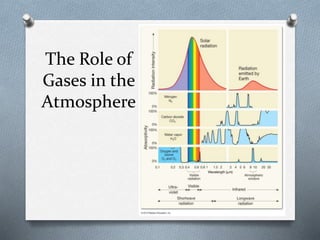
This document explores the atmosphere's significance, composition, and layers, including the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere. It details the interactive nature of Earth's systems—atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and geosphere—and discusses weather and climate factors such as temperature, humidity, and air pressure. Additionally, it highlights the mechanisms of heat transfer and the role of gases in shaping weather and climate patterns.