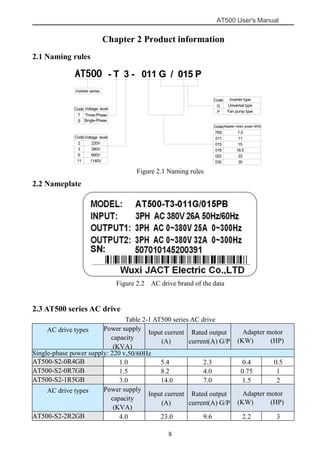
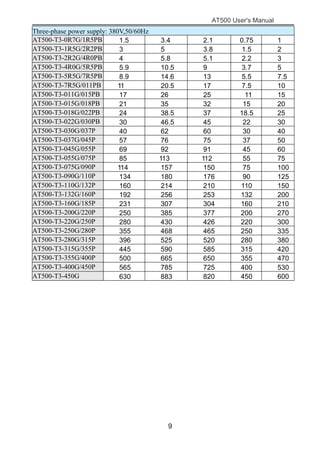
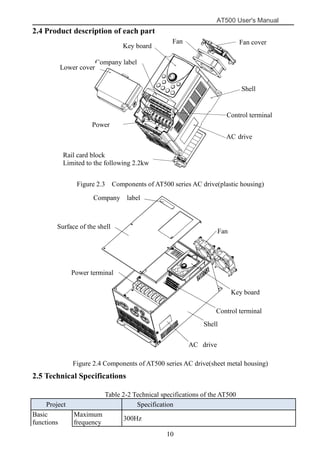
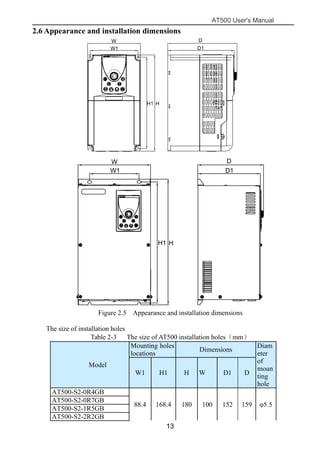
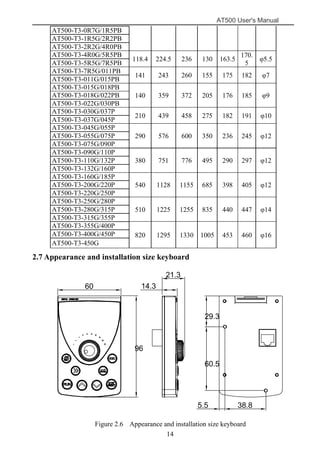
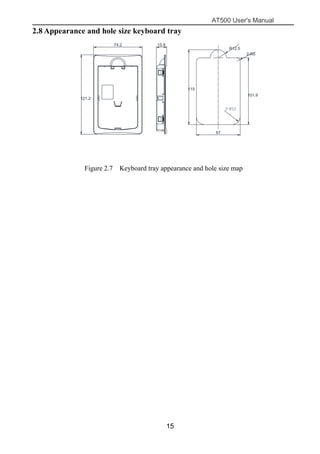
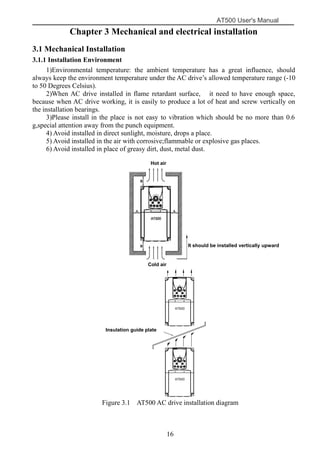
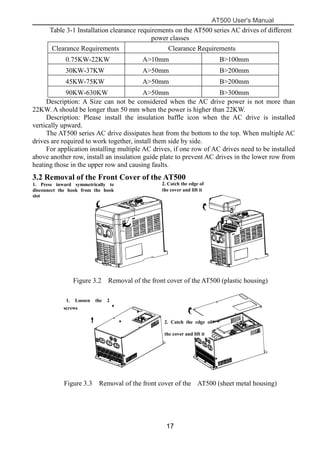
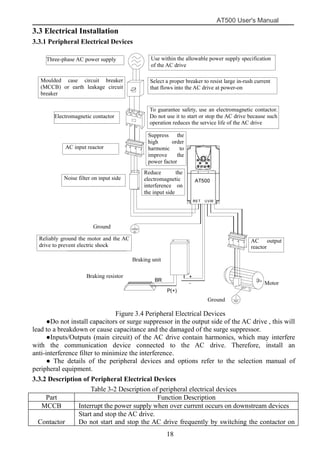
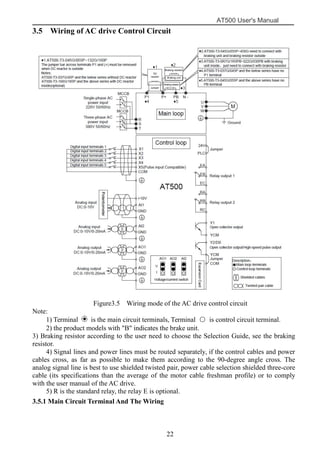
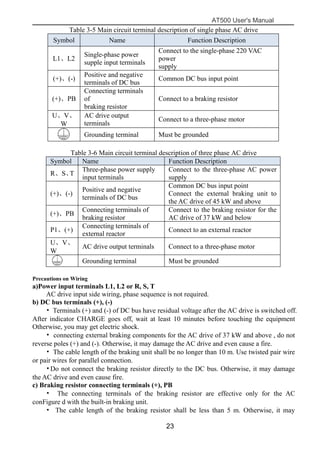
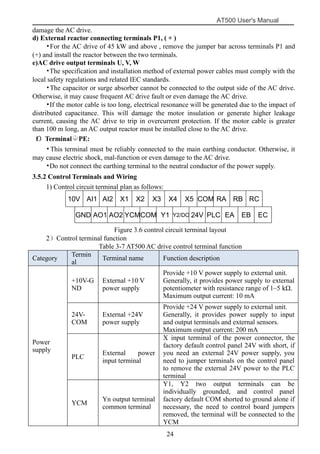
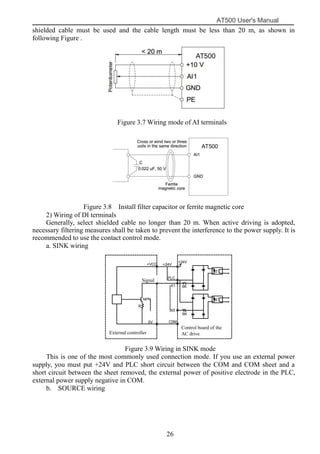
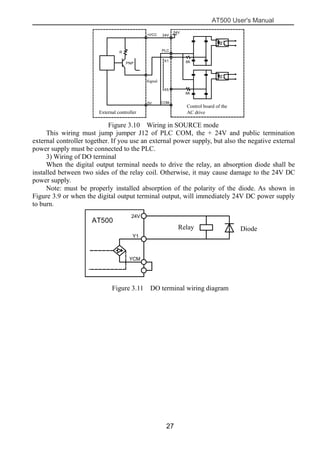
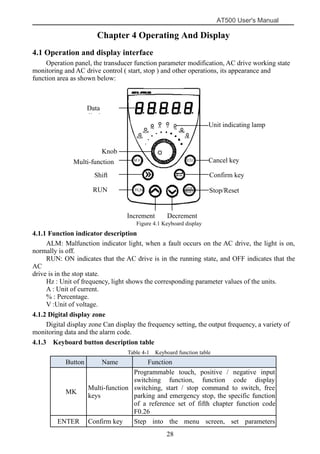
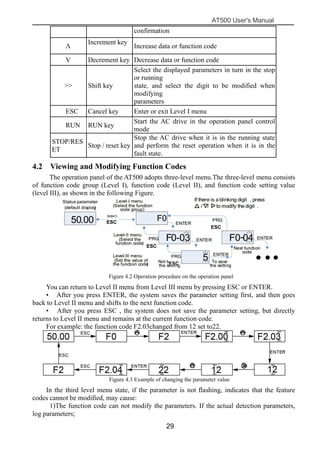
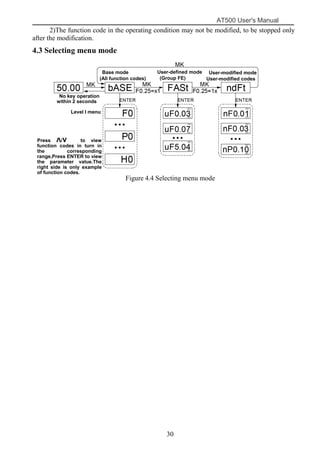
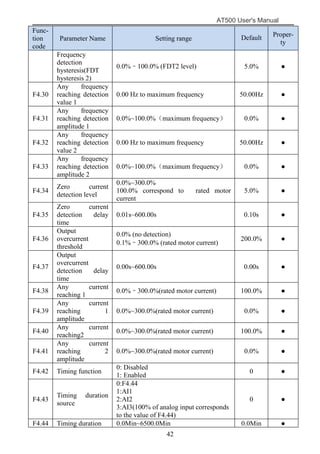
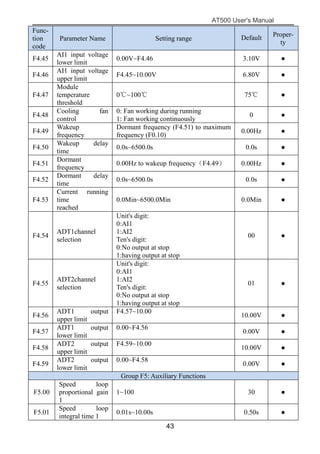
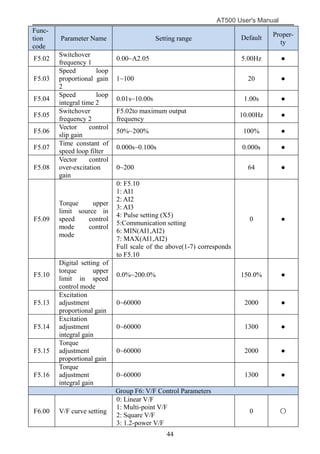
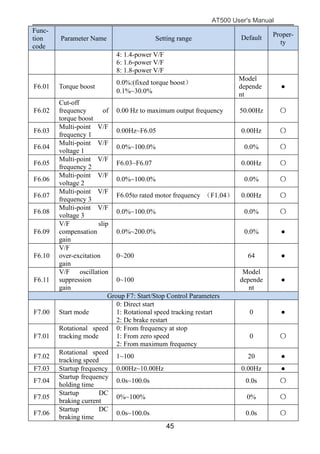
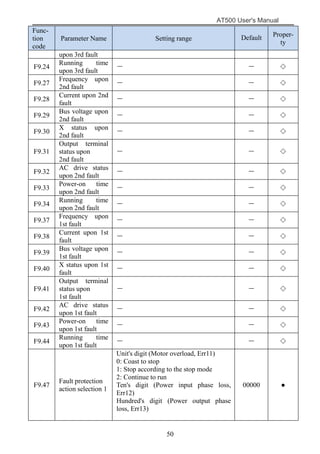
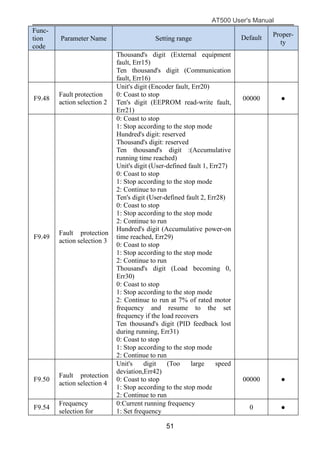
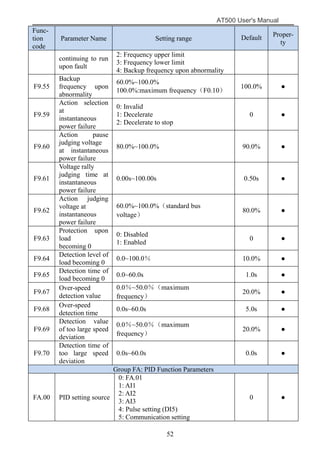
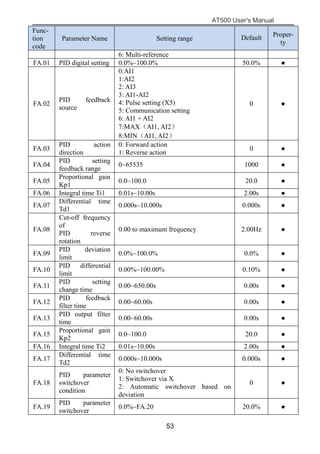
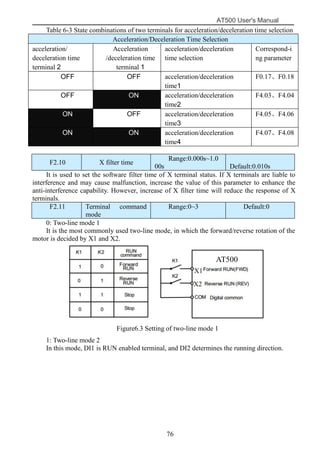
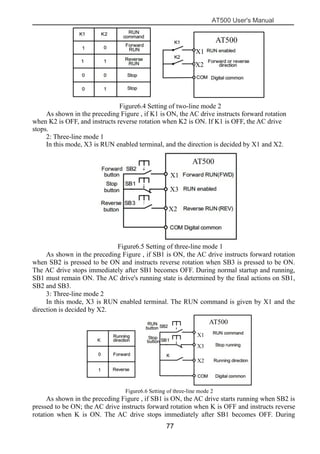
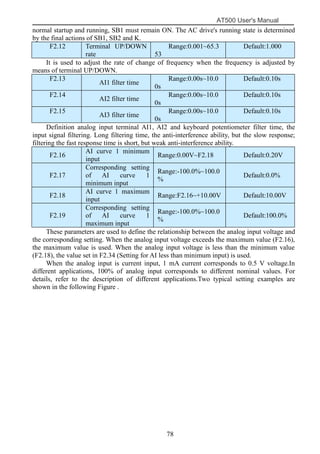
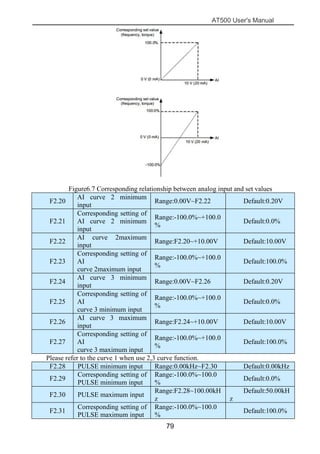
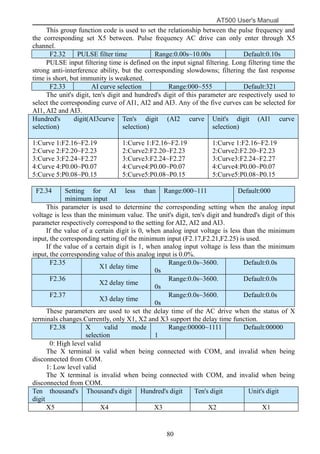
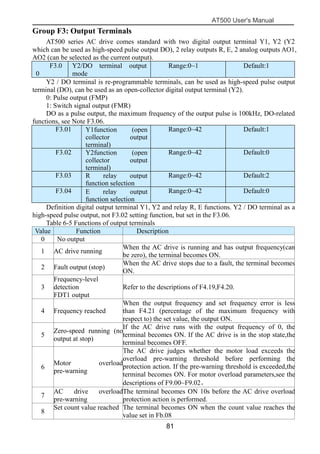
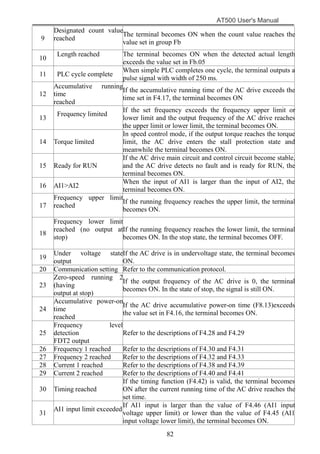
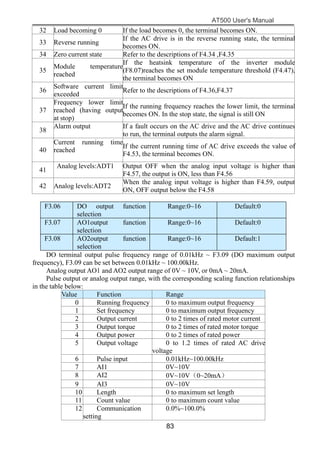
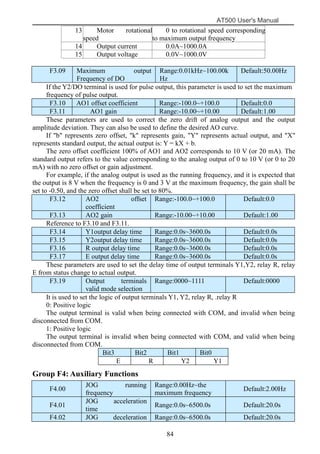
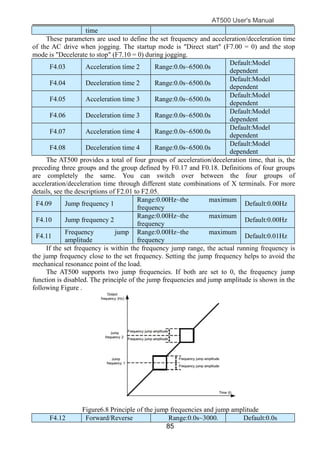
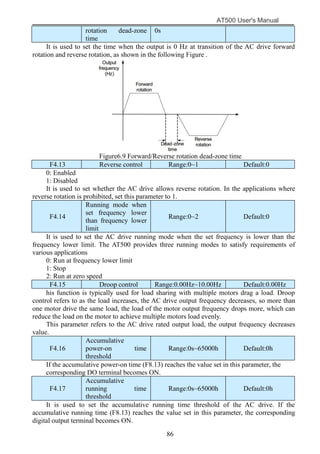
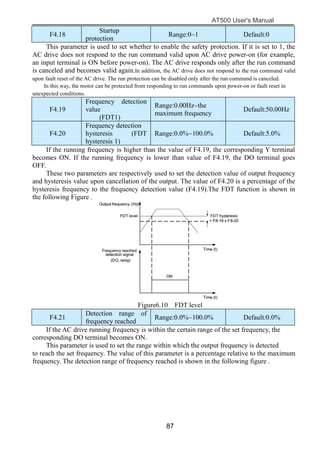
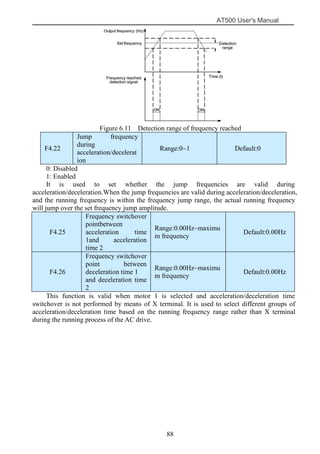
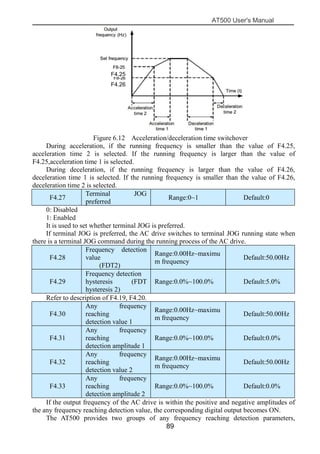
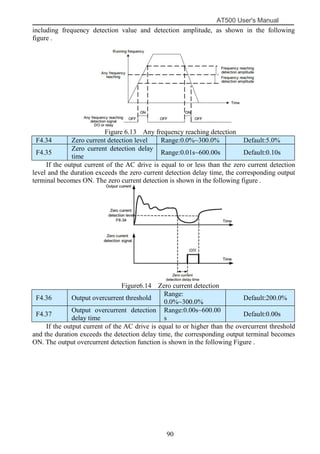
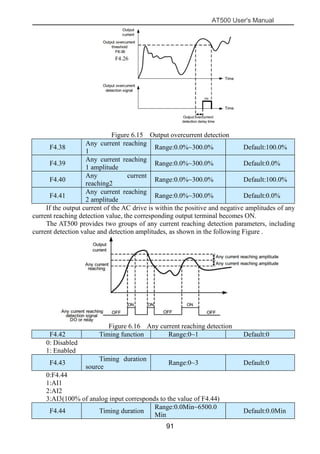
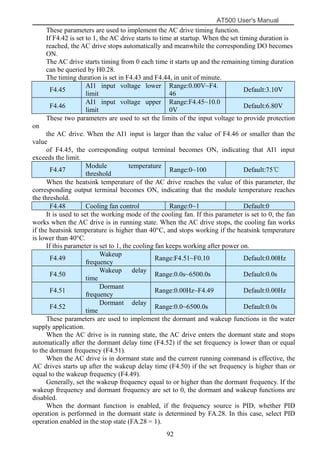
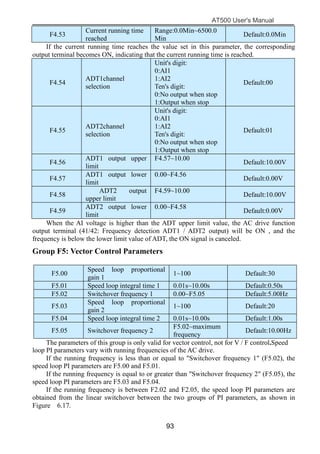
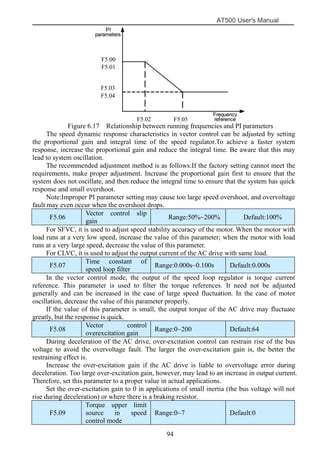
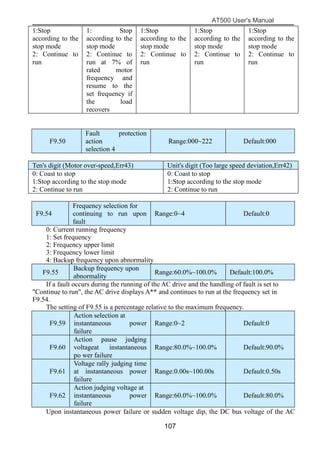
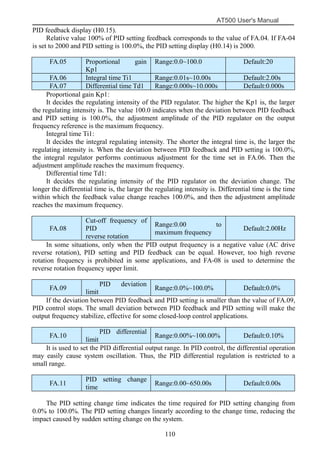
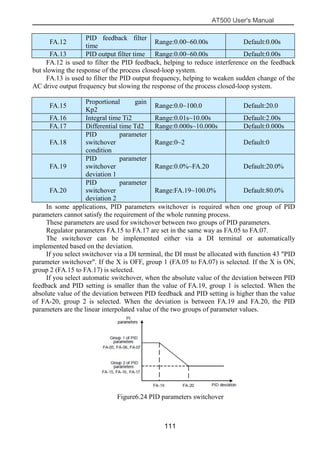
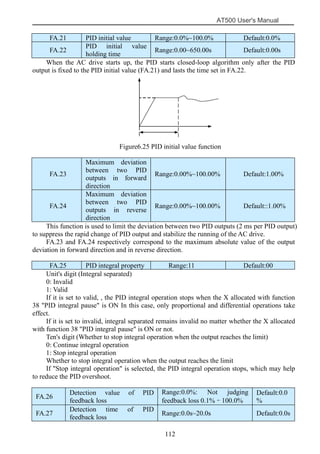
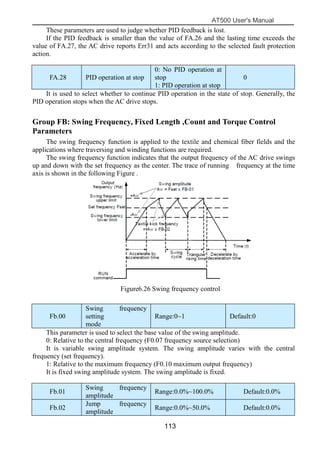
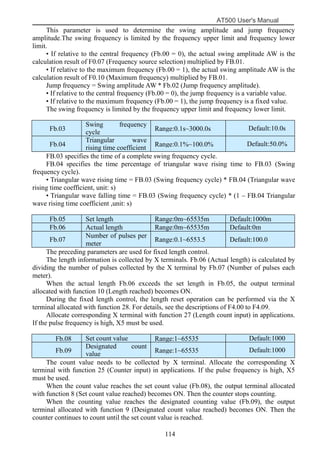
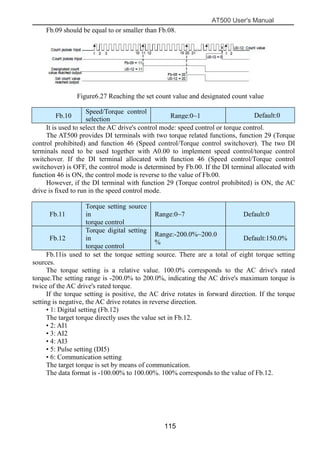
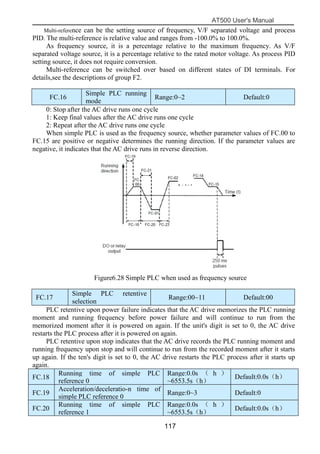
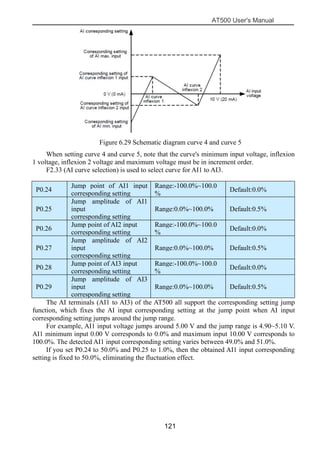
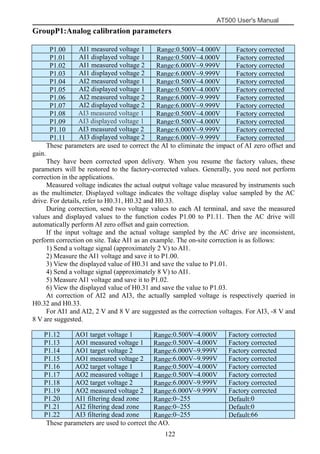
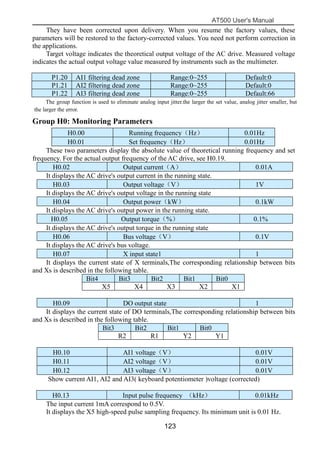
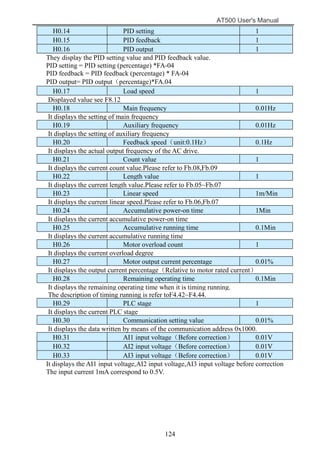
The document is the AT500 user's manual which provides instructions for selection, parameter setting, commissioning, maintenance, and inspection of the AT500 series AC drive. It describes the drive's product information including naming rules, technical specifications, dimensions, and installation. It also covers safety precautions, mechanical and electrical installation, operation and display, function parameters, and troubleshooting.