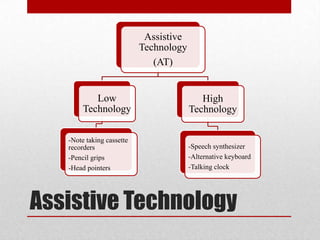
The document discusses assistive technology and its importance in providing equal learning opportunities for all students, including those with disabilities. It explains that assistive technology helps ensure students with disabilities can access the curriculum and learn in inclusive classroom environments as required by law. Examples of assistive technologies that can help with tasks like note-taking, writing, organization, and accessing materials are provided. The document emphasizes that integrating appropriate assistive technologies is necessary to effectively educate students with disabilities."