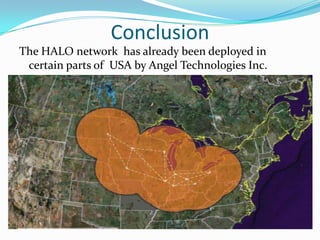
The document describes The Halo Network, a proposed broadband wireless metropolitan area network. The key aspects are:
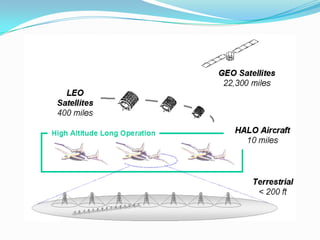
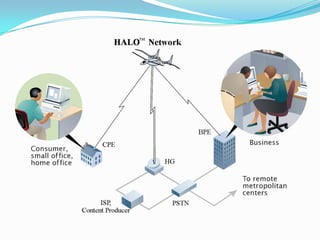
- It uses a high-altitude aircraft called HAAPS operating at 16km to serve as an airborne hub/central node for a star topology network.
- The HAAPS aircraft houses an antenna array to create hundreds of virtual cells on the ground to provide service to thousands of users within a 100km radius area.
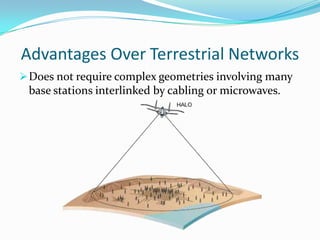
- It claims advantages over terrestrial and satellite networks like rapid deployment, high signal quality, availability and bandwidth, and lower costs.