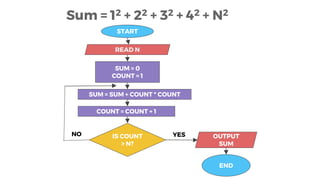
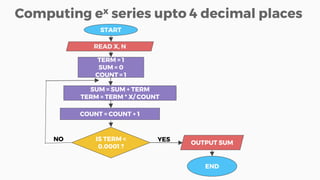
This document introduces some basic programming concepts including algorithms, programs, variables, constants, data types, and flowcharts. It defines an algorithm as a step-by-step procedure for solving a problem, independent of programming language. A program is the translation of an algorithm into a form a computer can process, typically written in a high-level language like C or Java. Variables and constants are used to store temporary and fixed values in memory. Common data types include integers, floating-point numbers, and characters. Several examples of programming problems and their solutions as algorithms/flowcharts are provided.