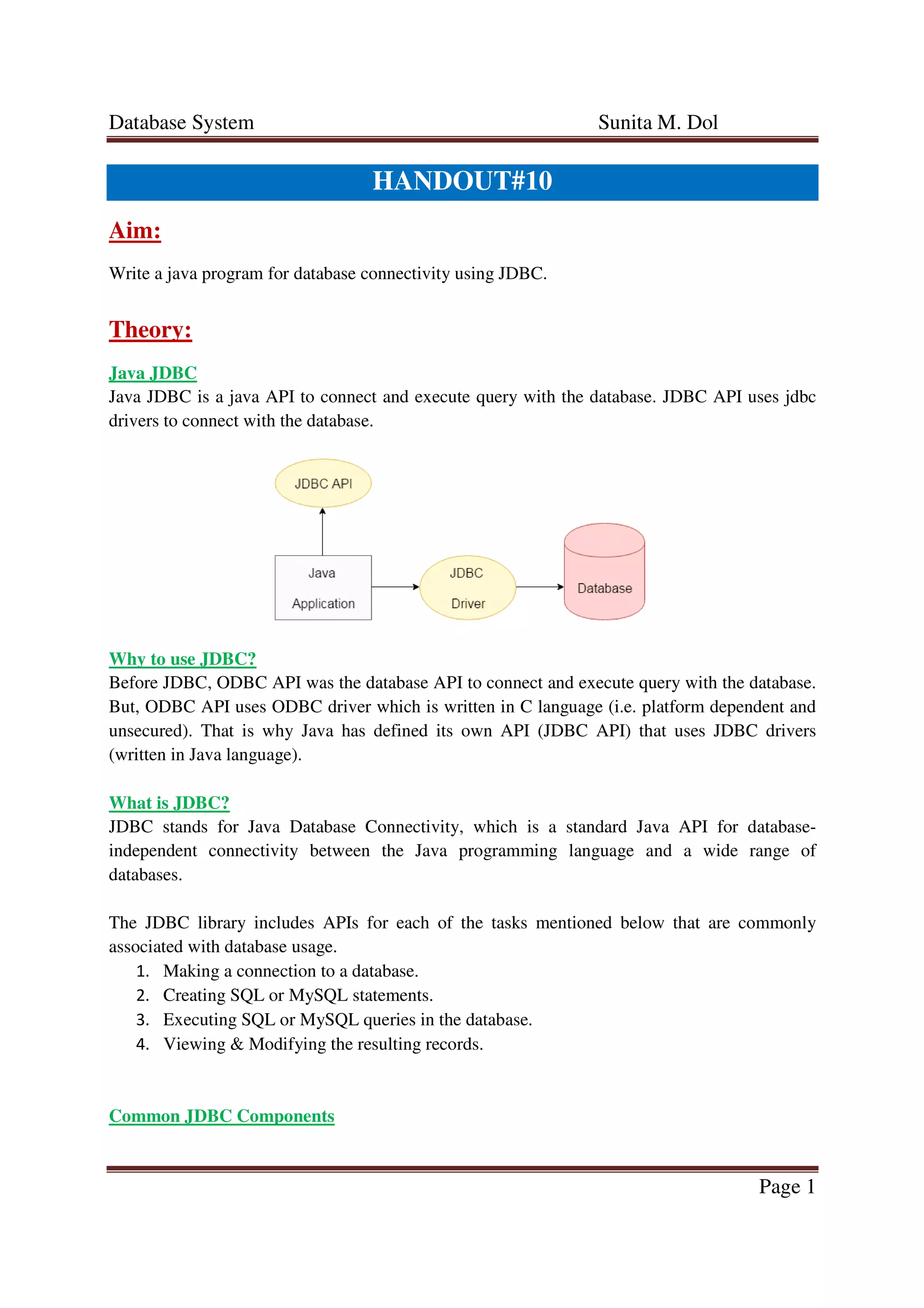
This document discusses Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) and how to connect to a database using JDBC. It explains that JDBC provides interfaces and classes to connect to a database, execute SQL statements, retrieve result sets, and handle exceptions. It also outlines the six steps to create a JDBC application: import packages, register the driver, open a connection, execute queries, extract data from result sets, and clean up resources. The goal is to write a Java program that demonstrates basic database operations like insert, search, delete, and modify using JDBC.