The document discusses Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) and provides details on connecting to a database from a Java program. It covers:
1. What JDBC is and its architecture, including key interfaces like Connection, Statement, and ResultSet.
2. The steps to connect to a database using JDBC: loading the driver, defining the connection URL, establishing a connection, creating a Statement, executing queries, processing results, and closing the connection.
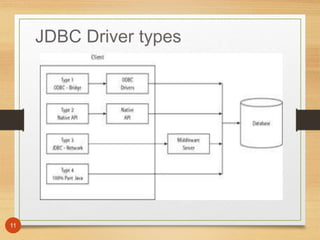
3. The different types of JDBC drivers and Statements that can be used.