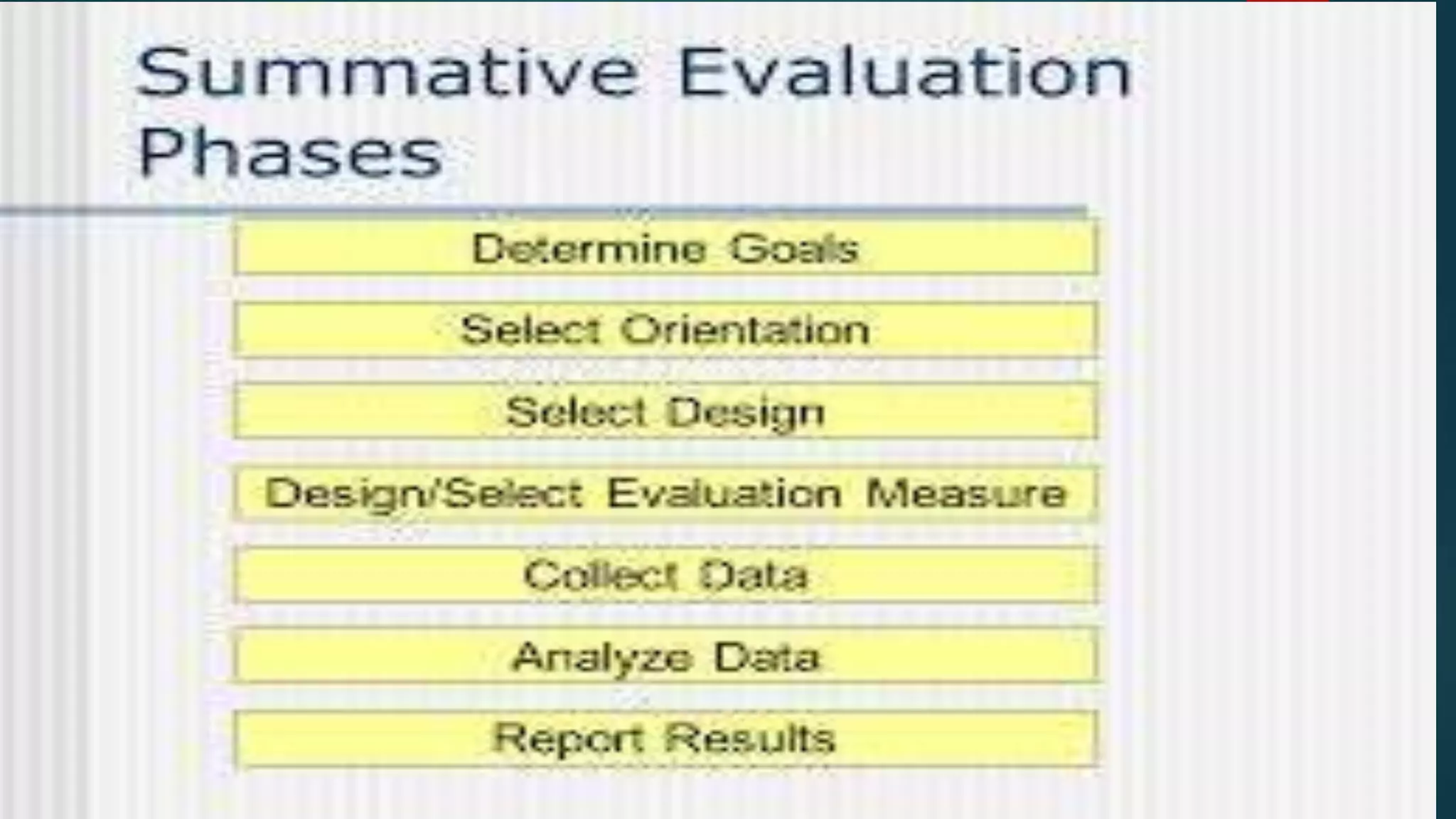
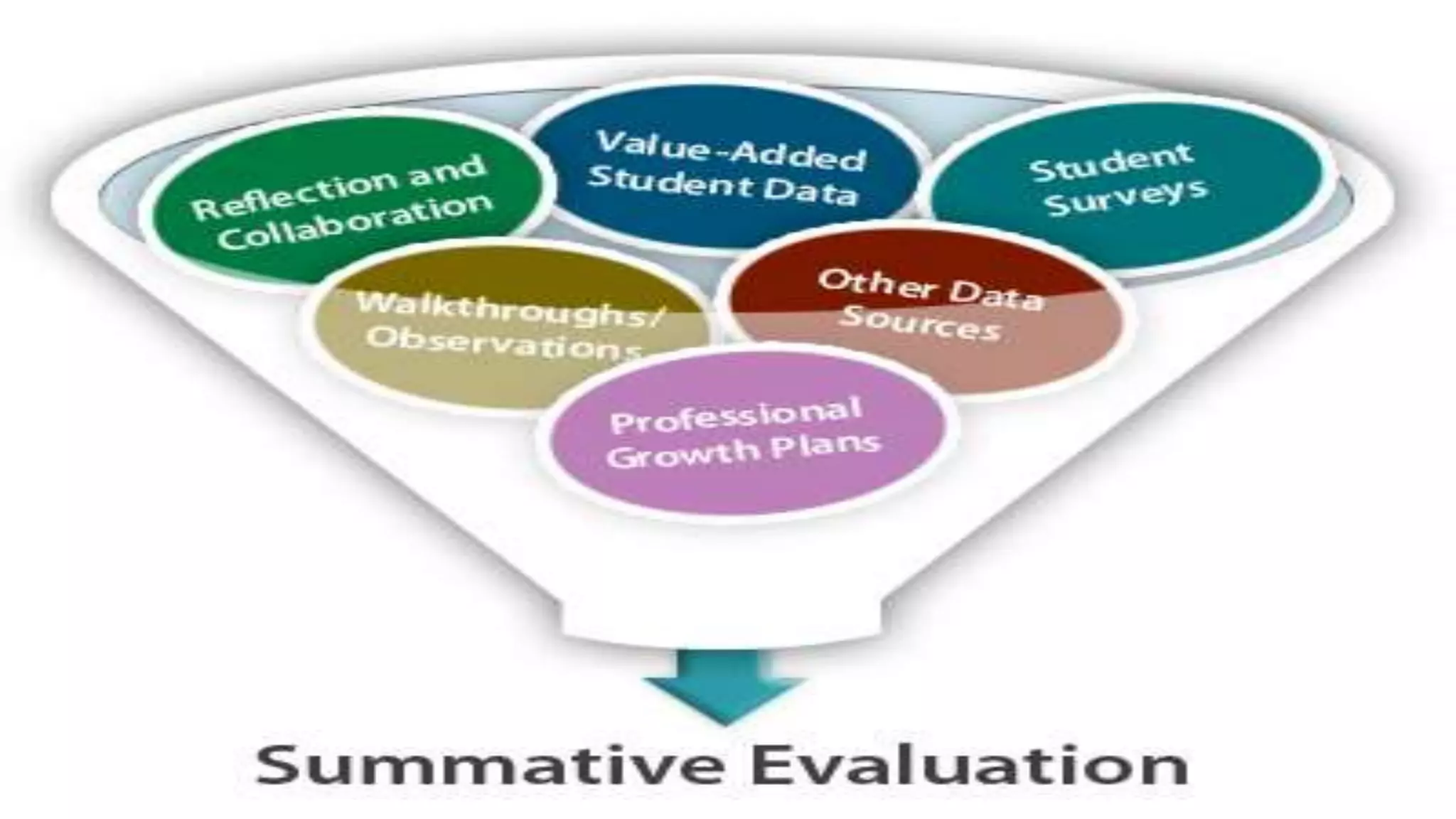
This document discusses summative evaluation, which assesses student learning at the end of a course or unit. Summative evaluation determines if learning objectives were achieved and identifies areas needing further instruction. It has two main phases: the expert judgement phase and field trial phase. The expert judgement phase involves content and design analysis by instructors and subject experts to determine if materials meet organizational needs. The field trial phase analyzes the materials' effectiveness on learners and impact on job and organization performance. Summative evaluation provides information to assess progress and determine if learning objectives were attained.