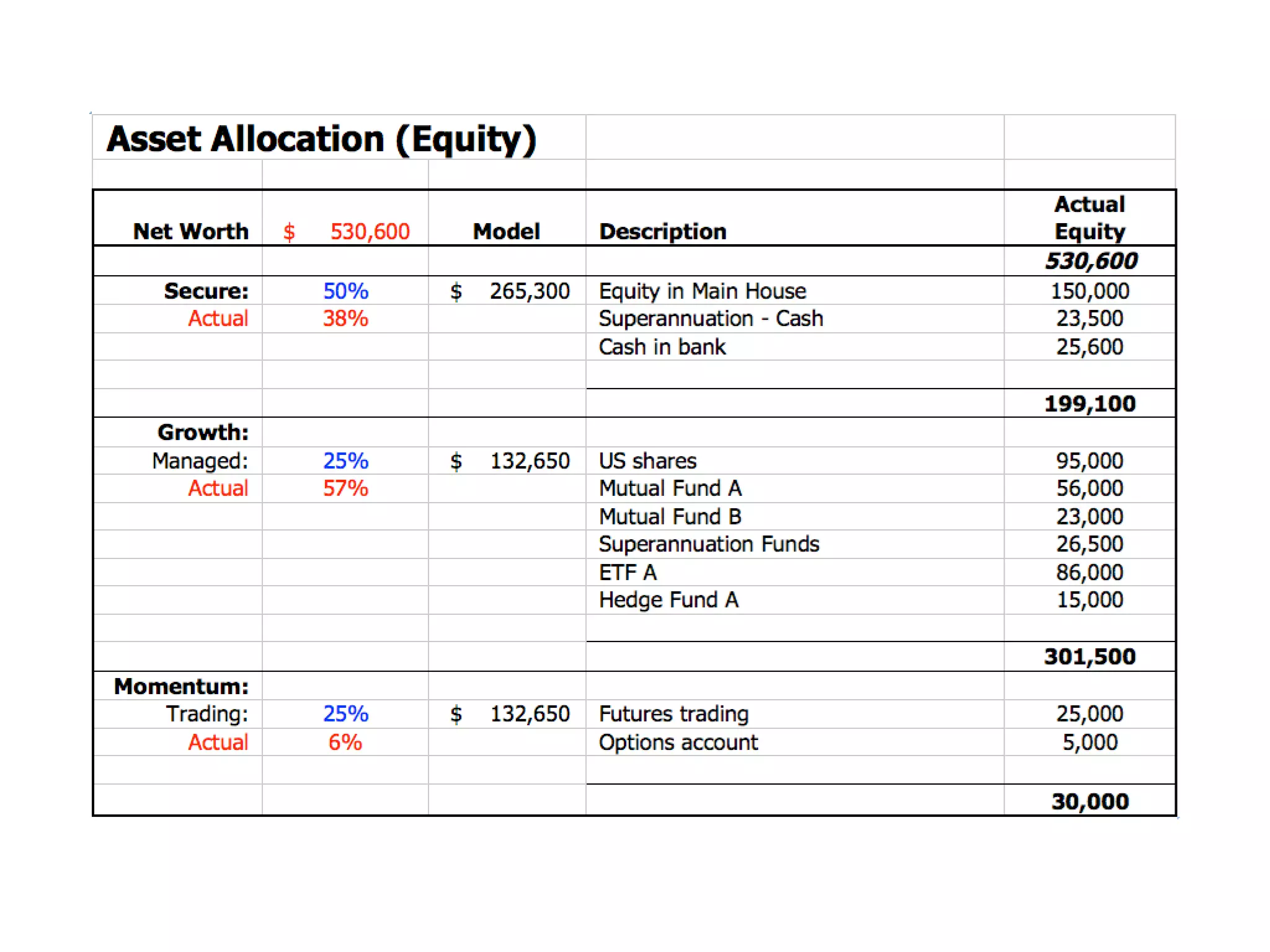
The document discusses asset allocation and its importance in financial planning. It defines asset allocation as a strategy for choosing between different types of investments like stocks and bonds. A large part of financial planning involves finding an asset allocation that matches a person's risk tolerance and needs. The document states that asset allocation is often the key determinant of long-term returns on a portfolio. It then presents a "bucket concept" that categorizes different asset types into security, growth, and momentum buckets with suggested allocations based on a person's age and risk profile.