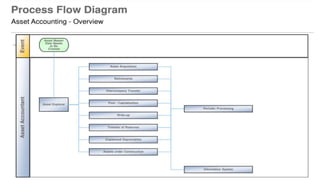
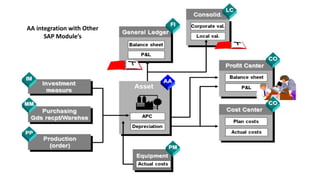
This document provides an overview of asset accounting in SAP ERP. It discusses key concepts like the general ledger, chart of accounts, asset classes, acquisitions, retirements, depreciation, and assets under construction. The purpose of asset accounting is to manage fixed assets over their entire lifetime, from purchase to retirement, while calculating depreciation. It integrates with other SAP modules like materials management and allows traditional asset accounting as well as processing leased assets and consolidated reporting. Standard reports are available to view asset balances, depreciation simulations, and asset histories.