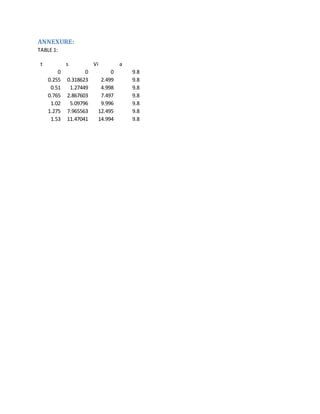
1. The document analyzes the kinematics of a ball thrown upward with an initial velocity (Vi) of 15 m/s, experiencing a constant downward acceleration (a) of 9.8 m/s^2.
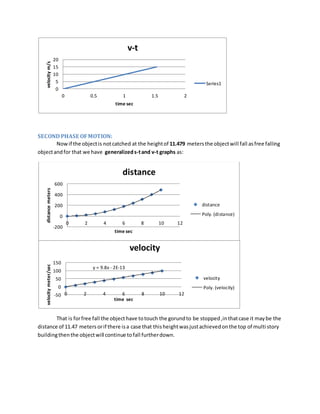
2. It is calculated that the ball reaches its maximum height of 11.479 meters after 1.5306 seconds, at which point its velocity is 0 m/s.
3. If not caught, the ball will then fall freely back to the ground, following the kinematic equations of constant downward acceleration and reaching higher velocities as it falls.