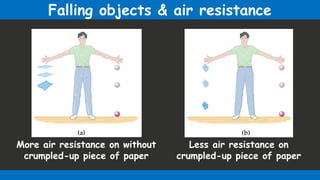
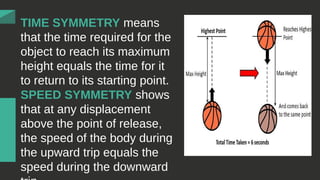
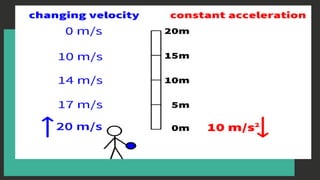
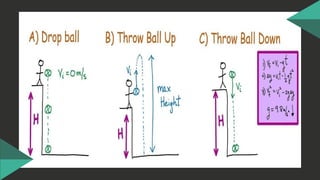
The document discusses the concept of free fall as a type of uniformly accelerated motion, emphasizing that all objects fall at the same rate regardless of mass when air resistance is ignored. It includes relevant formulas for calculating distance and velocity during free fall, with examples illustrating the concepts. Key points include that the acceleration due to gravity is approximately -9.8 m/s², and that the motion exhibits time and speed symmetry.