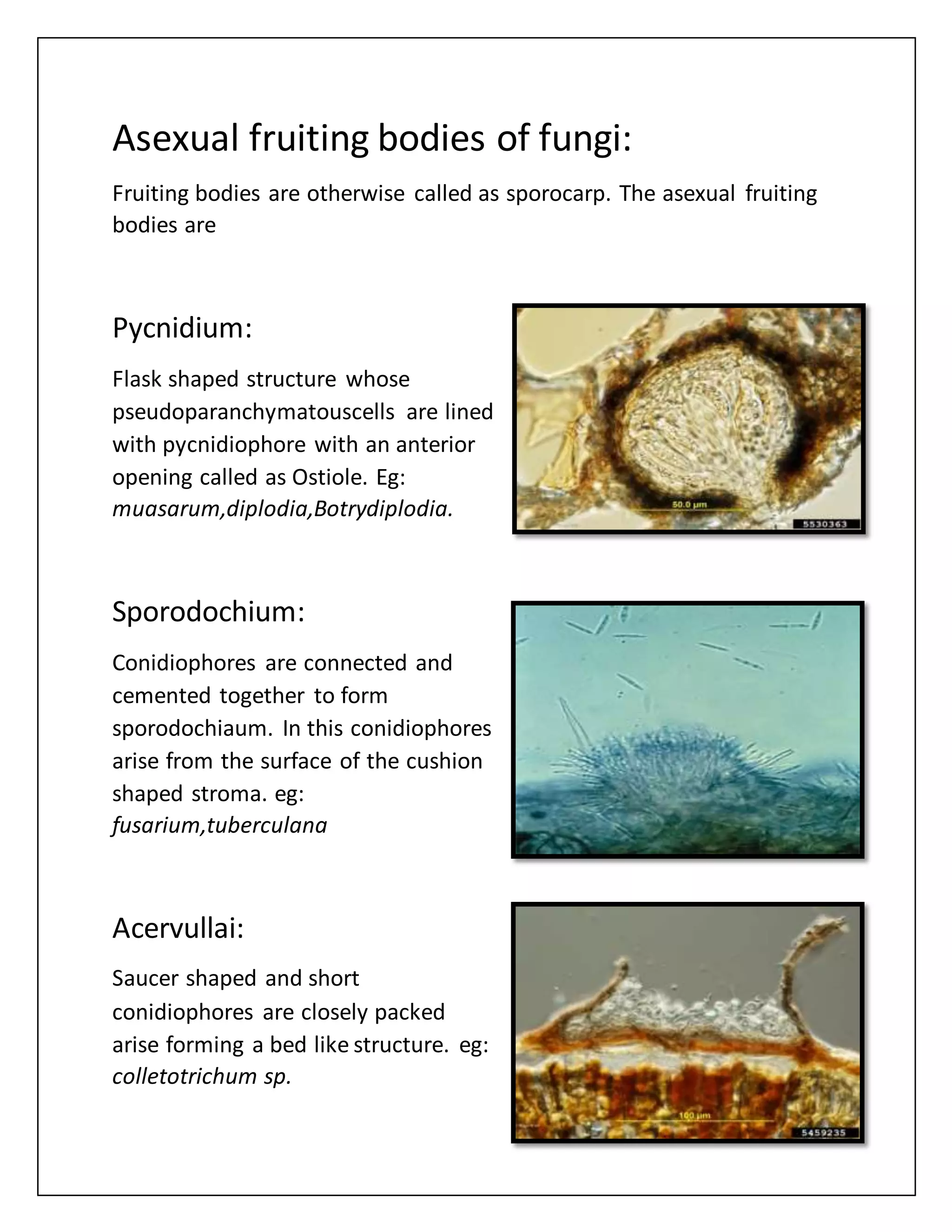
Fungi can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Asexual reproduction, which occurs more frequently than sexual reproduction, involves the production of mitospores through mitosis. There are several methods of asexual reproduction in fungi, including fragmentation, fission, and budding. Fungi also produce asexual spores and fruiting bodies for reproduction. Common asexual fruiting structures include pycnidia, sporodochia, acervuli, synnema, and sori.