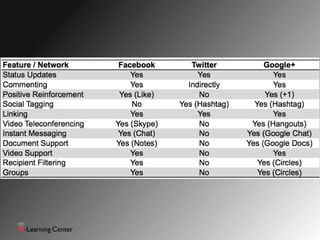
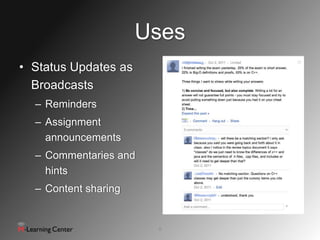
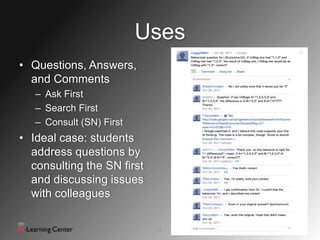
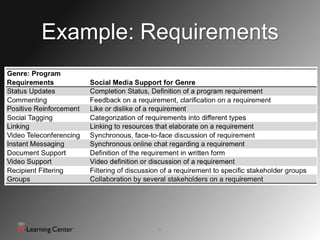
This document discusses using social networks for effective communication and collaboration in computing education. It identifies common modes of communication on social networks and how they can be used educationally. These include status updates, comments, links, videos and documents. The document suggests social networks can increase student engagement, decrease email usage, and support flipped classrooms. It provides recommendations for guidelines, policies and modeling behavior when using social media for education.