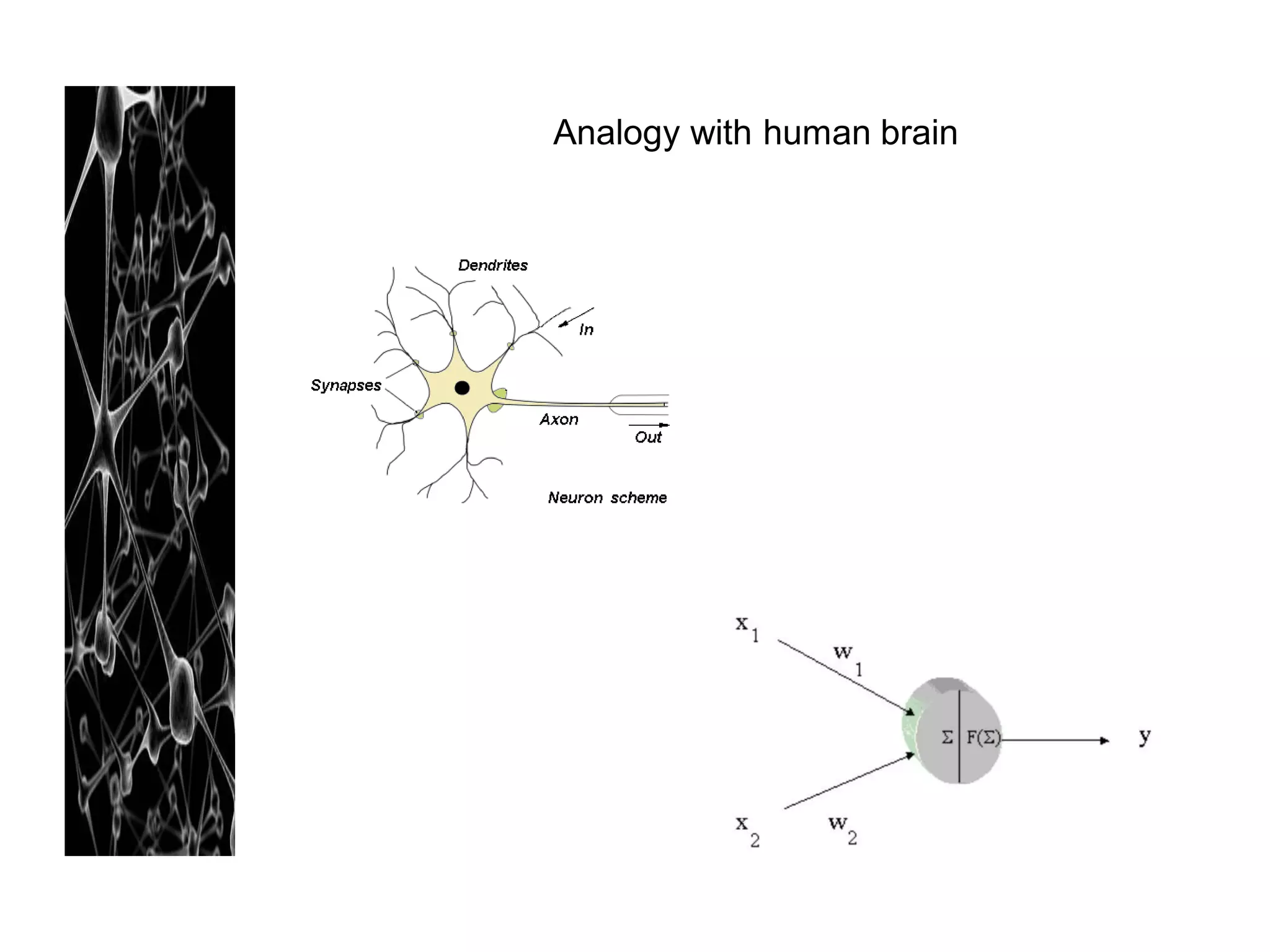
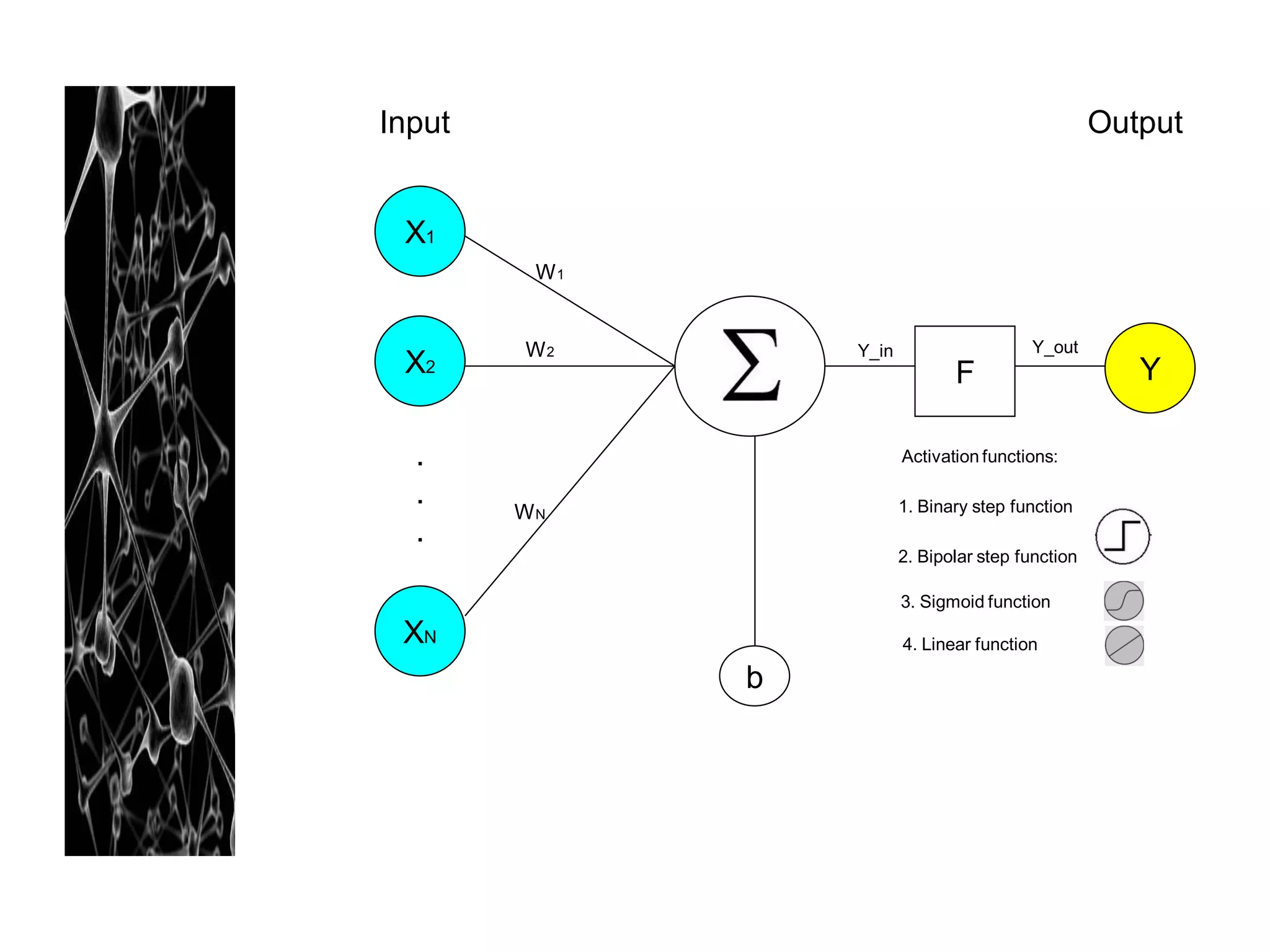
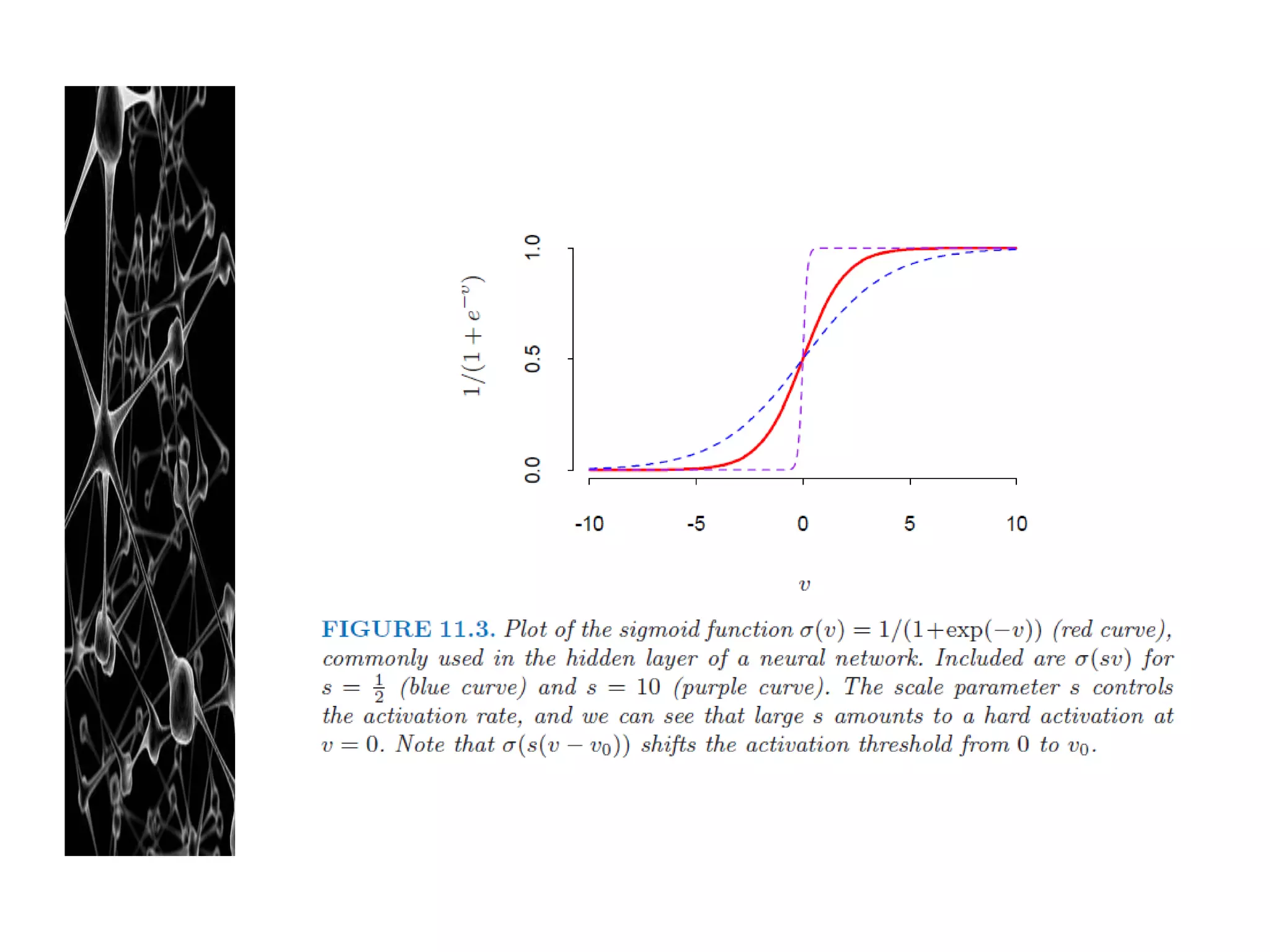
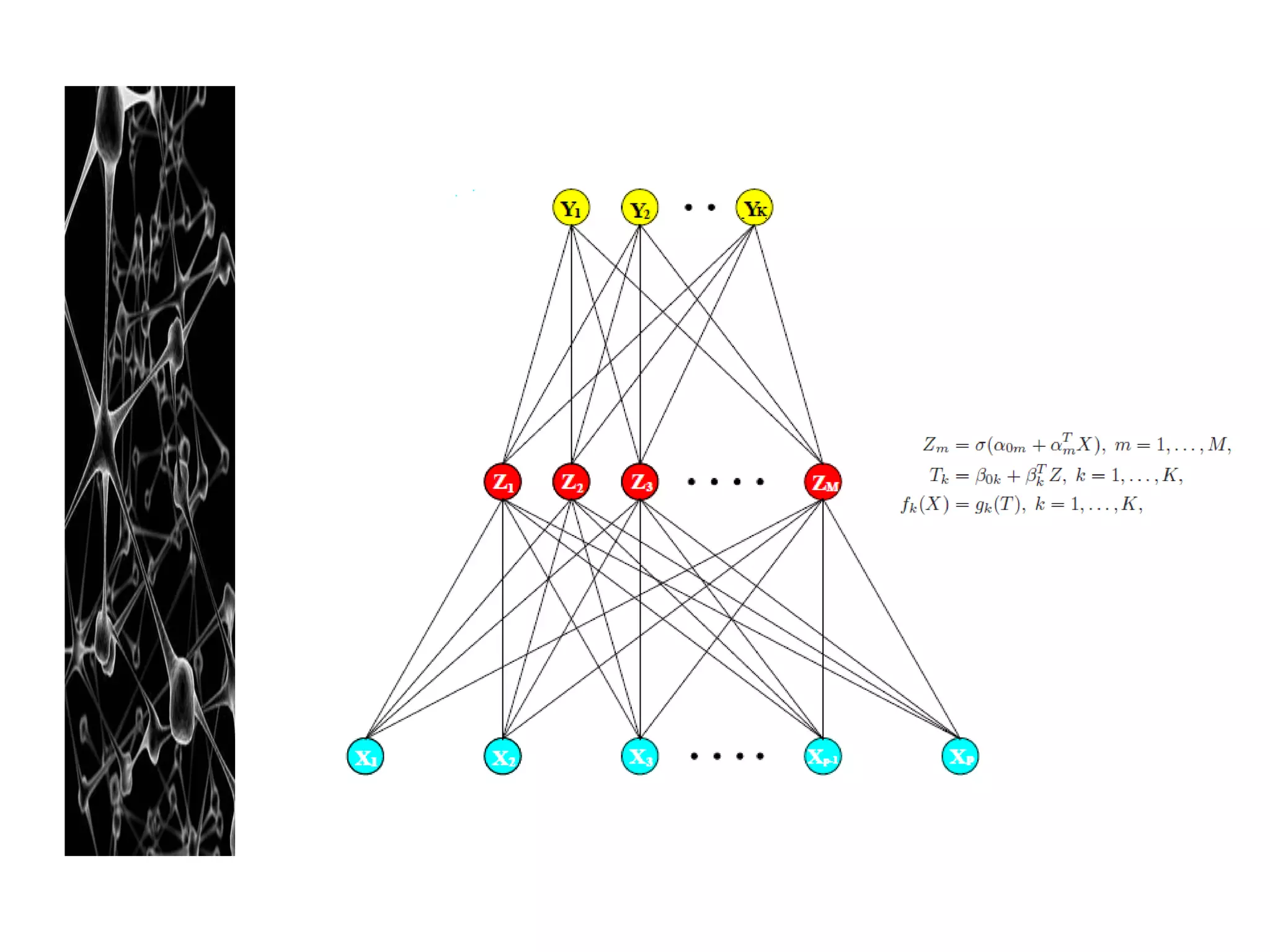
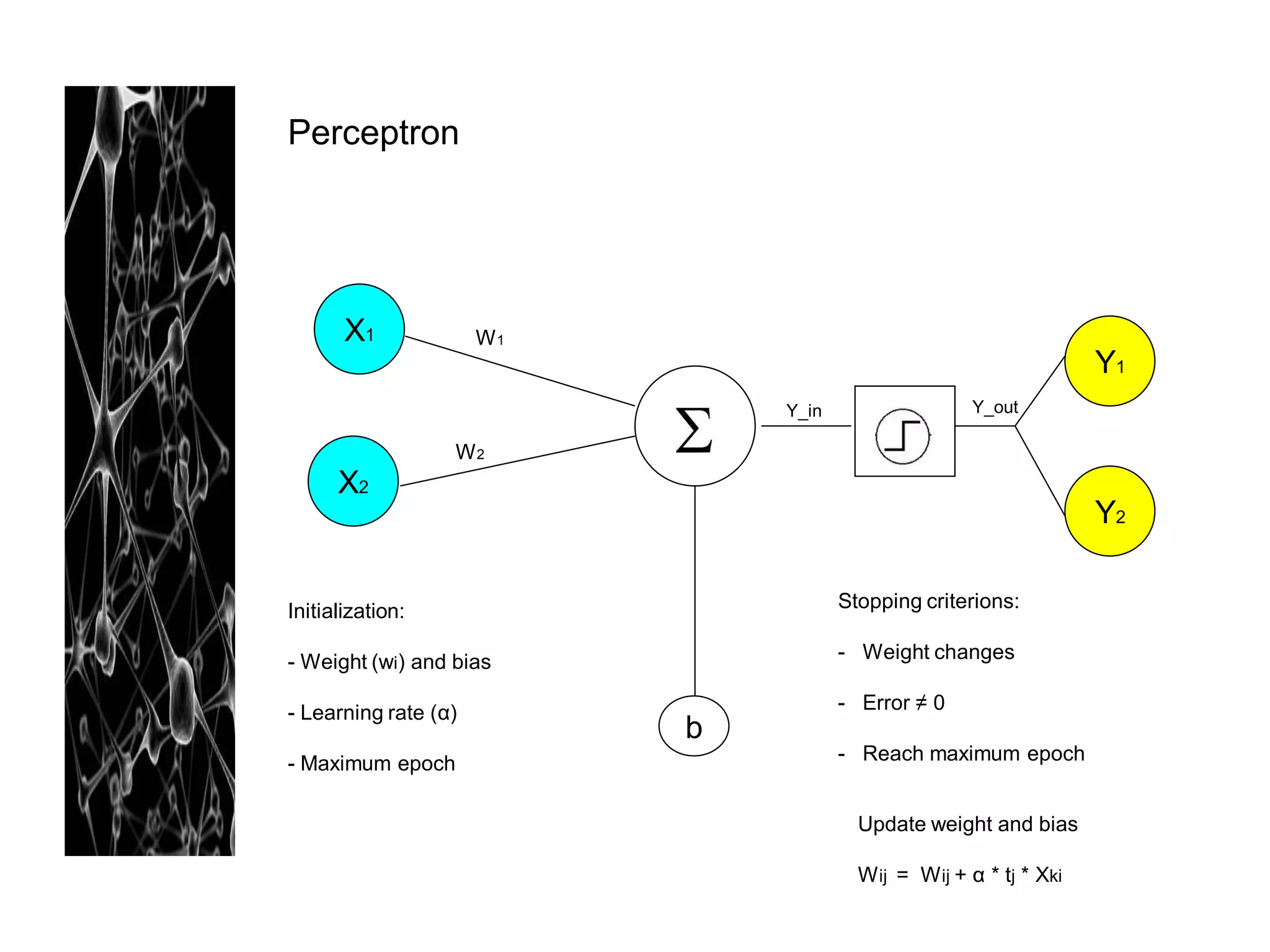
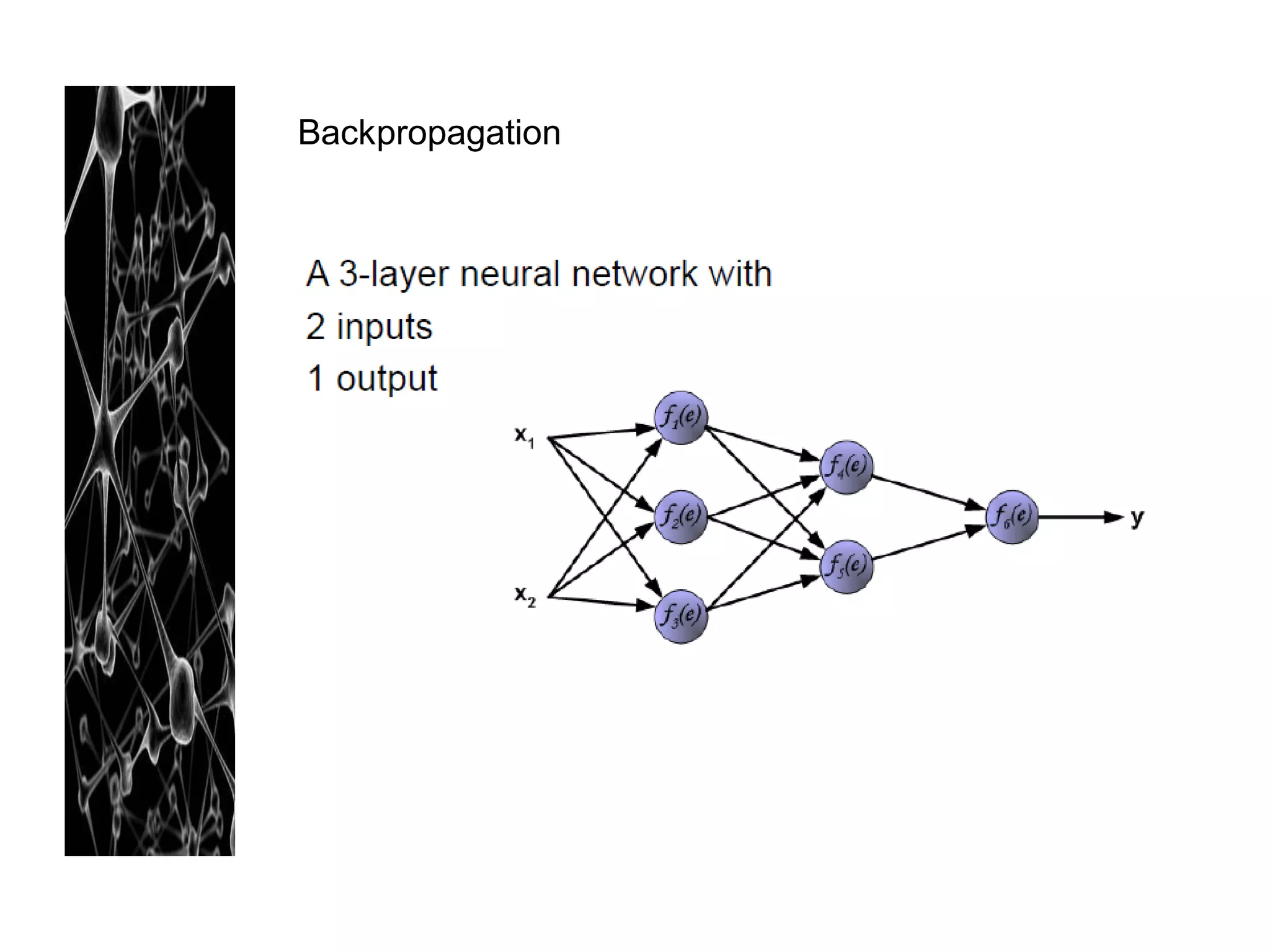
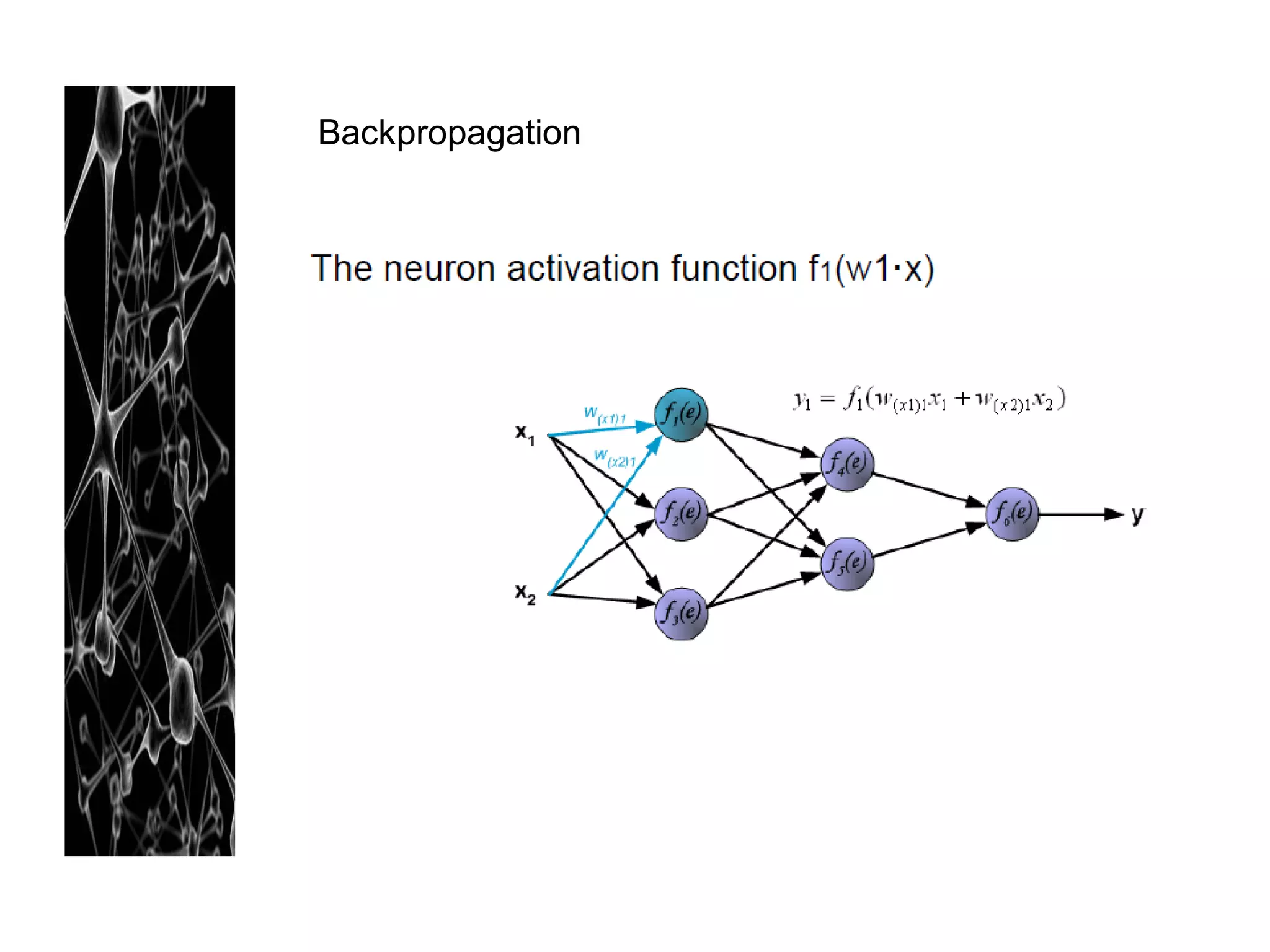
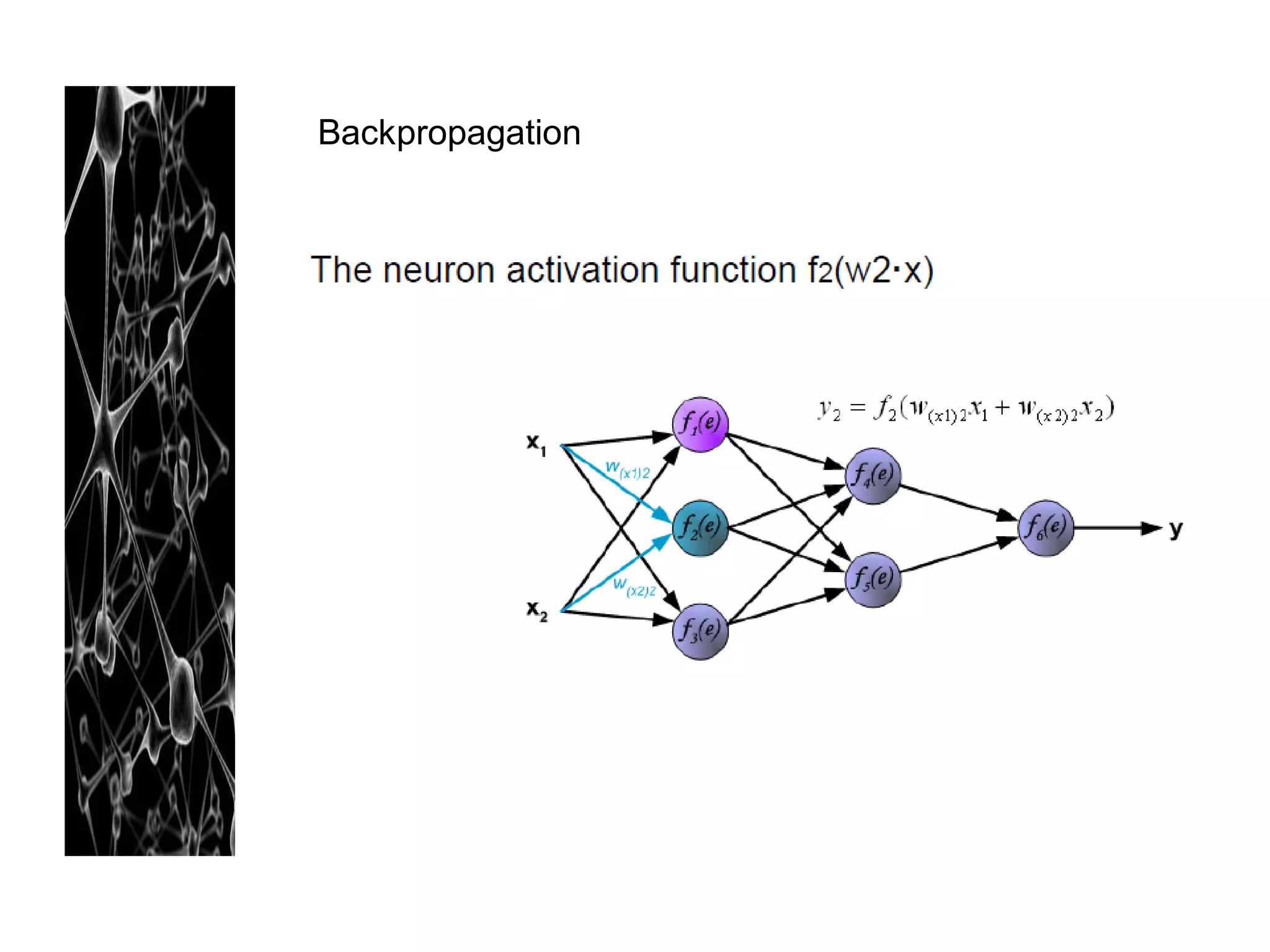
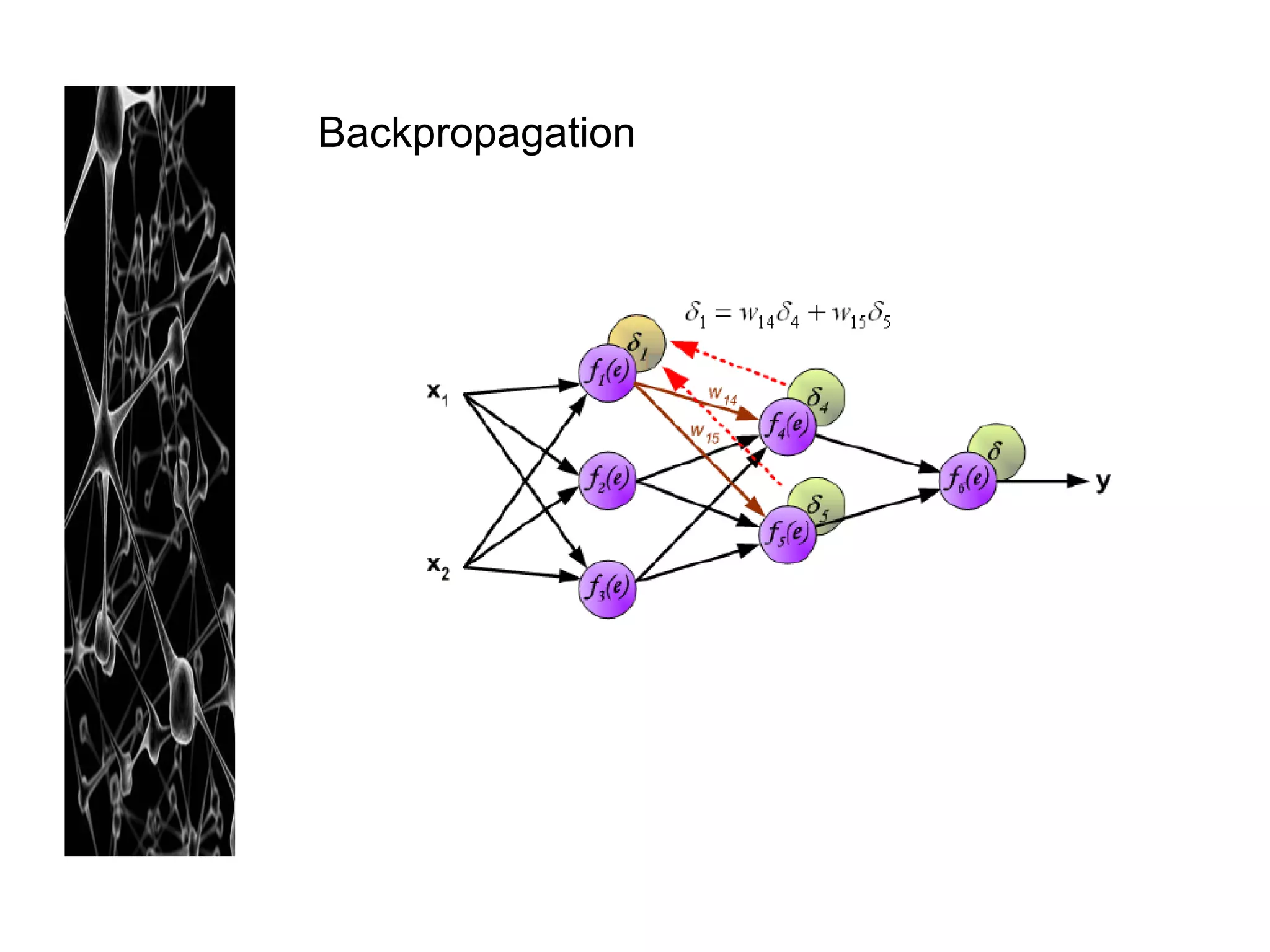
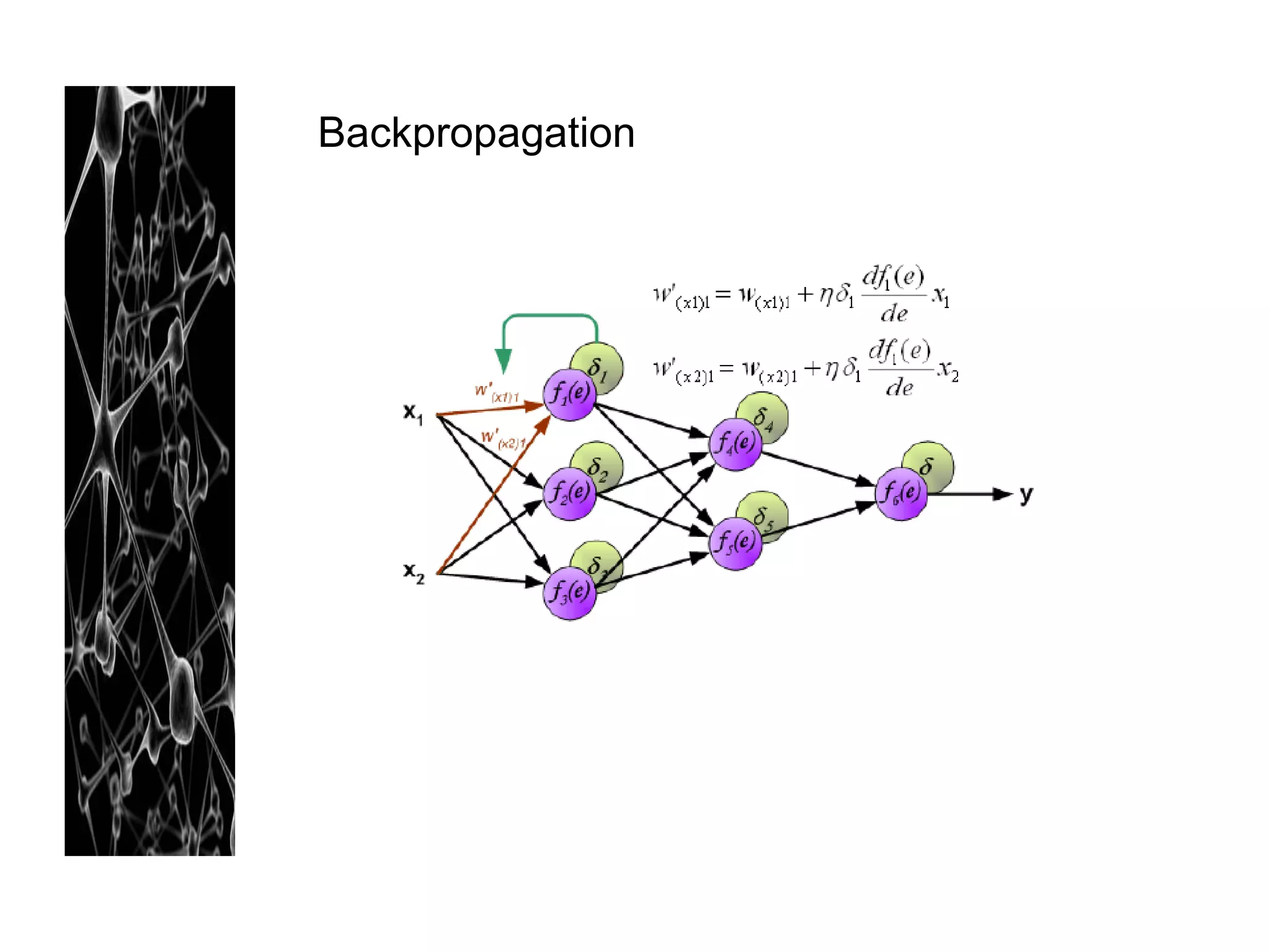
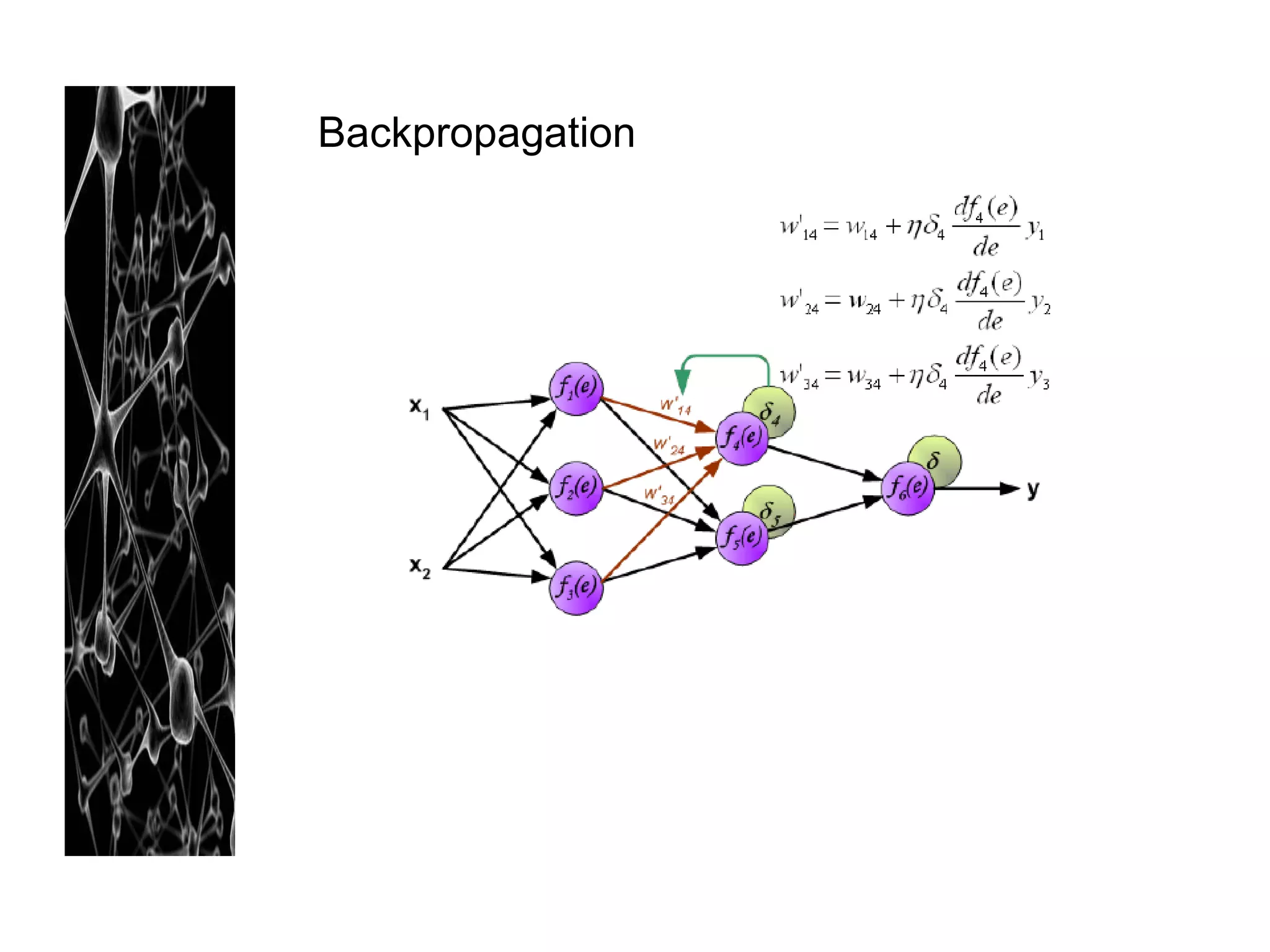
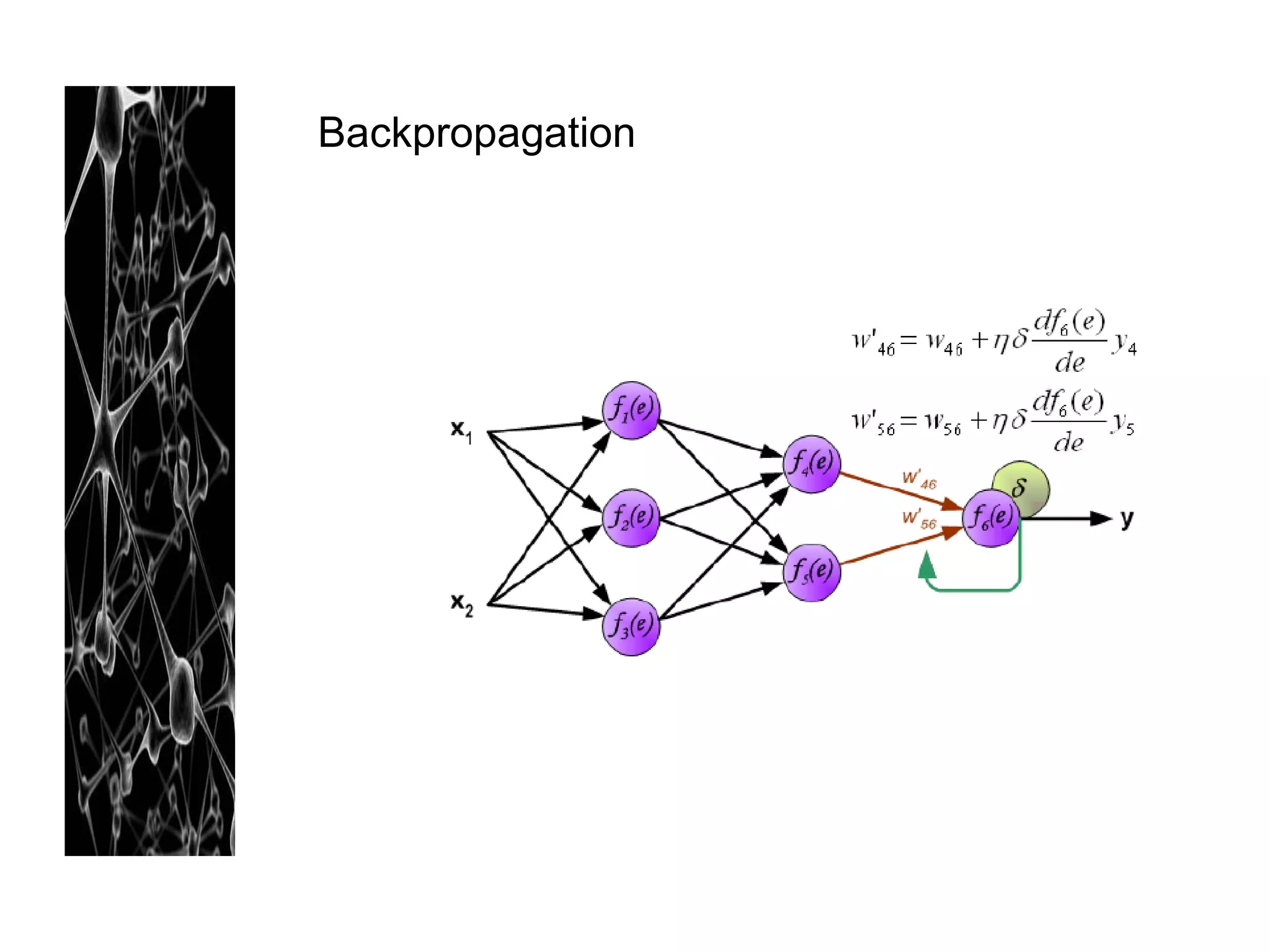
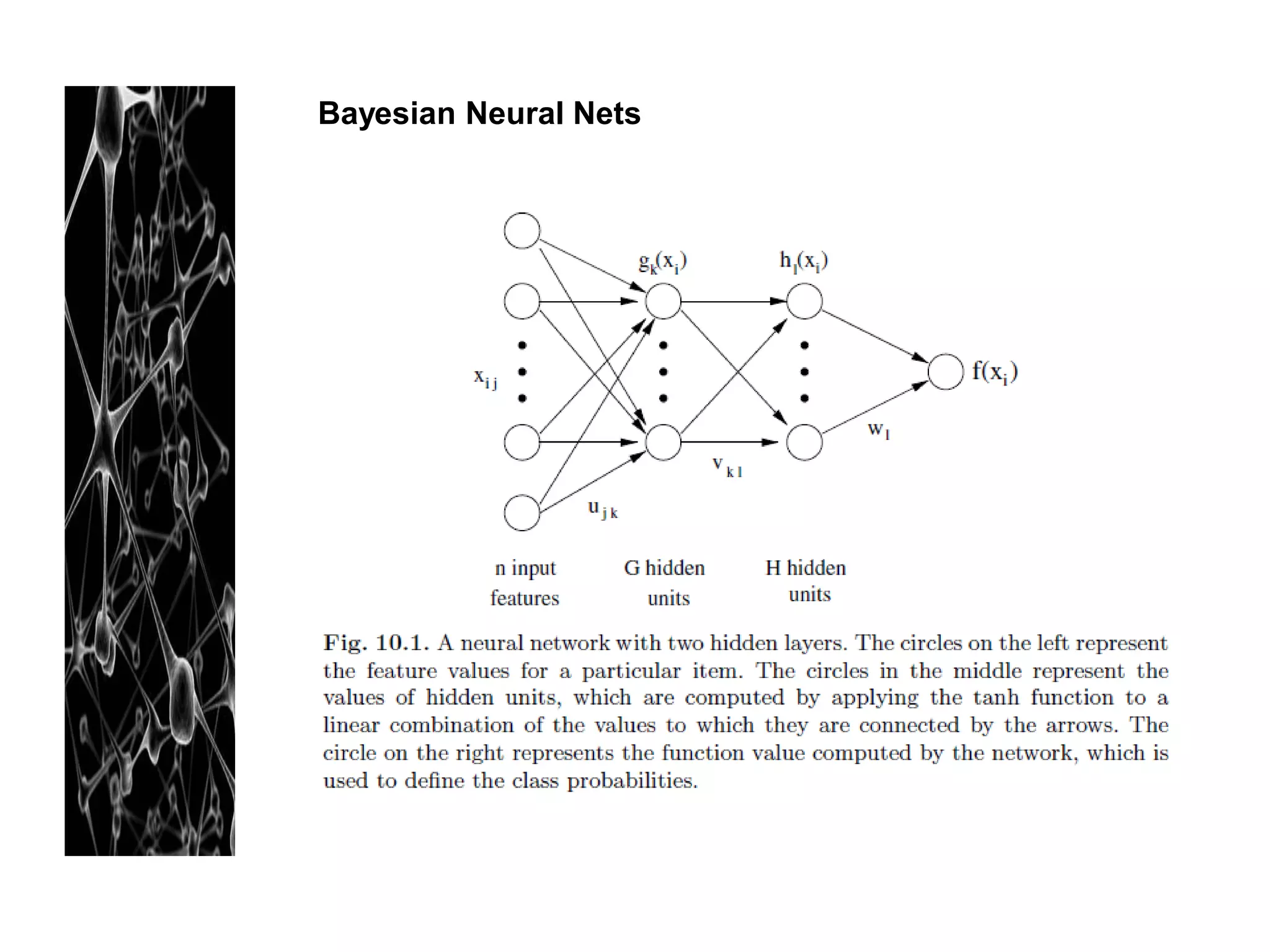
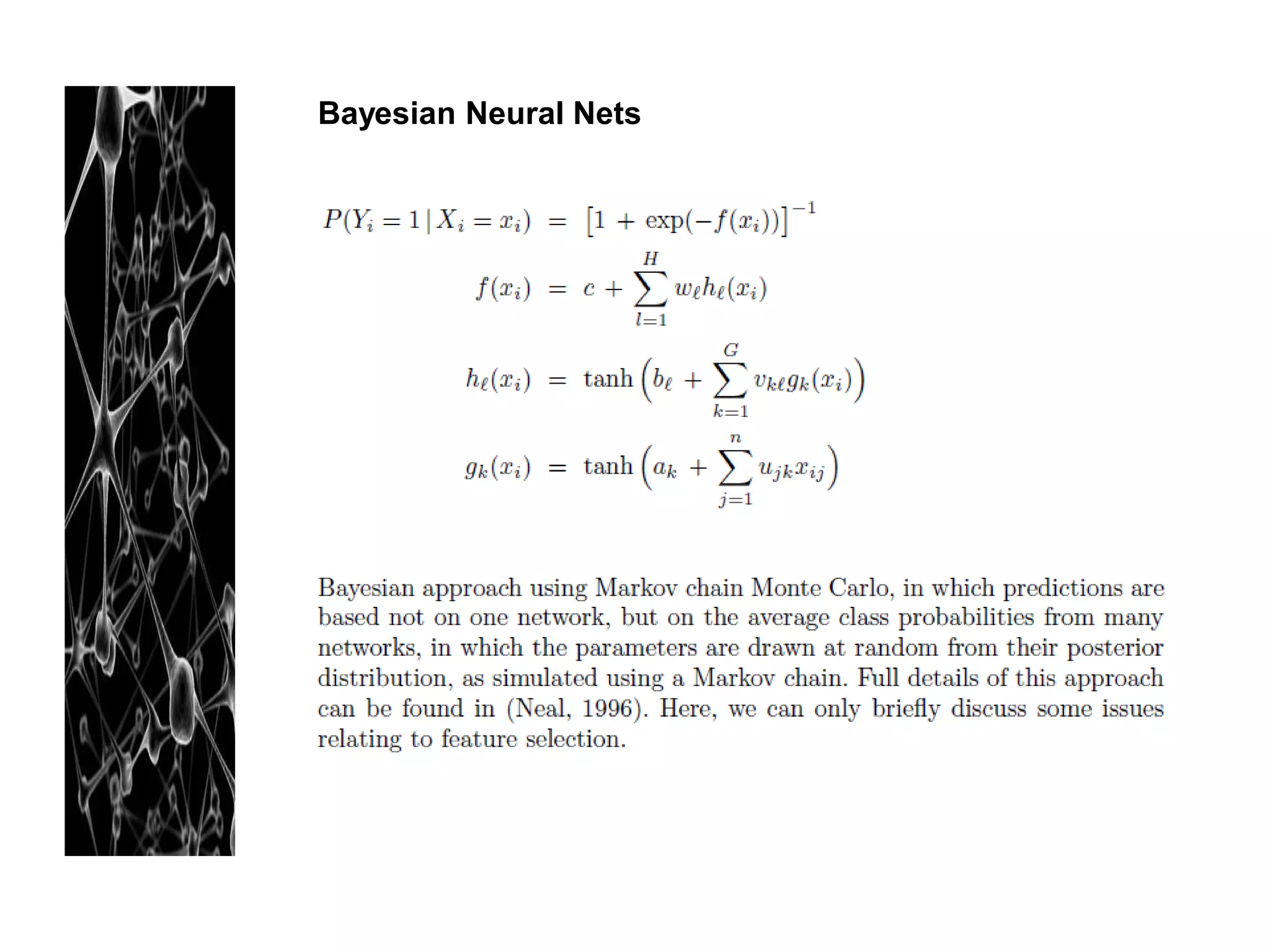
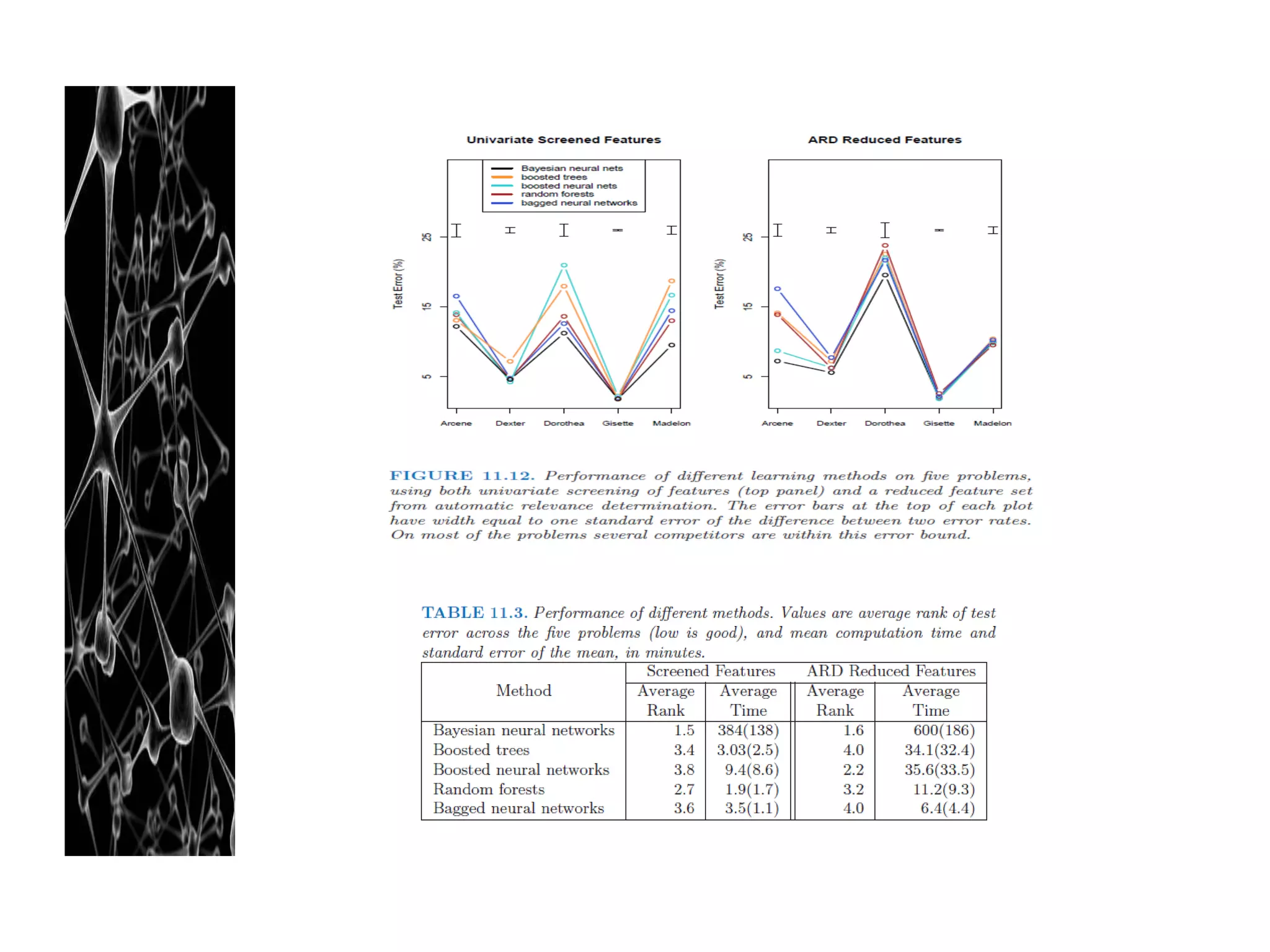
Neural networks are modeled after the human brain and consist of interconnected nodes that process information using activation functions. They can be trained to recognize patterns in data and make predictions. The network is initialized with random weights and biases then trained via backpropagation to minimize an error function by adjusting the weights. Issues that can arise include overfitting, choosing the number of hidden layers and units, and multiple local minima. Bayesian neural networks place prior distributions over the weights to better model uncertainty. Ensemble methods like bagging and boosting can improve performance.




![Some Issues in Training NN
3. Scaling the input
- Since scaling the input determines the effective scaling of the weight in the
bottom layer, It can have the large effect of the final model
- It is better to standardize all inputs (mean = 0 and std.dev = 1)
- Ensure all inputs are treated equally in regulation process and allows one to
choose a meaningfull range for random starting weights.
- Typical weight for standardized inputs: random uniform weight over the range
[-0.7, 0.7]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artificialneuralnetworkreadinggrouup-130102134440-phpapp02/75/Artificial-Neural-Network-21-2048.jpg)
![Some Issues in Training NN
4. Number of hidden units and layers
- Better to have too many hidden units than too few
Too few hidden units: Less flexibility of the model (hard to capture nonlinearity)
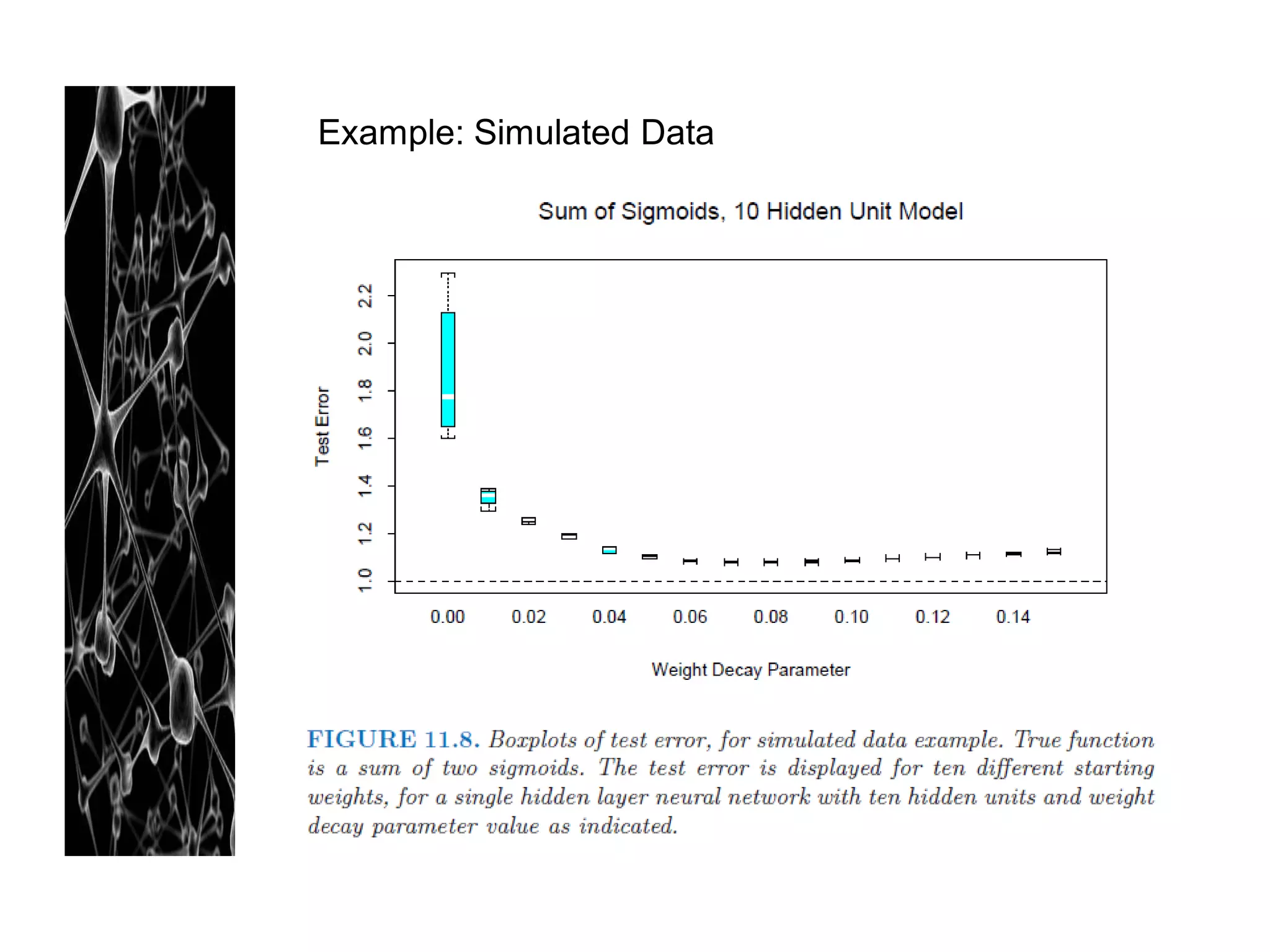
Too many hidden units: extra weight can be shrunk towards zero with
appropriate regularization used
- Typical # of hidden units : [5, 100]
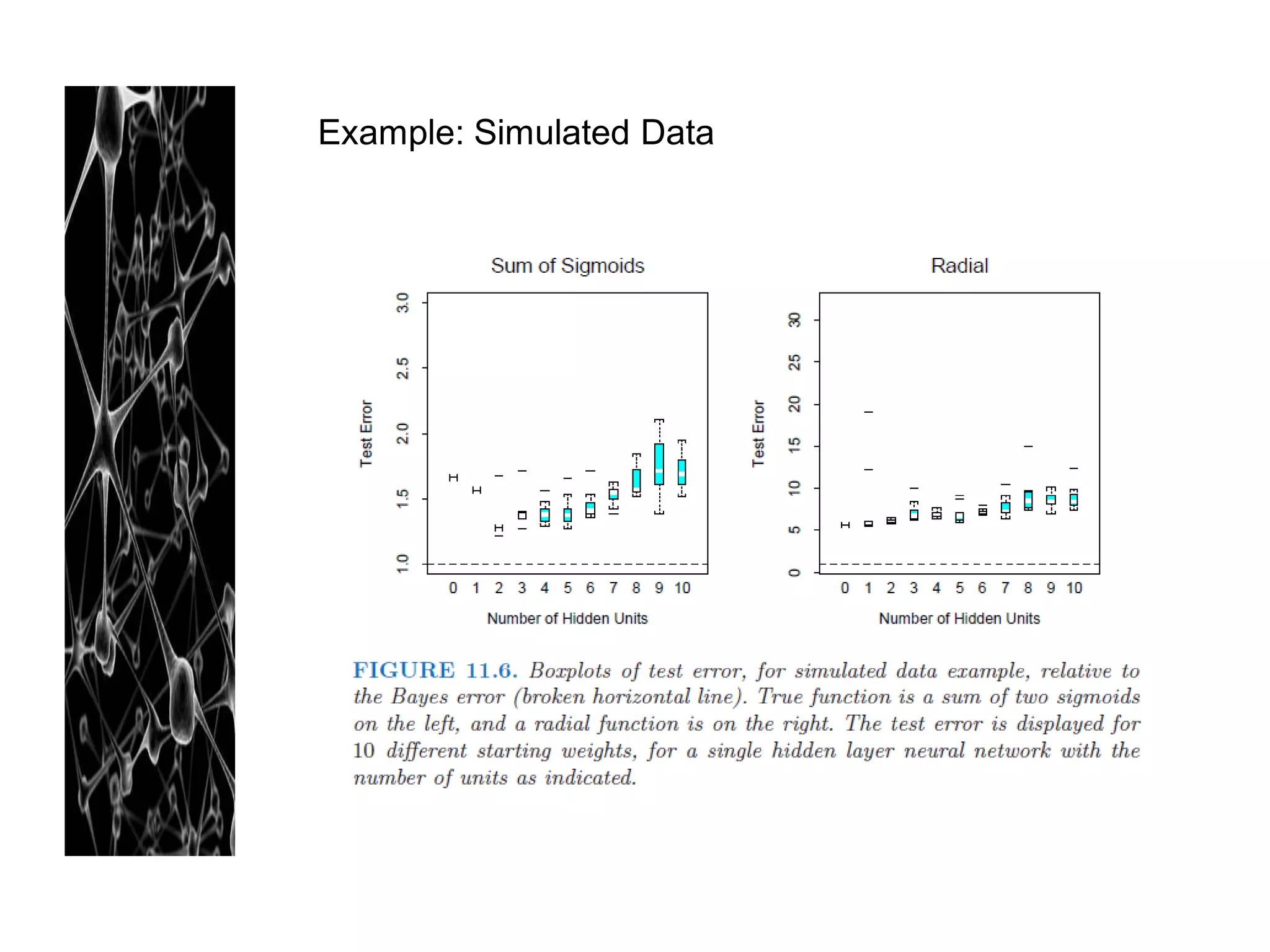
5. Multiple Minima
- The error function R(θ) is non-convex, possessing many local minima.
As result, the final solution quite depends on the choice of starting weight.
- Solution:
* averaging the predictions over the collection of networks as the final prediction
* averaging the weight
* bagging: averaging the prediction of the networks training from randomly
perturbed version of the training data.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artificialneuralnetworkreadinggrouup-130102134440-phpapp02/75/Artificial-Neural-Network-22-2048.jpg)



![References
[1] Zhang, X. Support Vector Machine. Lecture slides on Data Mining course. Fall 2010, KSA:
KAUST
[2] Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R., Friedman, J. The elements of statistical learning, second edition.
2009. New York: Springer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artificialneuralnetworkreadinggrouup-130102134440-phpapp02/75/Artificial-Neural-Network-37-2048.jpg)