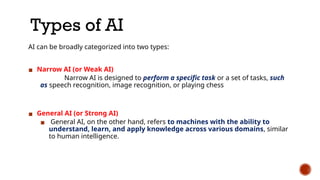
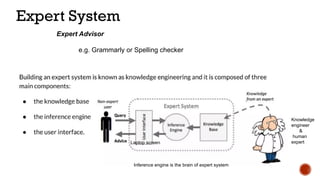
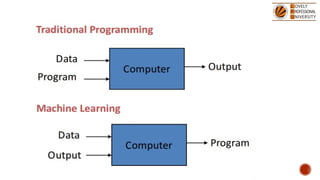
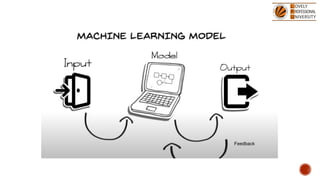
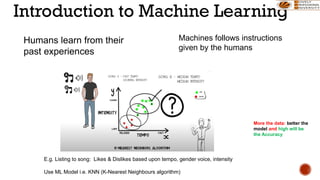
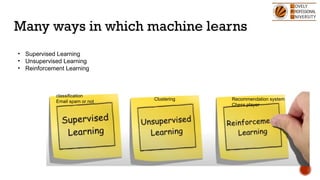
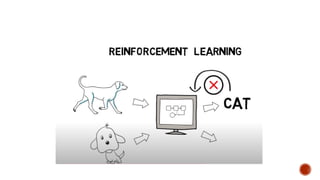
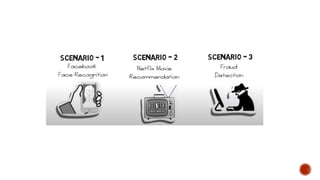
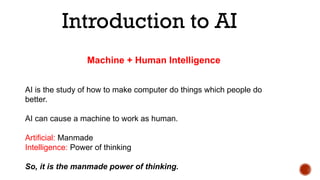
The document discusses artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), emphasizing their definitions, types, and applications. It details various ML paradigms including supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning, along with specific algorithms and tasks. Additionally, it covers components of AI, expert systems, and current trends, while also outlining necessary skills and job roles in the field.








![Reasons of Boost in AI
S/w or device can be made to solve real time problem.
Creation of virtual assistant. E.g. SIRI, CORTANA, ALEXA
Robots development [Helps in different dangerous environment
condition]
New Job opportunity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2aiml1-240822072156-c12ade4c/85/Unit-2-artificial-intelligence-and-machine-learning-18-320.jpg)