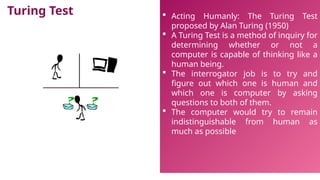
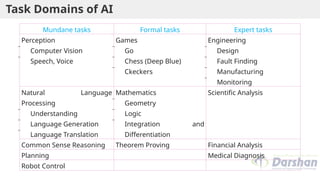
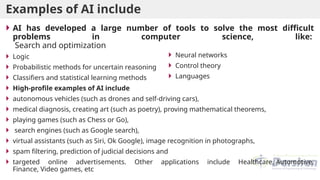
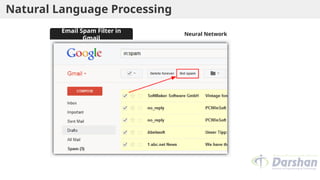
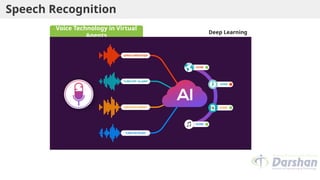
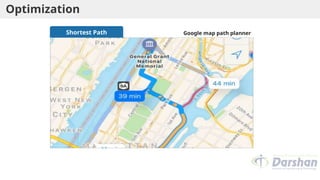
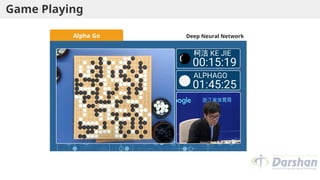
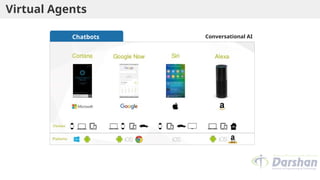
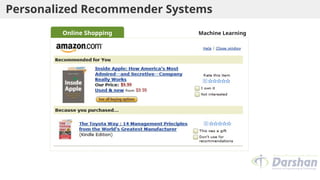
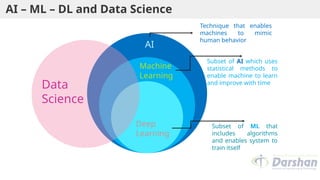
This document provides an introduction to artificial intelligence (AI), defining it as a branch of computer science focused on simulating intelligent behavior in machines. It outlines different approaches to AI, including the Turing Test and various techniques such as search, knowledge usage, and abstraction. The document also discusses applications of AI across various domains, such as healthcare, finance, and autonomous systems.