The document summarizes an introduction to artificial intelligence presented by the group "RAW AGENT". It lists the group members and then covers several key areas of AI including:
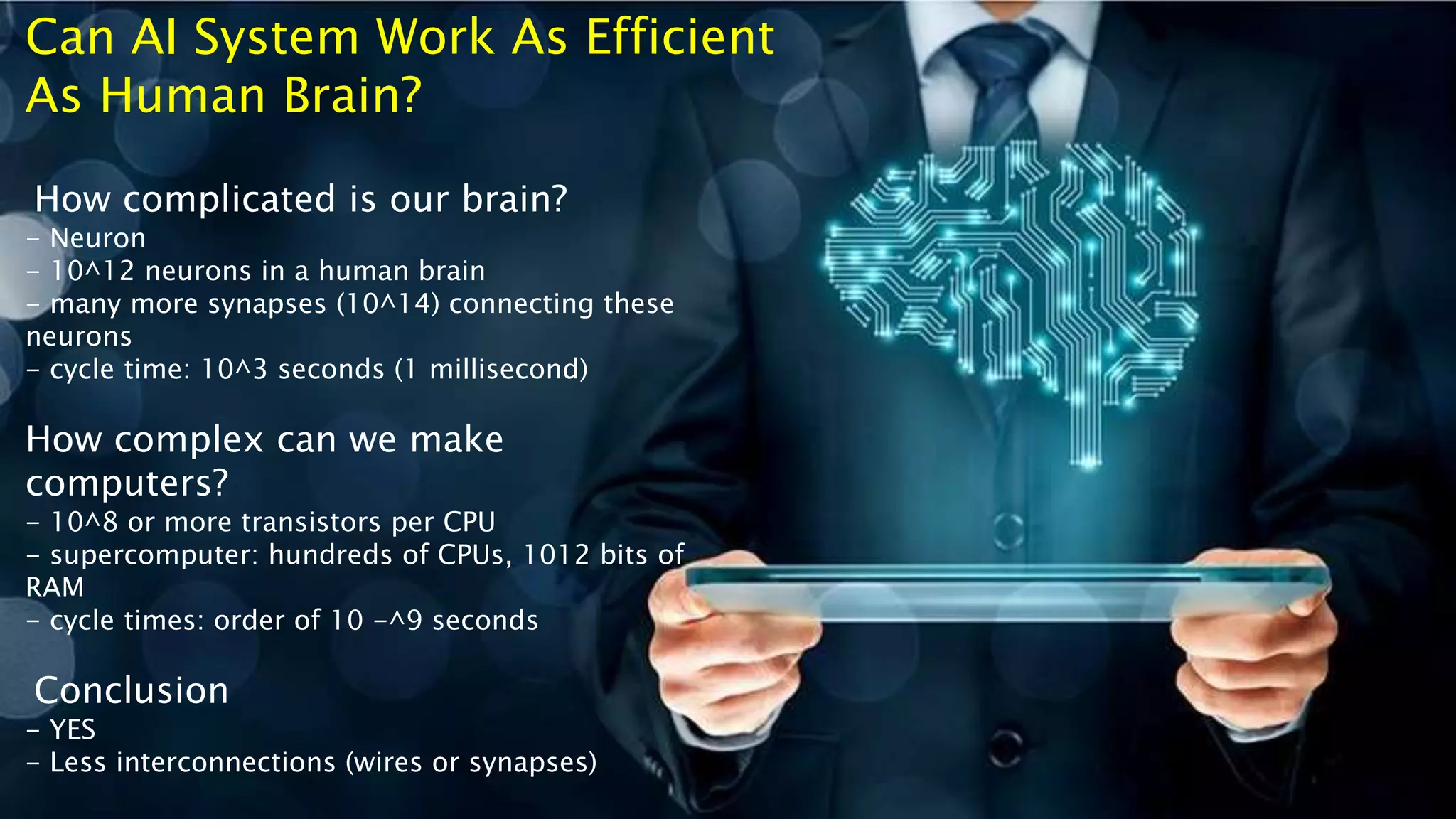
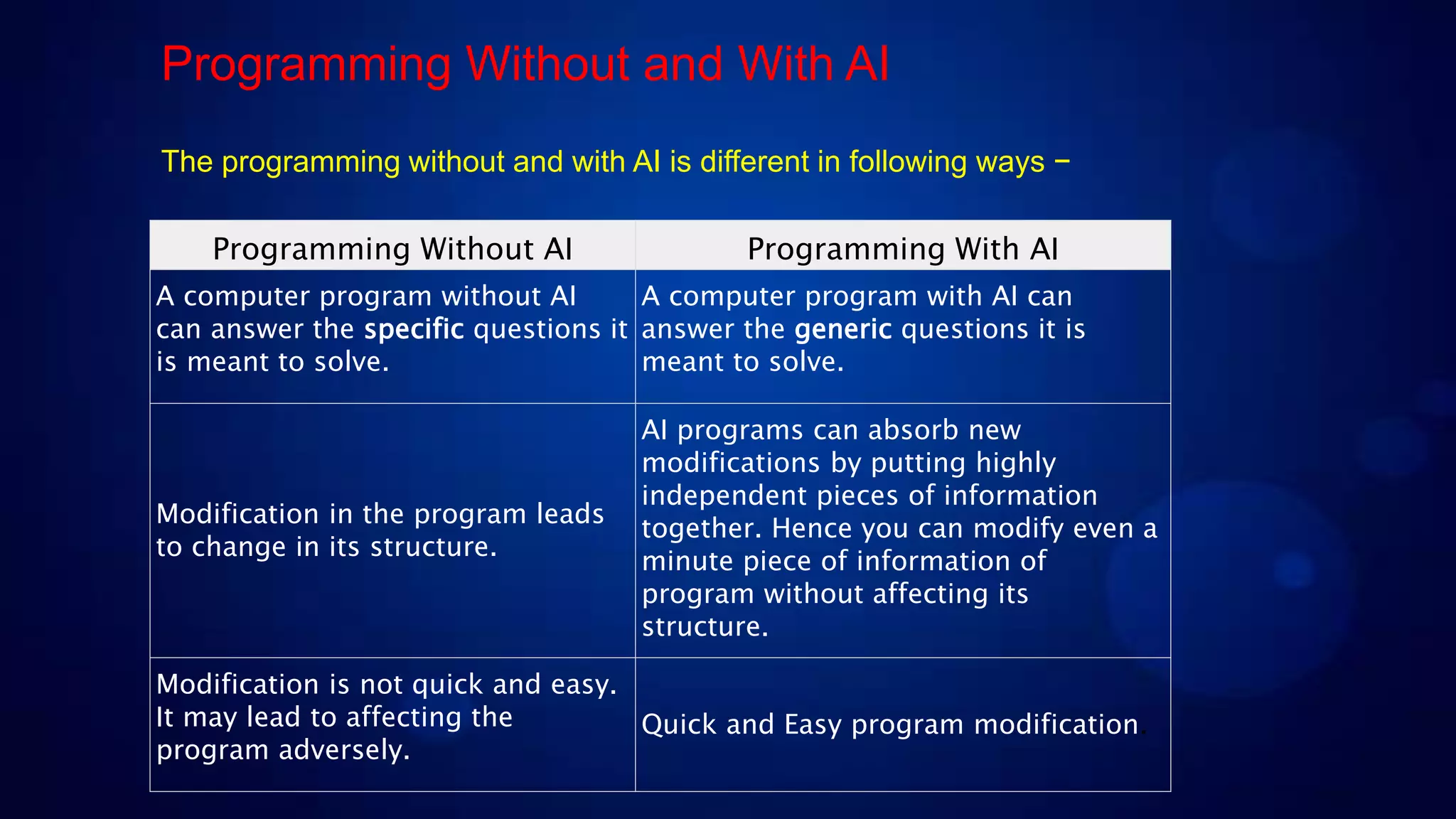
- An introduction to AI, how it aims to simulate human intelligence by studying how the human brain thinks and solves problems.
- Common AI programming languages like Lisp, Prolog which are well-suited for AI applications.
- Applications of AI like natural language understanding, expert systems, planning and robotics, machine learning, and game playing.
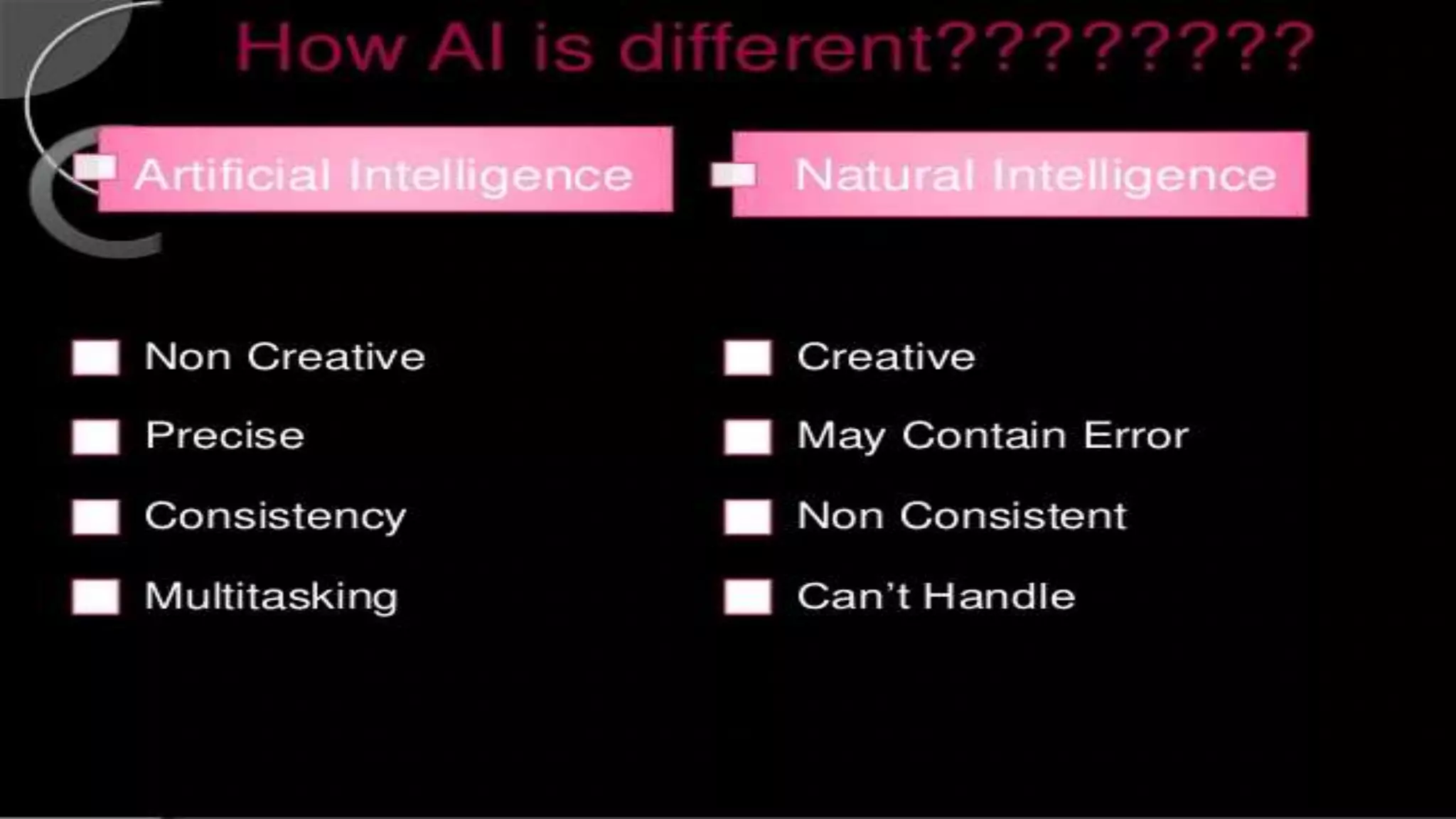
- Some drawbacks of current AI systems like limited abilities, slow real-time response, inability to handle emergencies, difficult coding, and high costs.