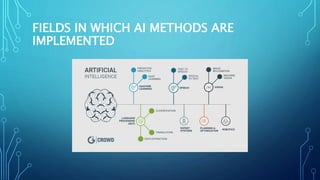
The presentation discusses artificial intelligence (AI), defining it as the discipline focused on helping machines solve complex problems in a human-like manner. It covers the history, goals, categories, and applications of AI, as well as its future potential in achieving human-level capabilities and the risks associated with AI development. Ultimately, it emphasizes the importance of understanding and managing AI as it becomes increasingly integrated into various fields.