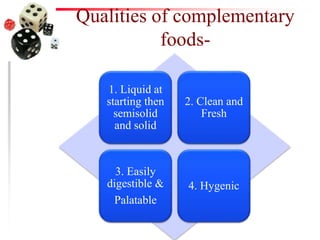
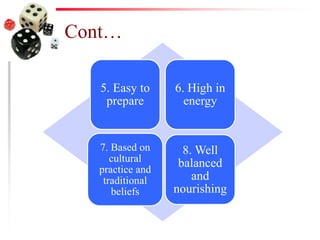
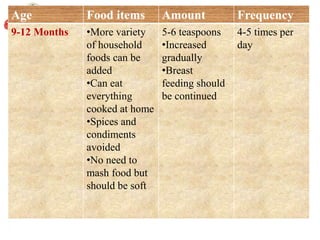
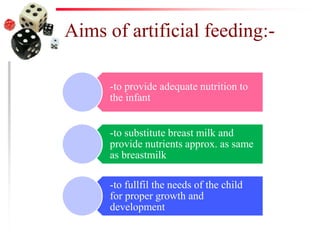
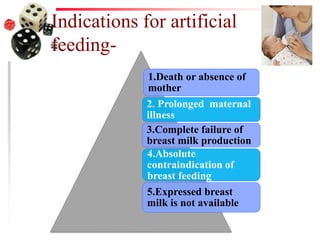
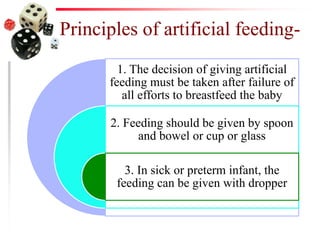
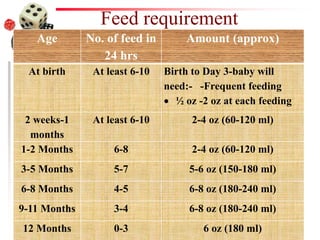
The document discusses the process of weaning and artificial feeding for infants, defining weaning as the gradual transition from breastfeeding to family diet while continuing breastfeeding as needed. It highlights the characteristics and introduction principles of complementary foods, emphasizes the importance of hygiene in food preparation and storage, and covers the guidelines for artificial feeding when breastfeeding is not possible. Additionally, it outlines the nutritional comparisons between cow's milk and human milk, and provides feeding requirements based on the infant's age, while indicating the hazards associated with artificial feeding.