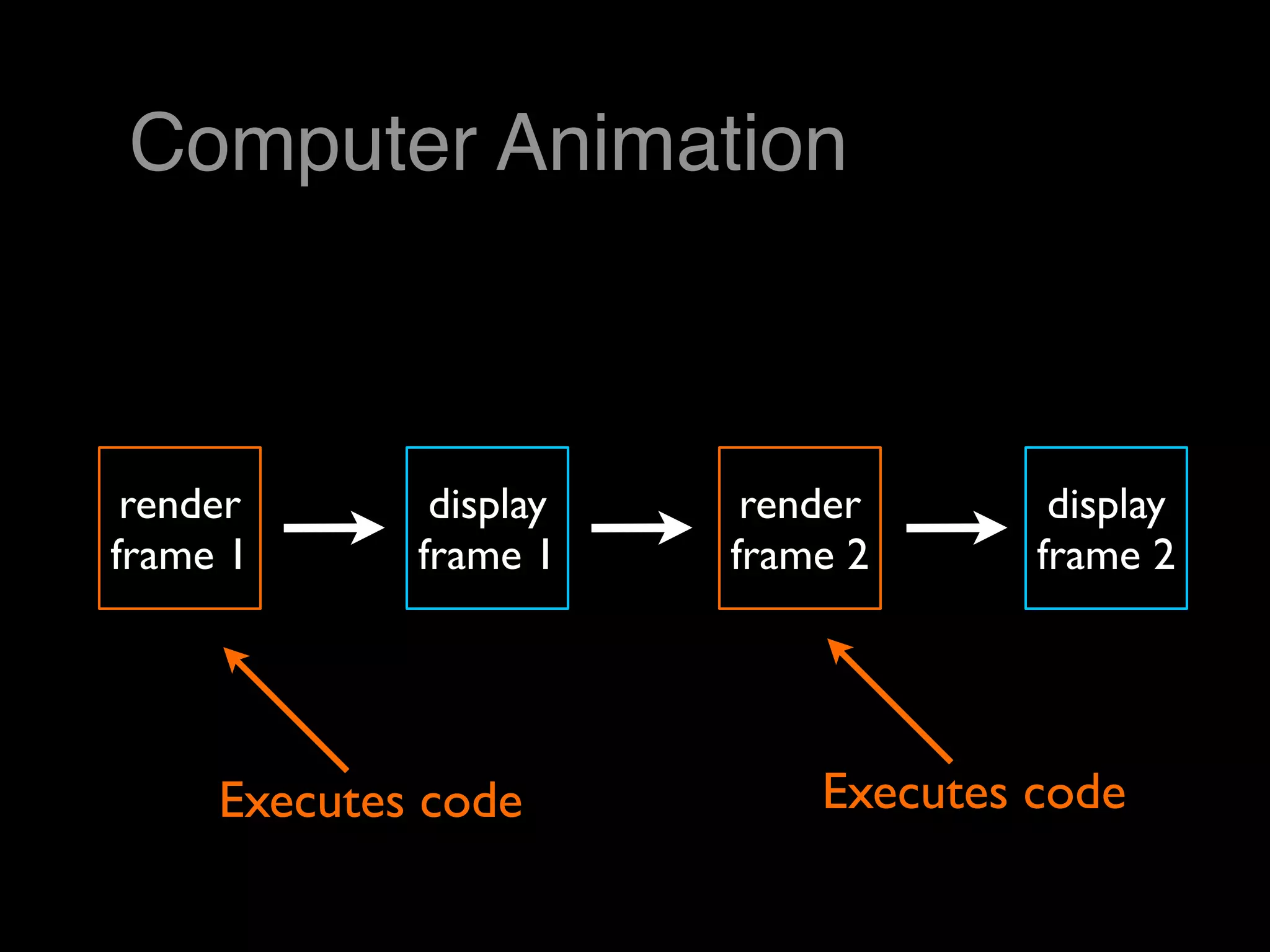
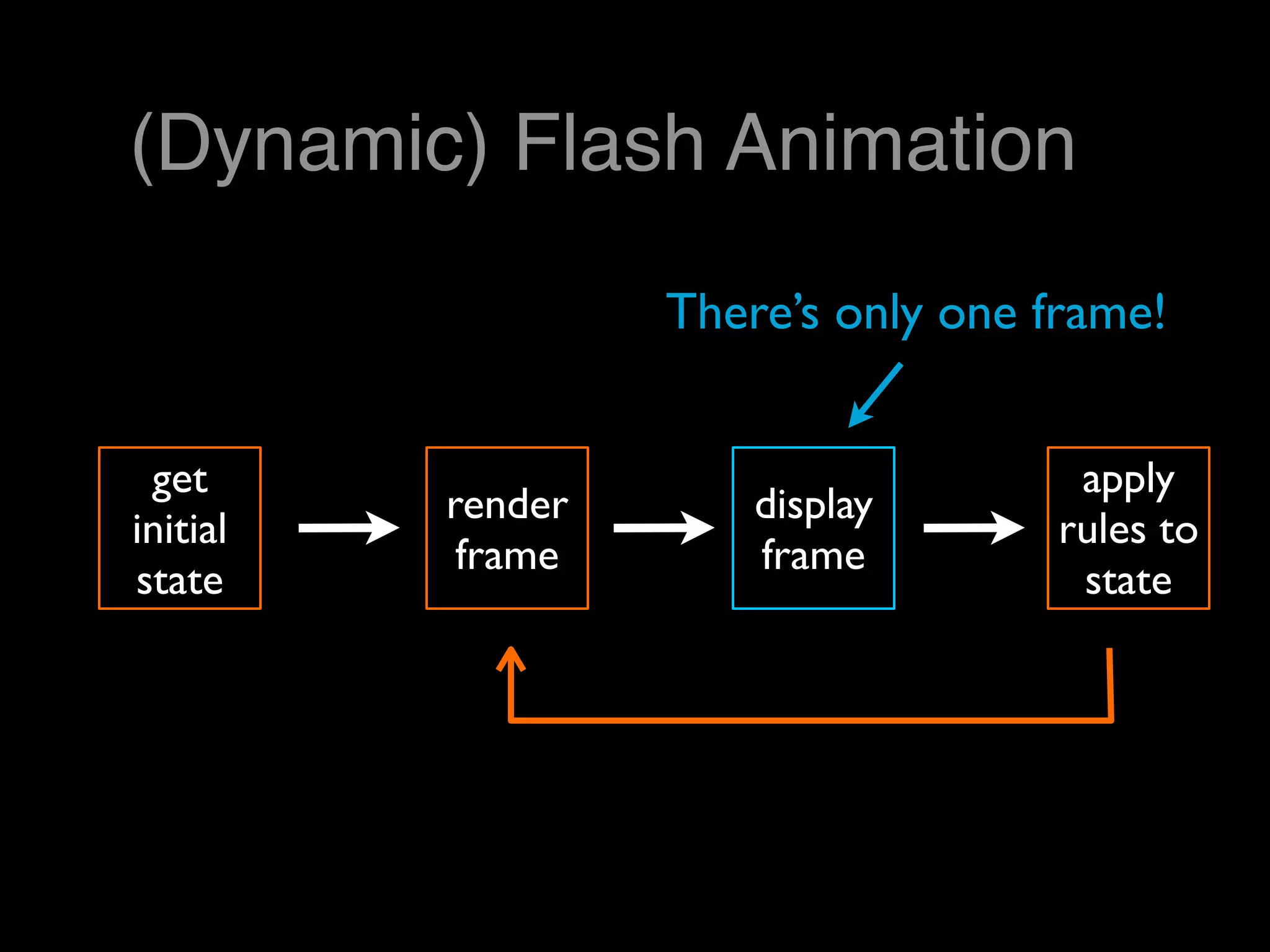
This document provides an overview of using objects and scripting motion in Adobe Flash. It discusses creating ActionScript classes, placing objects on the stage programmatically and from the library, and drawing objects like circles with code. It then covers moving objects by updating x and y coordinates, using event listeners like ENTER_FRAME to trigger movement, bouncing objects off edges by changing movement direction, and detecting edge collisions more precisely using an object's width and height. The homework assignment is to read a chapter on game elements and create a Flash file with an object moving across the stage via ActionScript.