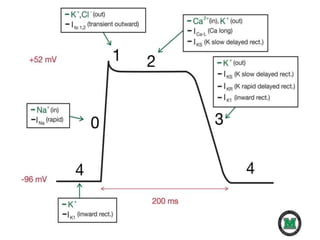
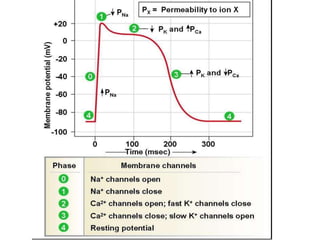
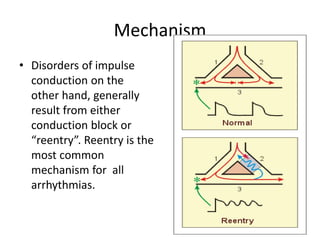
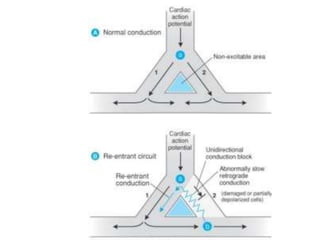
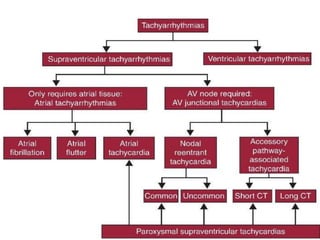
This document provides an overview of antiarrhythmic medications, including their mechanisms of action, classification, clinical uses, and potential risks. It discusses how antiarrhythmics work by decreasing or increasing conduction velocity or altering cardiac cell excitability. Drugs are classified into Classes I-IV based on their mechanisms and effects. Class I drugs are sodium channel blockers, while Class II are beta blockers, Class III are potassium channel blockers, and Class IV are calcium channel blockers. Specific drugs from each class are outlined along with their indications, dosing, and adverse effects.