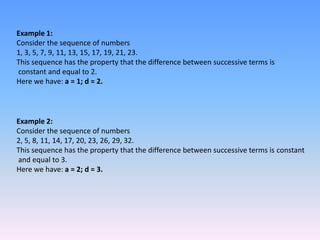
The document discusses arithmetic progressions (AP), which are sequences where the difference between consecutive terms is constant. It provides examples of AP sequences and formulas to find the nth term, the sum of terms, and other properties. Some key points:
- The nth term of an AP is given by an = a + (n-1)d, where a is the first term and d is the common difference.
- The sum of the first n terms is given by Sn = n/2 * [2a + (n-1)d].
- Examples show how to use the formulas to find individual terms, sums, number of terms, etc. given information about an AP sequence.
- Questions at







![1. Find the 10th term of -5,-8,-11,...... 5.Find the 100th term. if the first term is 4 and
[A] -28 the common difference is 7?
[C] -32 [A] 150
[B] -18 [C] 800
[D] -20 [B] 120
2. Find the 32nd term in the following series [D] 697
3,7,11,....... 6.Find the number of terms in the series
[A] 120 8,11,14,....95
[C] 220 [A] 25
[B] 230 [C] 27
[D] 127 [B] 26
[D] 30
3.Find the position of 98 in the following
7.Find the number of terms in the series
series 3,8,13 ....?
11,6,1,...-54?
[A] 20th term
[A] 12
[C] 12th term
[C] 14
[B] 36th term
[B] 13
[D] 34th term
[D] 15
4. Find the 35th term if the first term is 8 and 8.Find the number of terms in the series
common difference is 1.5 2,3.5,5,...62 ?
[A] 35 [A] 50
[C] 18 [C] 41
[B] 59 [B] 62
[D] 24 [D] 42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/starrpvt-ltd-rachitsgroupppt1-130331035642-phpapp01/85/Starr-pvt-ltd-rachit-s-group-ppt-1-9-320.jpg)
![9.Find the values of x in the Arithmetic series 10. In an A.P the 12th term is 61 and common
3x+1,5x-1,5x+1,...... difference is 5 then find the series
[A] 2 [A] 6,11,16
[C] 8 [C] 5,8,11
[B] 3 [B] 4,7,11
[D] 7 [D] 3,9,12
1. : [C] 6. : [D]
2 : [D] 7. : [C]
3. : [A] 8. : [C]
4. : [B] 9. : [A]
5. : [D] 10. : [A]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/starrpvt-ltd-rachitsgroupppt1-130331035642-phpapp01/85/Starr-pvt-ltd-rachit-s-group-ppt-1-10-320.jpg)
![Calculate the sum of a given A.P
FORMULA
Sn=n/2x[2a+(n-1)d]
Where Sn=Sum of the given A.P
Where a=first term of the A.P
Where n=number of terms in the given A.P
Where d=common difference of the A.P](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/starrpvt-ltd-rachitsgroupppt1-130331035642-phpapp01/85/Starr-pvt-ltd-rachit-s-group-ppt-1-11-320.jpg)

![EXAMPLES
Example 1: Find the sum of first 28 terms of the A.P:8,3,-2……..
Solution- No. of terms=28
calculate d =
3-8=-5
a=8
put these values in the Sn formula=n/2x[2a+(n-1)d] and
calculate the sum
Sn(S28)= 28/2x[2x8+(28-1)x-5]
14x{16+(27x-5)}
14x(16-135)
14x(-119)
=-1666
So S28=-1666 for the given A.P](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/starrpvt-ltd-rachitsgroupppt1-130331035642-phpapp01/85/Starr-pvt-ltd-rachit-s-group-ppt-1-13-320.jpg)
![Example 2: If the sum of the first 14 terms of an AP is 1050 and its first term is
10,find the 20th term.
Solution- n=14
Sn(S14)=1050
a=10
From the Sn formula=n/2x[2a+(n-1)d] calculate d by equating the Sn value
to the formula.
1050=14/2x[2x10+(14-1)d]
1050=7x[20+13d]
1050=140=91d
1050-140=91d
d=910/91=10
So d=10
From the An formula=a+(n-1)d calculate the value of a20
A20=10+(20-1)x10
=10+190
=200
So a20=200](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/starrpvt-ltd-rachitsgroupppt1-130331035642-phpapp01/85/Starr-pvt-ltd-rachit-s-group-ppt-1-14-320.jpg)

![Example 5: Find the sum of the series 5+7+9+11+13……to 40 terms.
Solution- a=5
d=7-5=2
9-7=2
n=40
Put these values in the formula=n/2x[2a+(n-1)d]
Sn=40/2x[2x5+(40-1)x2]
=20x[10+39x2]
=20x(10+78)
=20x88
=1760
So the sum of 40 terms of the A.P=1760](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/starrpvt-ltd-rachitsgroupppt1-130331035642-phpapp01/85/Starr-pvt-ltd-rachit-s-group-ppt-1-16-320.jpg)

![QUESTIONS-
(Q1)Find the sum of first 21 terms of the A.P whose 2nd term is 8 and 4th term is 14
(Ans-1) a2=8
a4=14
a2=8 can be written as a+d=8 and a4=14 can be written as a+3d=14.
Solve a+d=8,a+3d=14 by elimination method and find the common
difference d.
a+d=8
a+3d=14
d=3
a=a2-3
8-3
=5
A.P:5,8,11,14…….
We now put the values of a,d and n in the formula n/2[2a+(n-1)D] to find S21
S21=21/2x[2x5+(21-1)x3]
21/2x(10+20x3)
21/2(70)
21x35=735
So the sum of 21 terms of the A.P=735](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/starrpvt-ltd-rachitsgroupppt1-130331035642-phpapp01/85/Starr-pvt-ltd-rachit-s-group-ppt-1-18-320.jpg)

![(Q3) Find the sum of the first 40 positive integers divisible by 6.
(Ans-3) Smallest positive integer divisible by 6=6
A.P=6,12,18,24……….
d=6
a=6
We fin the sum of 40 terms in this series by using the Sn formula=n/2x[2a+(n-1)xd]
S40=40/2x[2x6+(40-1)x6]
=20x[12+39x6]
=20[12+234]
=20x[246]
=4920
So the sum of 40 integers divisible by 6=4920](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/starrpvt-ltd-rachitsgroupppt1-130331035642-phpapp01/85/Starr-pvt-ltd-rachit-s-group-ppt-1-20-320.jpg)
![(Q4) Find the sum of first 80 negative terms divisible by 10.
(Ans-4) Smallest negative number divisible by 10=-10
A.P:-10,-20,-30…………
d=-10
a=-10
We now calculate the sum of 80 terms of this series by using the
formula=n/2x[2a+(n-1)xd]
S80=80/2x[2x-10+(80-1)x-10]
=40x[-20+79x-10]
=40x[-20-790]
=40x[-810]
=-32,400](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/starrpvt-ltd-rachitsgroupppt1-130331035642-phpapp01/85/Starr-pvt-ltd-rachit-s-group-ppt-1-21-320.jpg)
![(Q5) How many terms of the A.P, 9,17,25... Must be taken to give a sum of 636?
(Ans-5) A.P: 9,17,25…
d=17-9=8
=25-17=8
a= 9
Sn=636
We calculate the number of terms by the formula=n/2x[2a+(n-1)xd]. In place of Sn
we put 636.
636=n/2x[2x9+(n-1)x8]
636=n/2[18+8n-8]
636=n/2x(10+8n)
636x2=10n+8n sq.
1272=10n+8n sq.
8n sq.+10n-1272=0
Solve this by quadratic formula and calculate n.
By solving the equation,2 values of n are calculated. N=12, n=-12
N=-12 has to be rejected because the no. of terms cannot be in negative.
So the no. of terms in this series=12.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/starrpvt-ltd-rachitsgroupppt1-130331035642-phpapp01/85/Starr-pvt-ltd-rachit-s-group-ppt-1-22-320.jpg)
![(Q6) In an A.P, the sum of its first ten terms is -150 and the sum of its next ten terms is -
550. Find the A.P
(Ans-6) S10=-150
S11 to 20=-550
S10 can be written as= 10/2x[2a+(10-1)xd]
S11 to 20 can be written as= S20-S10
= 20/2x[2a+(20-1)xd]-10/2x[2a+(10-1)xd]
S10= 10/2x[2a+(10-1)xd]
-150=5x(2a+9d)
150=10a+45d →1
S20-S10= 20/2x[2a+(20-1)xd]-10/2x[2a+(10-1)xd]
-550= 10x(2a+19d)-5x(2a+9d)
-550=20a+190d-10a-45d
-550=10a+145d→2
Solve equation 1 and 2 to get a and d by elimination method.
10a+45d=-150
10a+145d=-550
By solving the equations d=-4 and a=3.
A.P:3,-1,-5,-9………](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/starrpvt-ltd-rachitsgroupppt1-130331035642-phpapp01/85/Starr-pvt-ltd-rachit-s-group-ppt-1-23-320.jpg)
![(Q7) Find the sum of first 22 terms of the A.P in which d=7 and 22nd term is 149.
(Ans-7) d=7
a22=149
A22 can be written as=a+21d
149=a+21d
149=a+21x7
149=a+147
a=149-147
a=2
A.P:2,9,16…………….
Calculate the sum of 22 terms of this A.P by the formula=n/2x[2a+(n-1)xd]
S22=22/2x[2x2+(22-1)x7]
=11x(4+21x7)
=11x(4+147)
=11x(151)
=1661
So the sum of 22 terms of the A.P=1661](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/starrpvt-ltd-rachitsgroupppt1-130331035642-phpapp01/85/Starr-pvt-ltd-rachit-s-group-ppt-1-24-320.jpg)
![(Q8) A contract on construction job specifies a penalty for delay of completion
beyond a certain date as follows: Rs 200 for the first day, Rs 250 for the second
day, Rs 300 for the third day, etc. , the penalty for each succeeding day being Rs
50 more than for the preceding day. How much money the contractor has to
pay as penalty, if he has delayed the work by 30 days?
(Ans-8) A.P formed= 200,250,300……
d=50 , a=200
Work delayed by=30 days
Work delayed=n
n=30
Amount to be paid in 30 days =S30
Calculate the total amount of money in 30 days by the formula=n/2x[2a+(n-1)xd]
S30=30/2x[2x200+(30-1)x50]
=15x[400+29x50]
=15x[400+1450]
=15x[1850]
=27750
So the amount to be paid in 30 days= Rs 27750](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/starrpvt-ltd-rachitsgroupppt1-130331035642-phpapp01/85/Starr-pvt-ltd-rachit-s-group-ppt-1-25-320.jpg)
