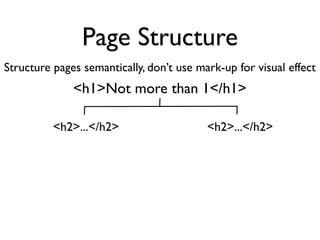
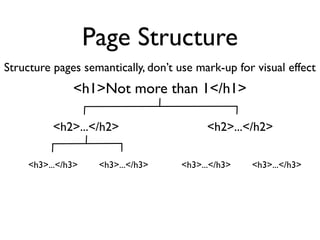
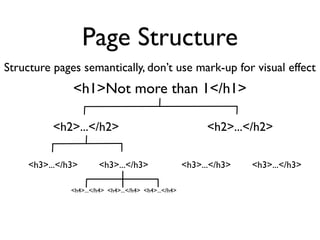
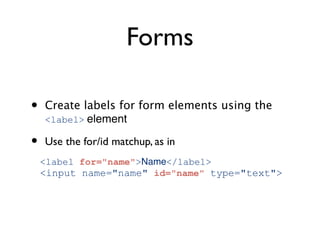
The document discusses why accessibility is important from humanitarian, legal, market, and technical perspectives. It provides examples of individuals with disabilities and how accessibility features would help them. It notes growing disability populations and legal requirements in various jurisdictions. Technical principles of perceivability, operability, understandability and robustness are introduced. Specific accessibility guidelines are then covered for page structure, images, keyboard, links, tables, forms, and testing.