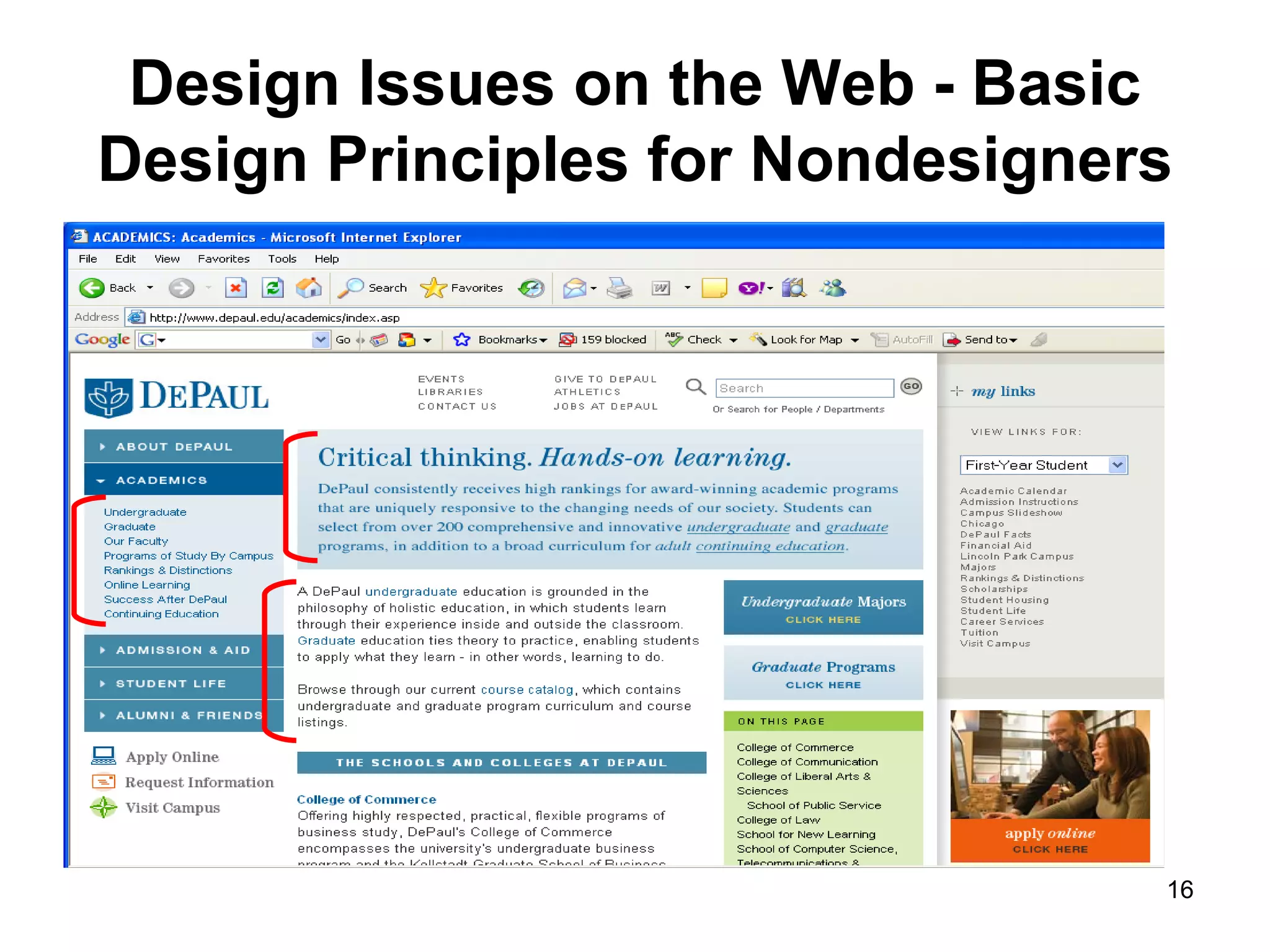
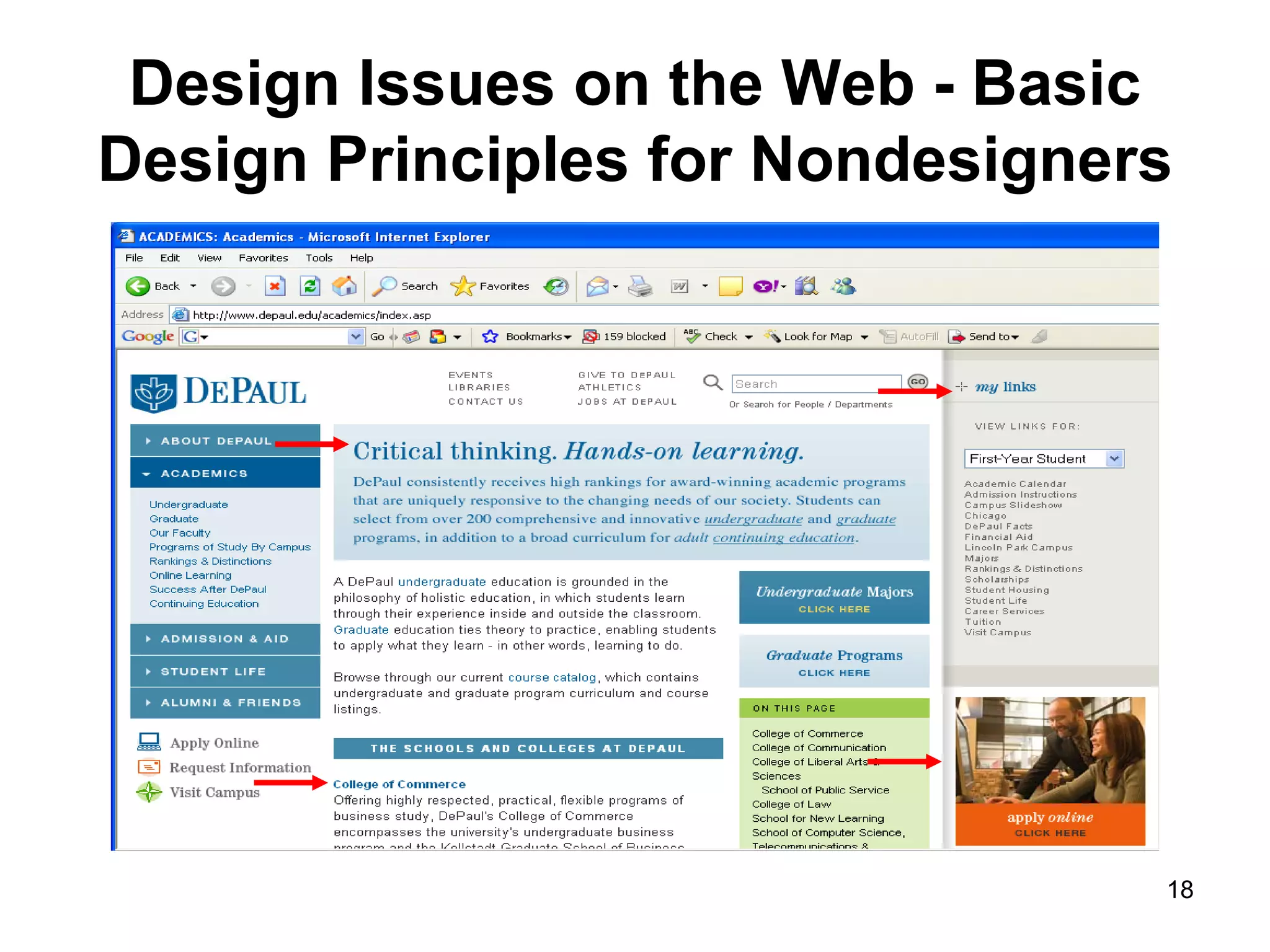
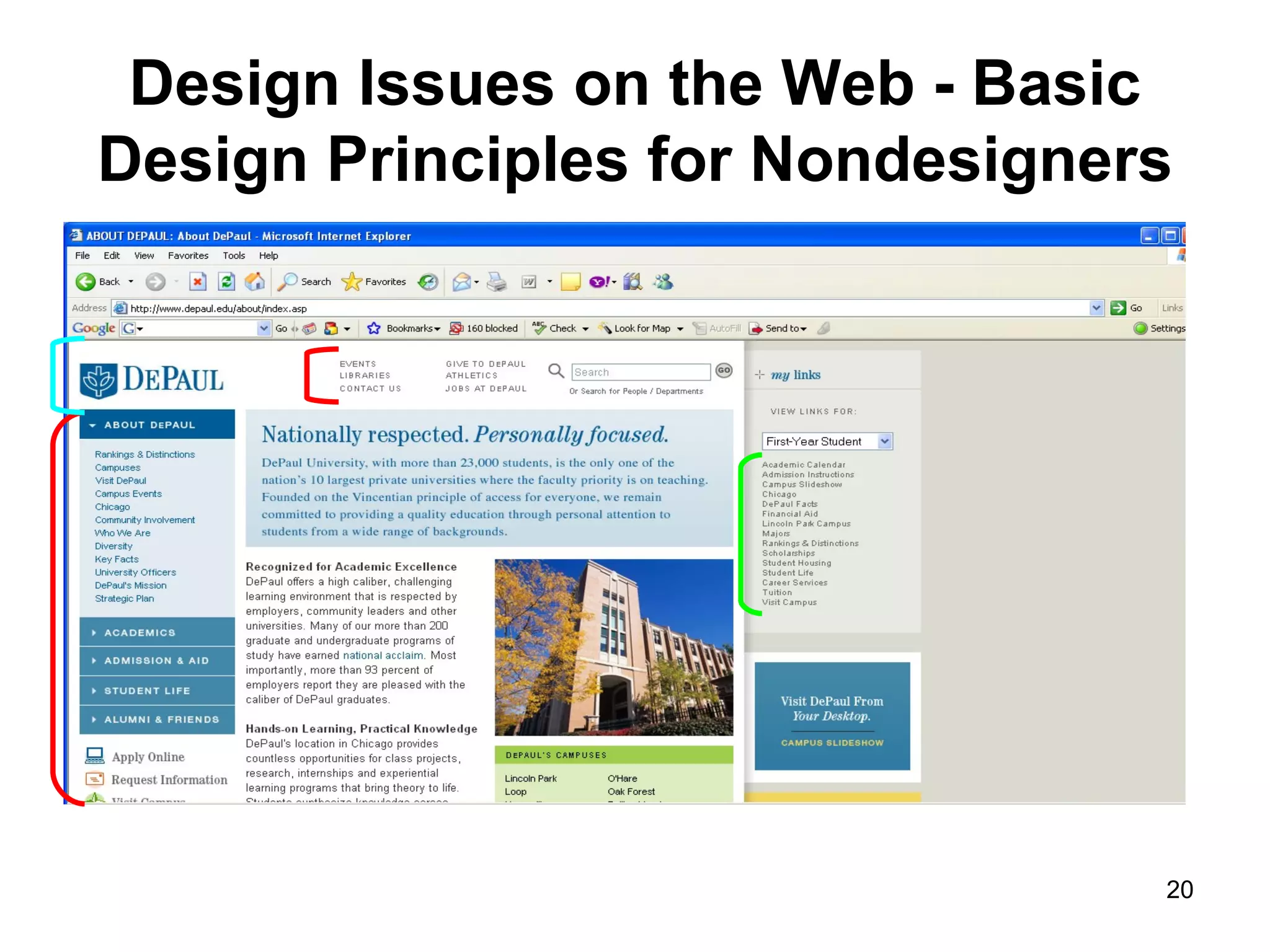
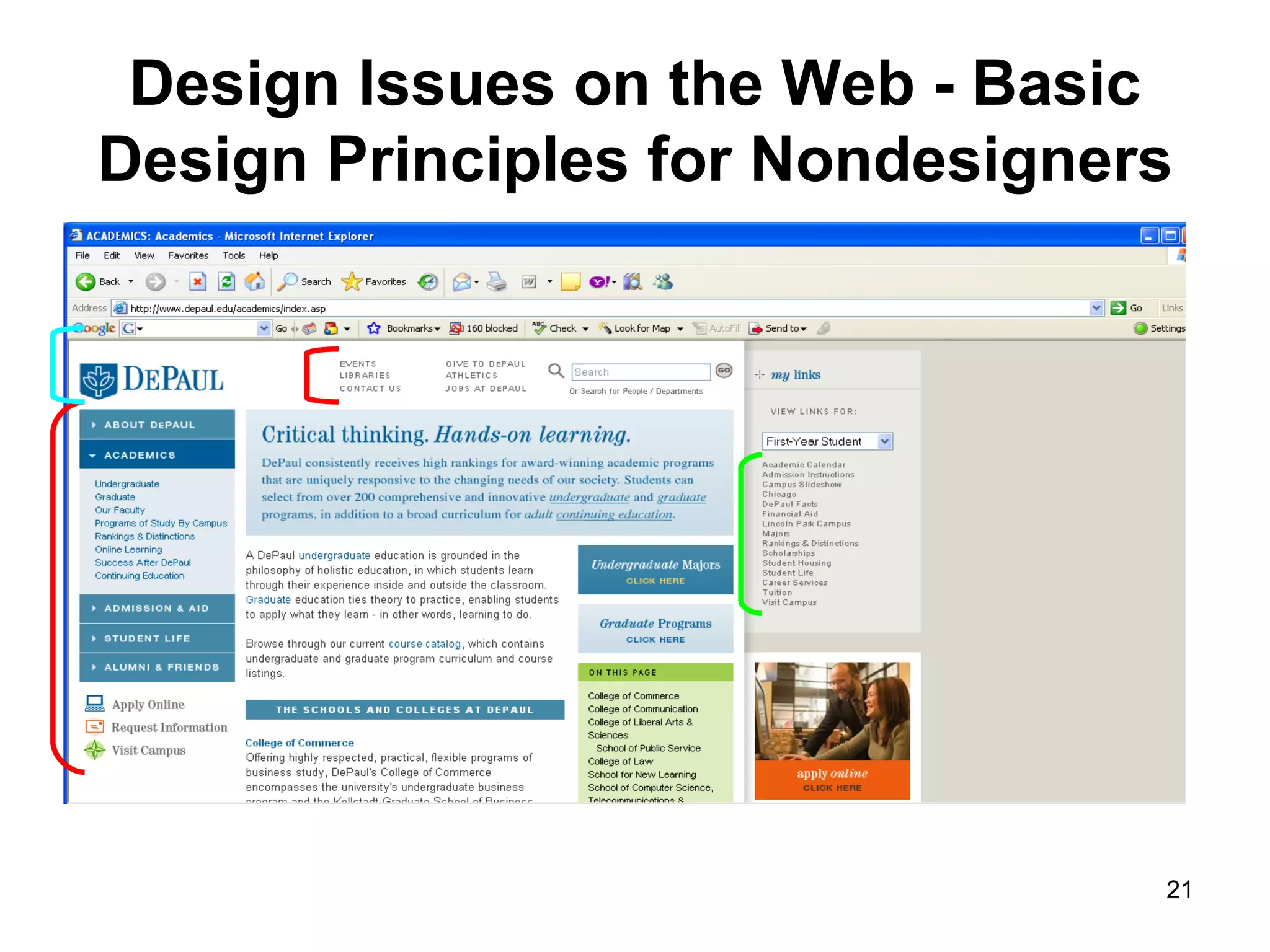
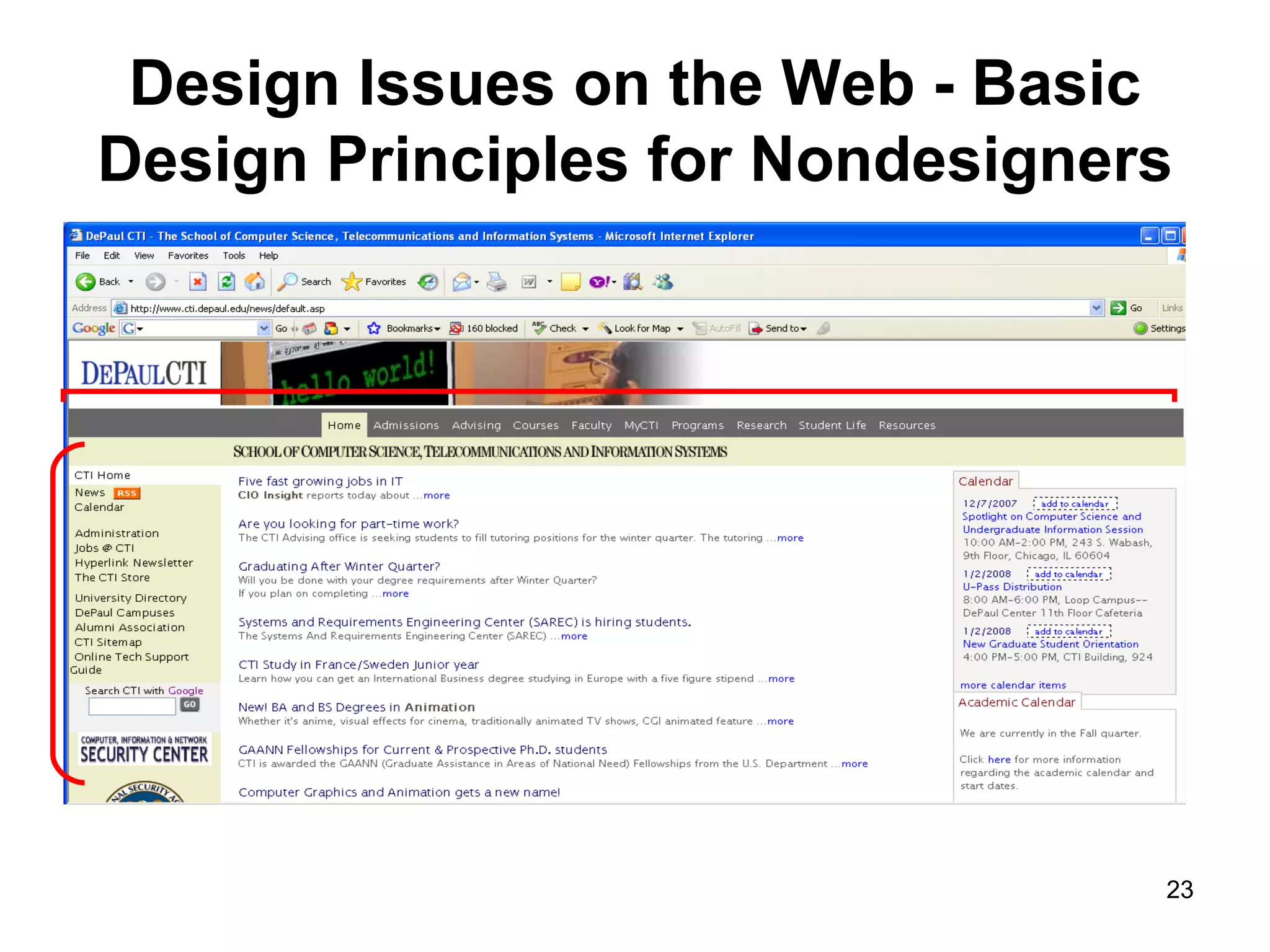
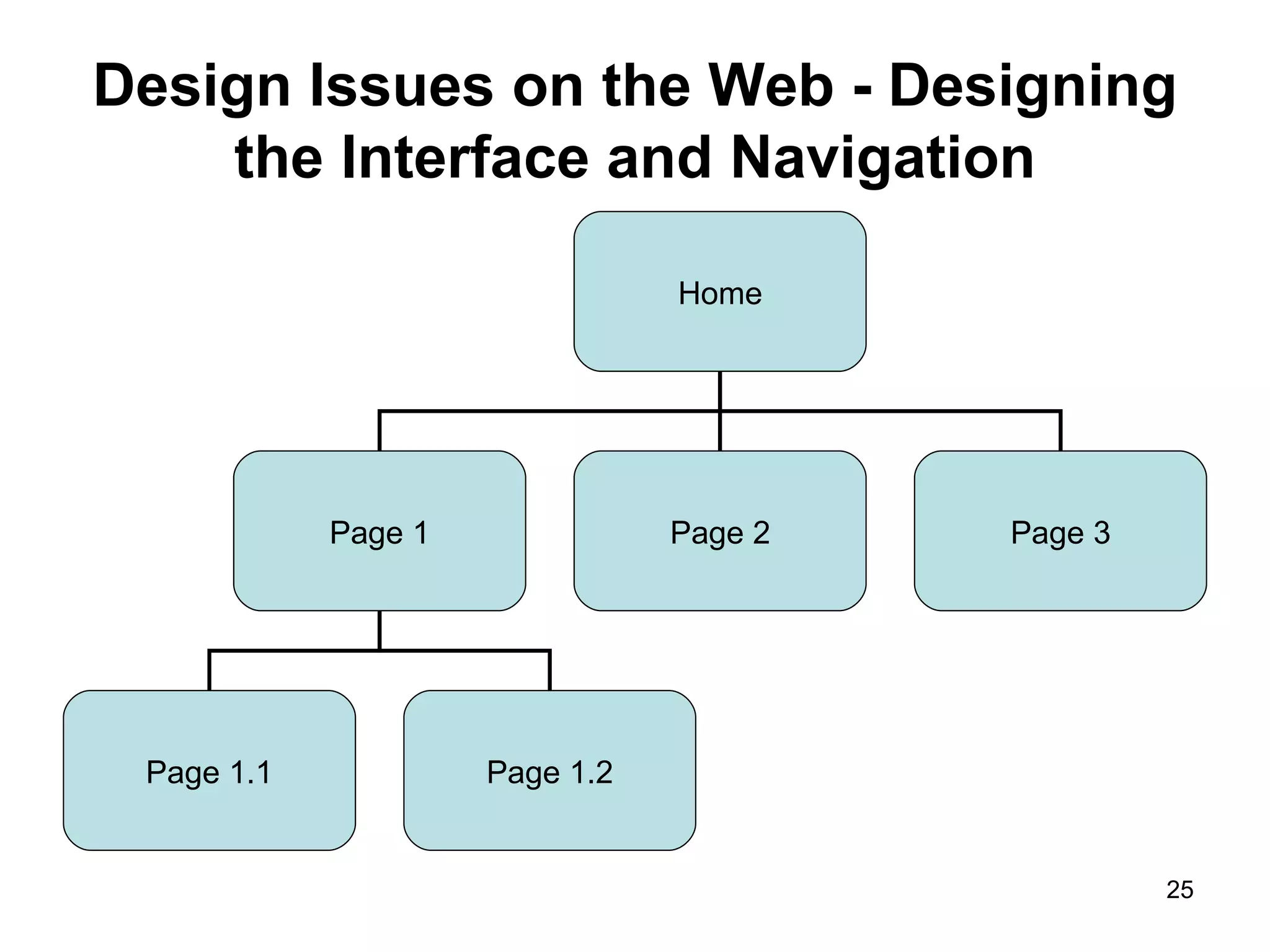
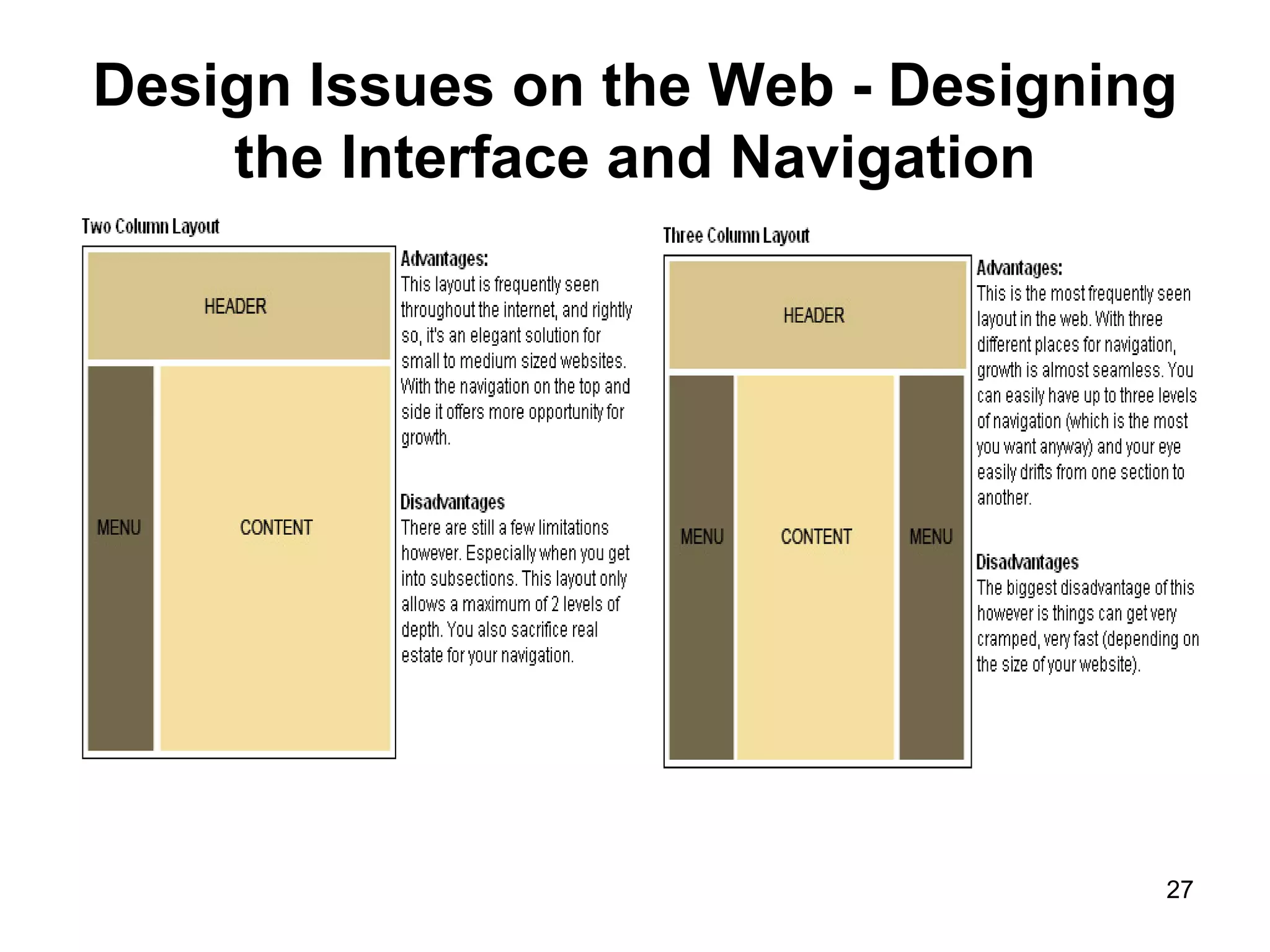
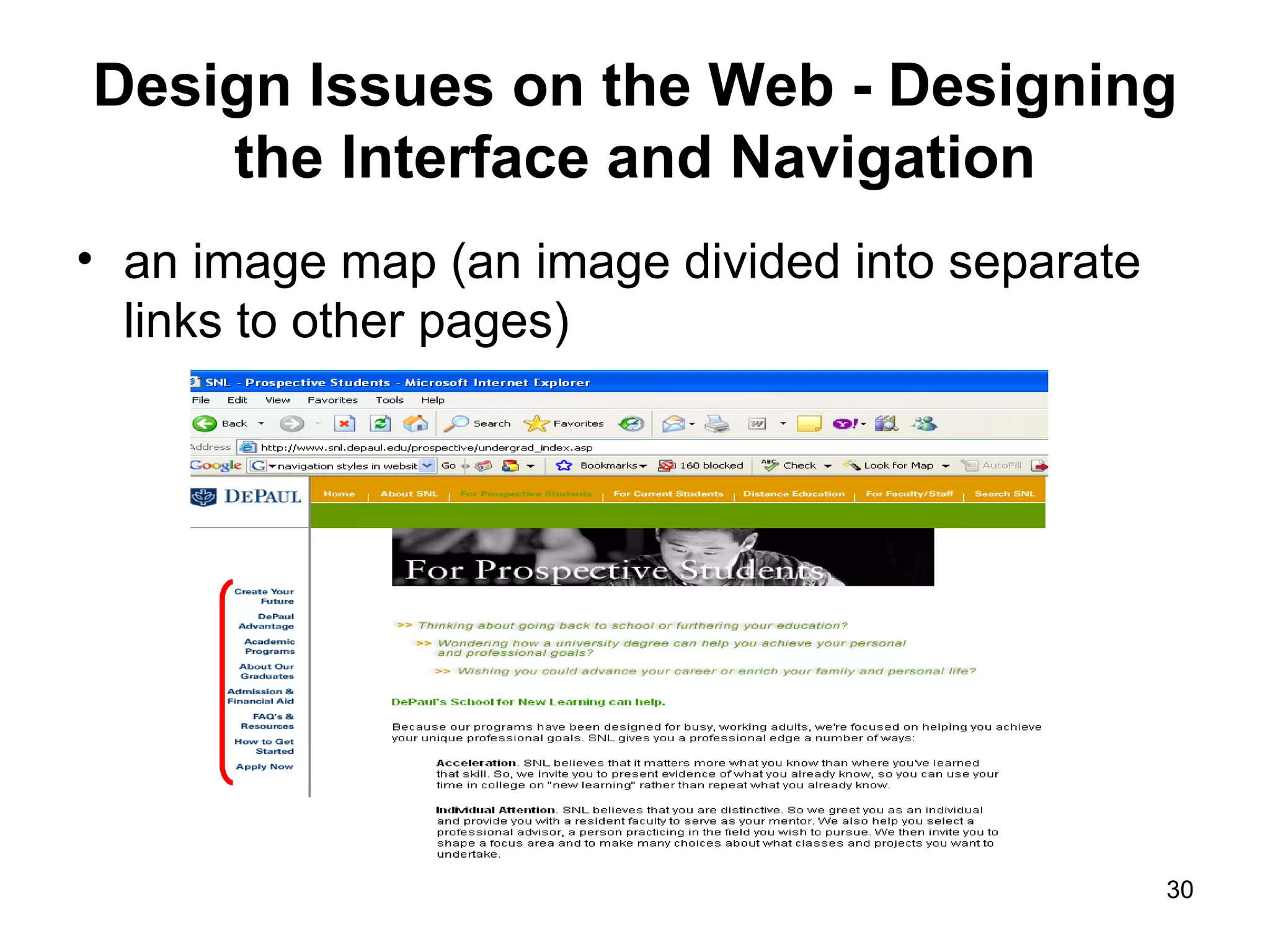
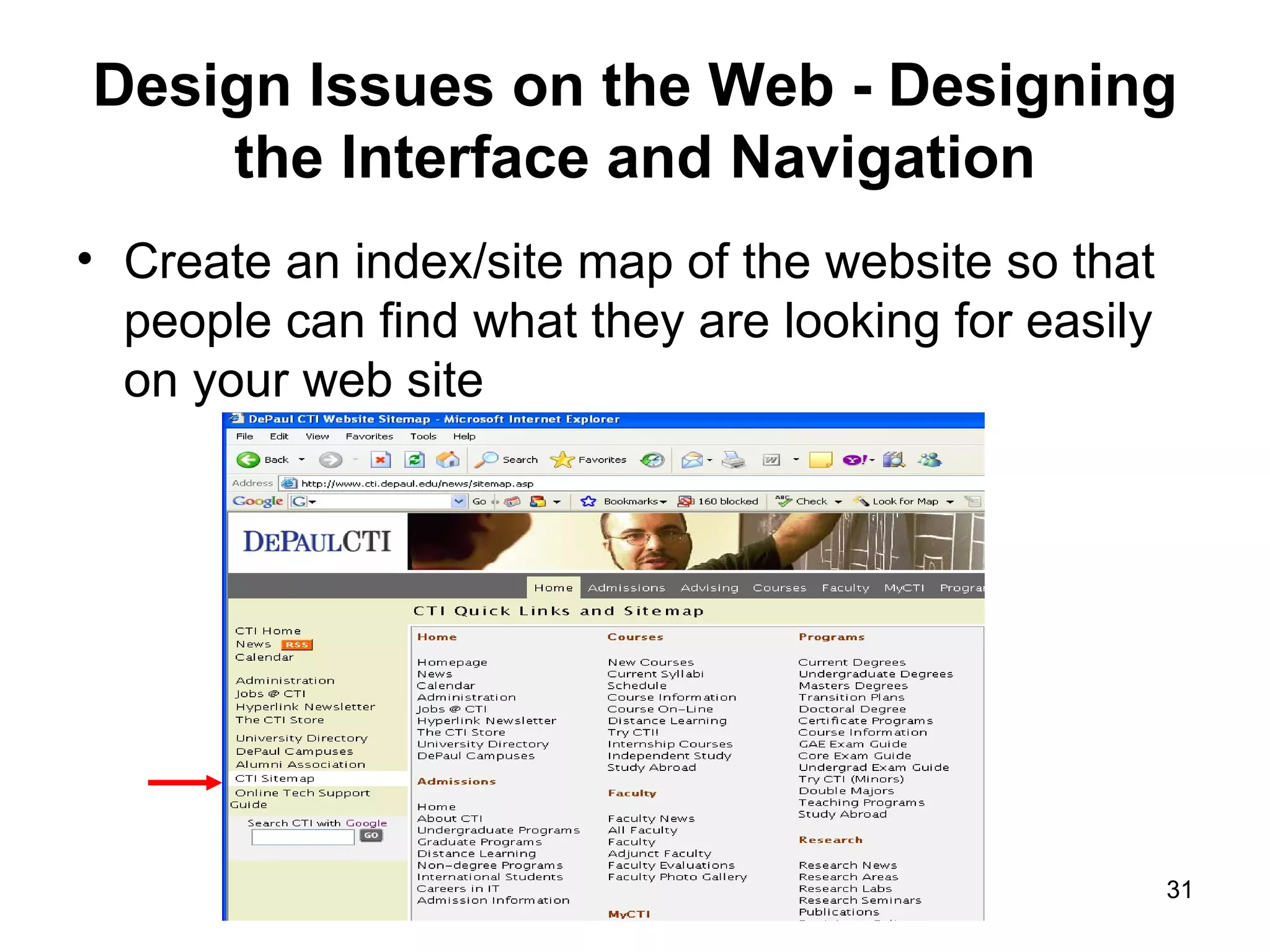
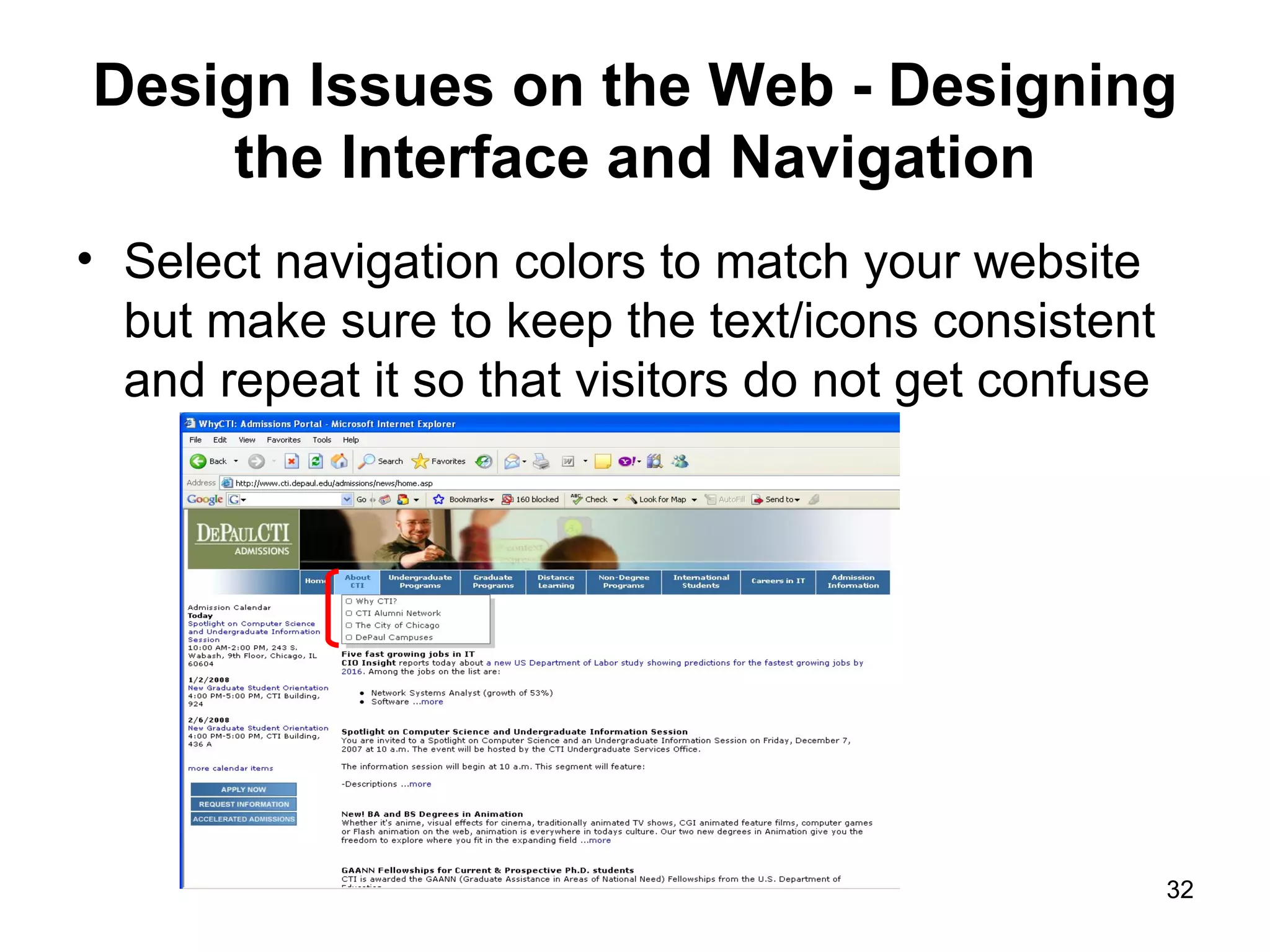
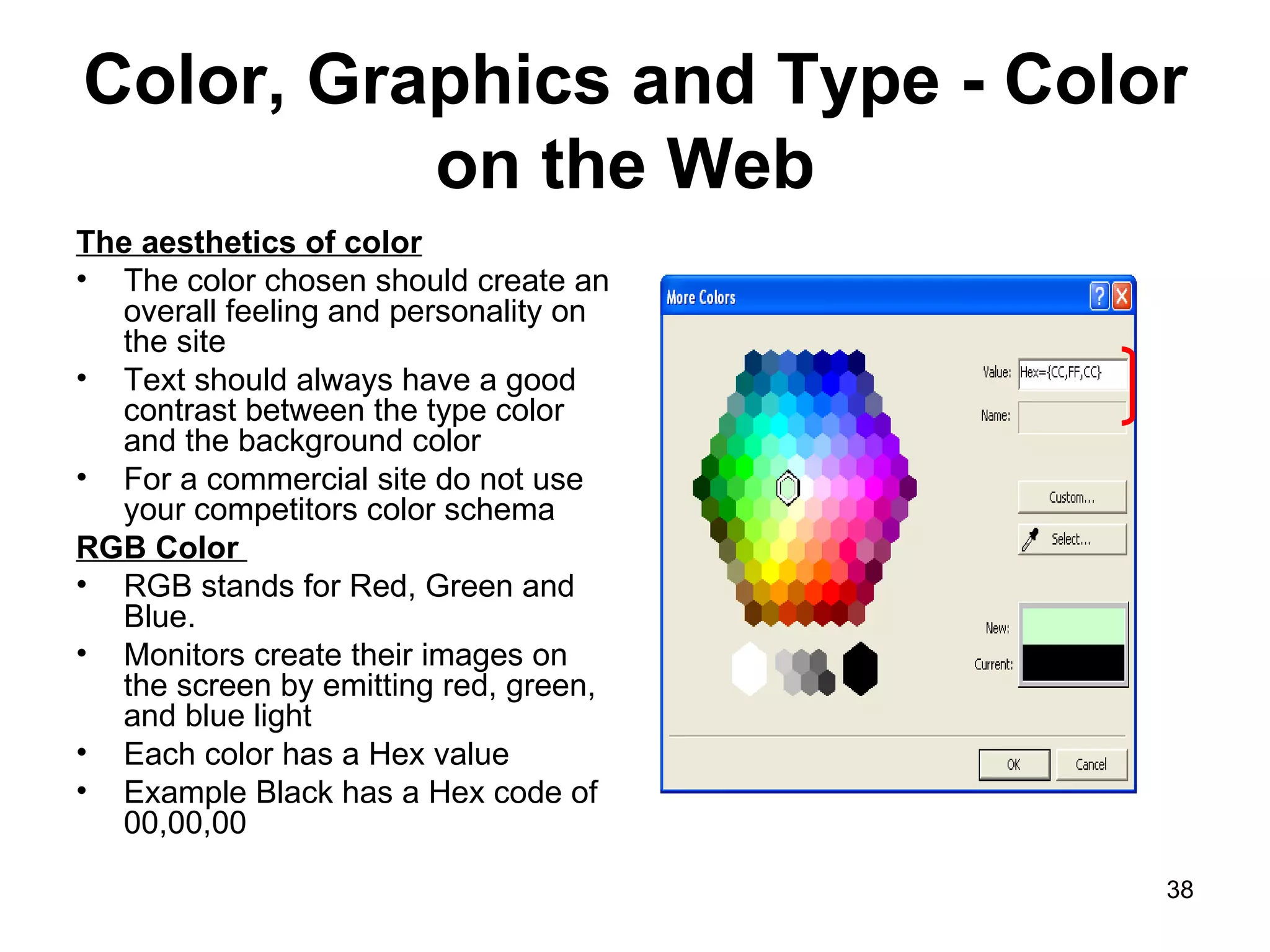
The document provides guidance on various aspects of web design, including things to consider when designing a website, making webpages, design issues, navigation, color, graphics and typography. It emphasizes key principles like alignment, proximity, repetition, contrast and legibility. It also covers testing a site, uploading files, registering the site with search tools and additional resources for web design basics.