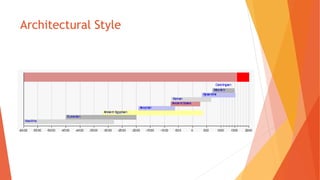
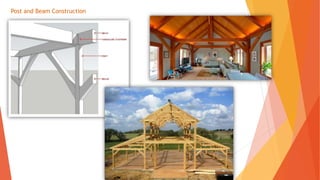
This document discusses the topic of architecture. It defines architecture as the art or science of designing and constructing buildings or structures with durable materials following certain standards. It then covers various architectural elements like lines, color, texture, form, space and styles. It discusses different materials used in architecture like stone, wood, cast iron, steel, reinforced concrete and steel cables. It also covers principles of architectural planning and building materials. Finally, it provides an overview of indigenous and Spanish colonial architecture in the Philippines as well as some examples of modern Philippine architecture.