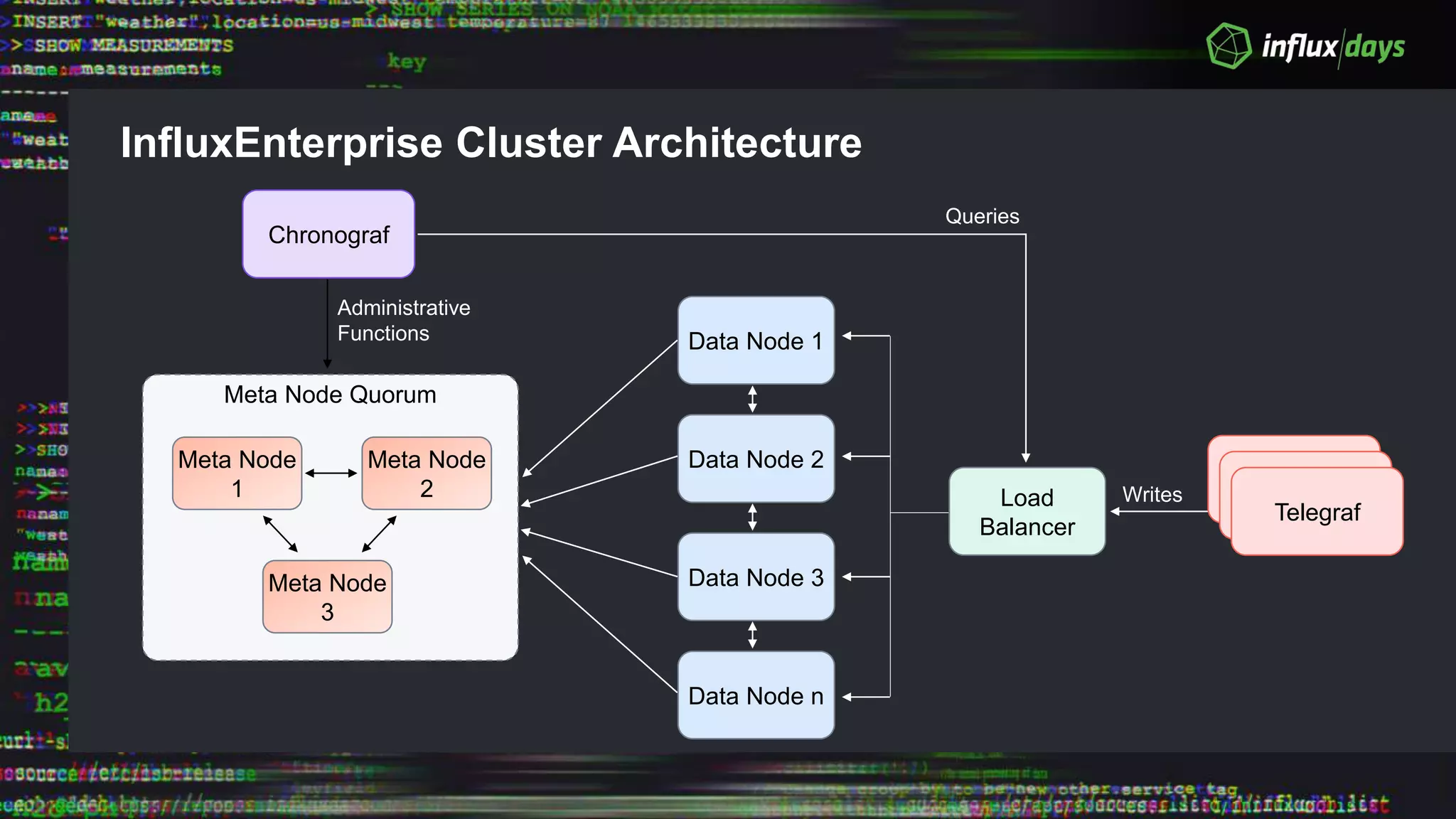
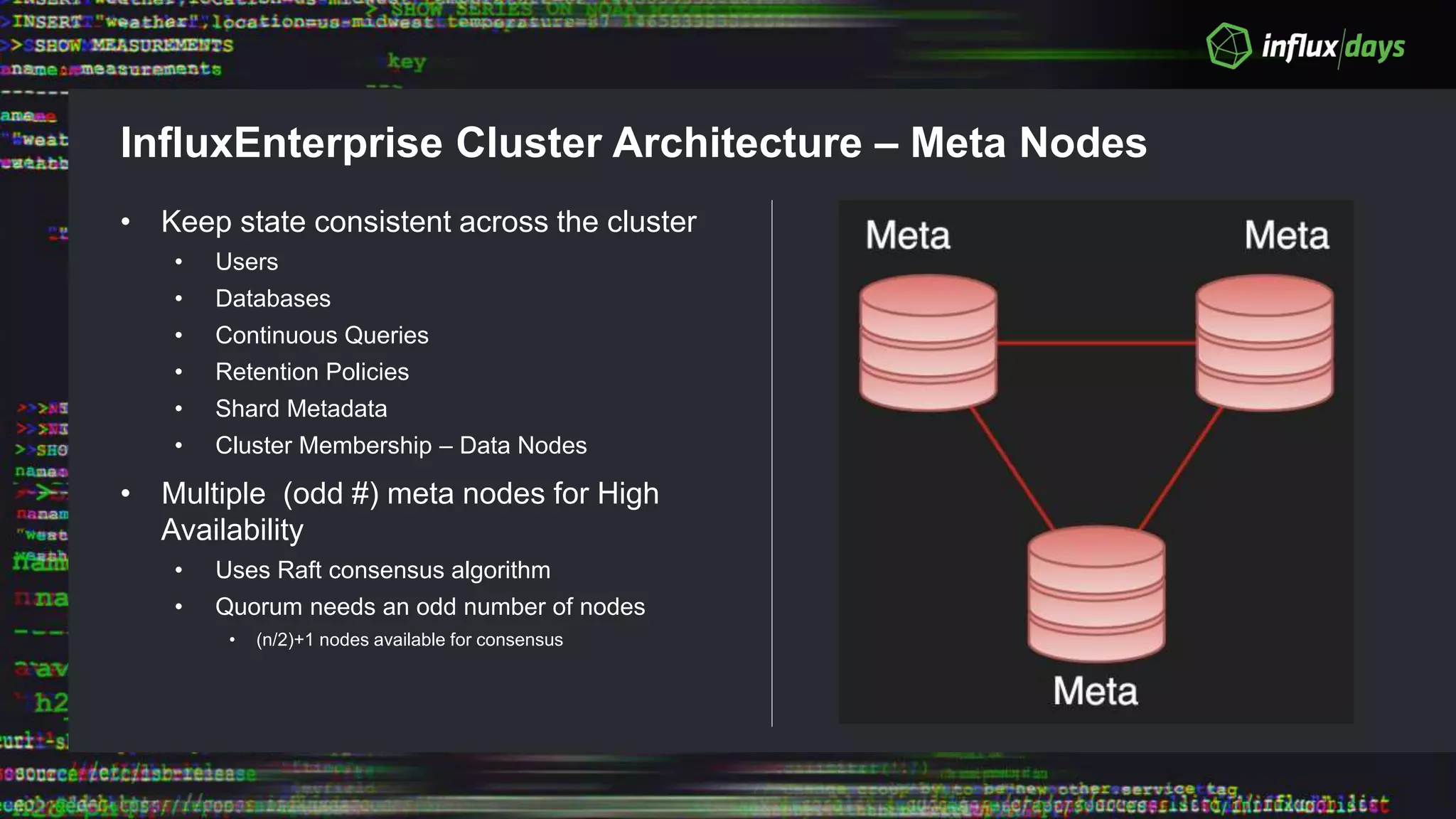
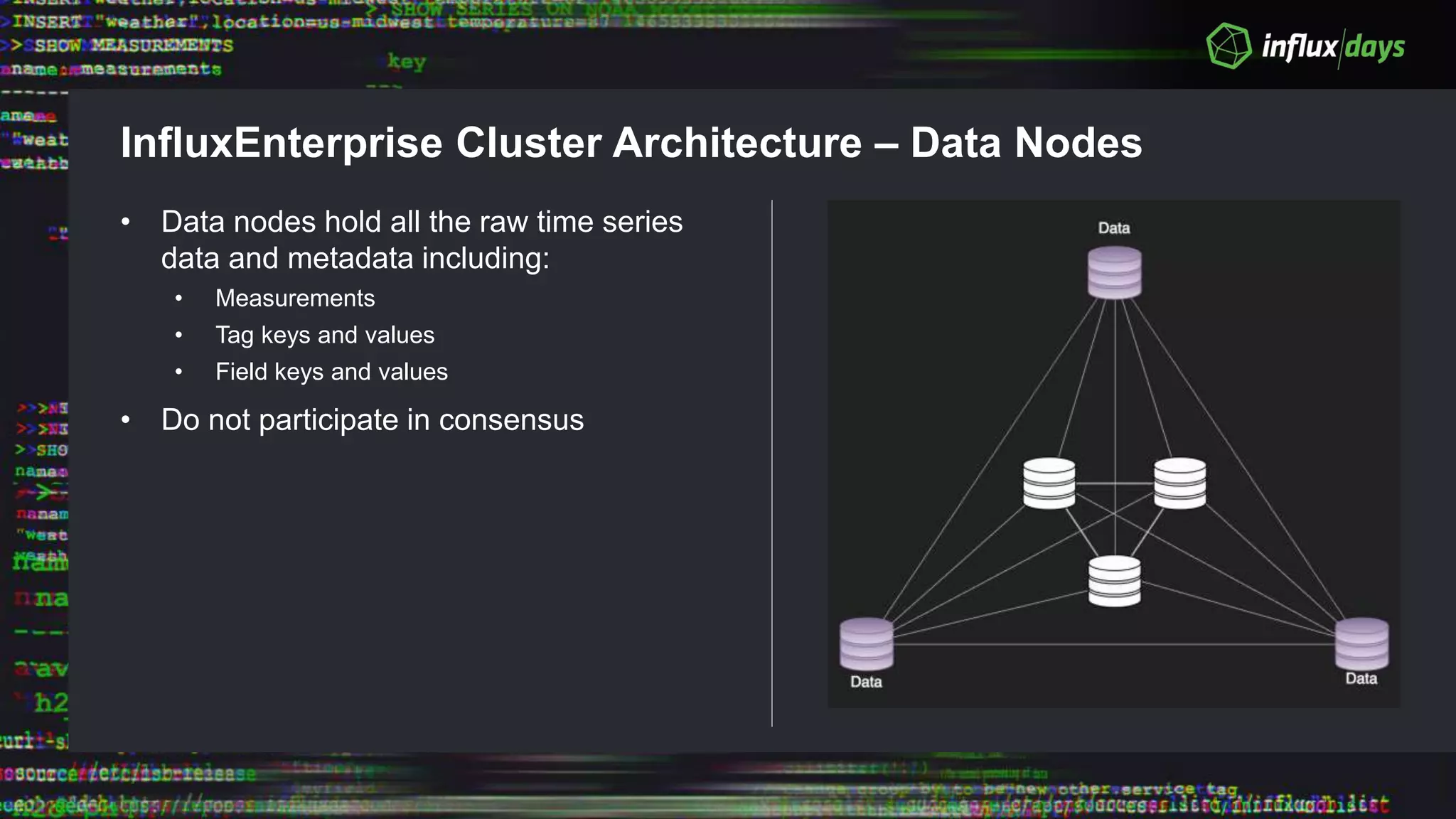
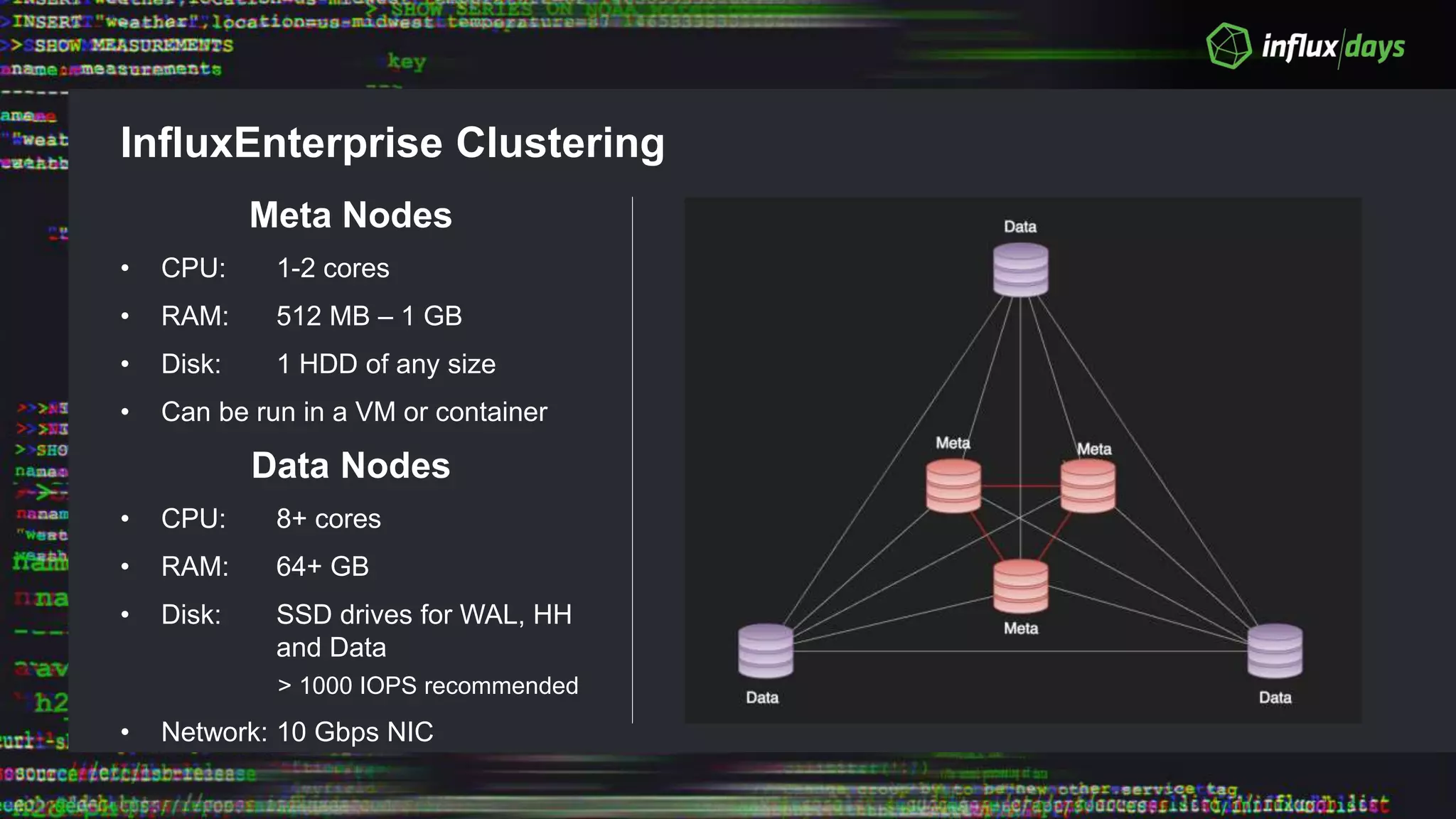
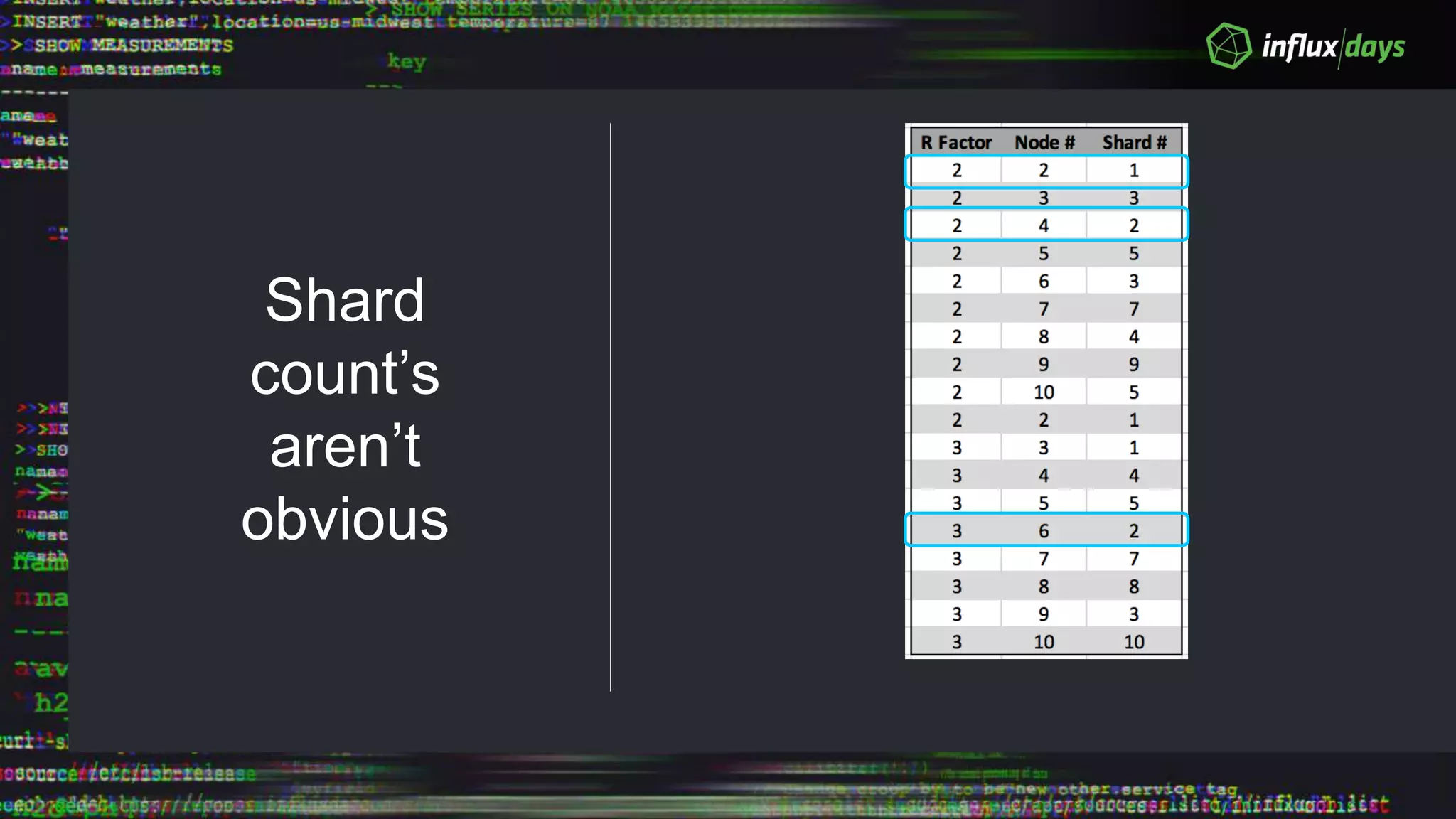
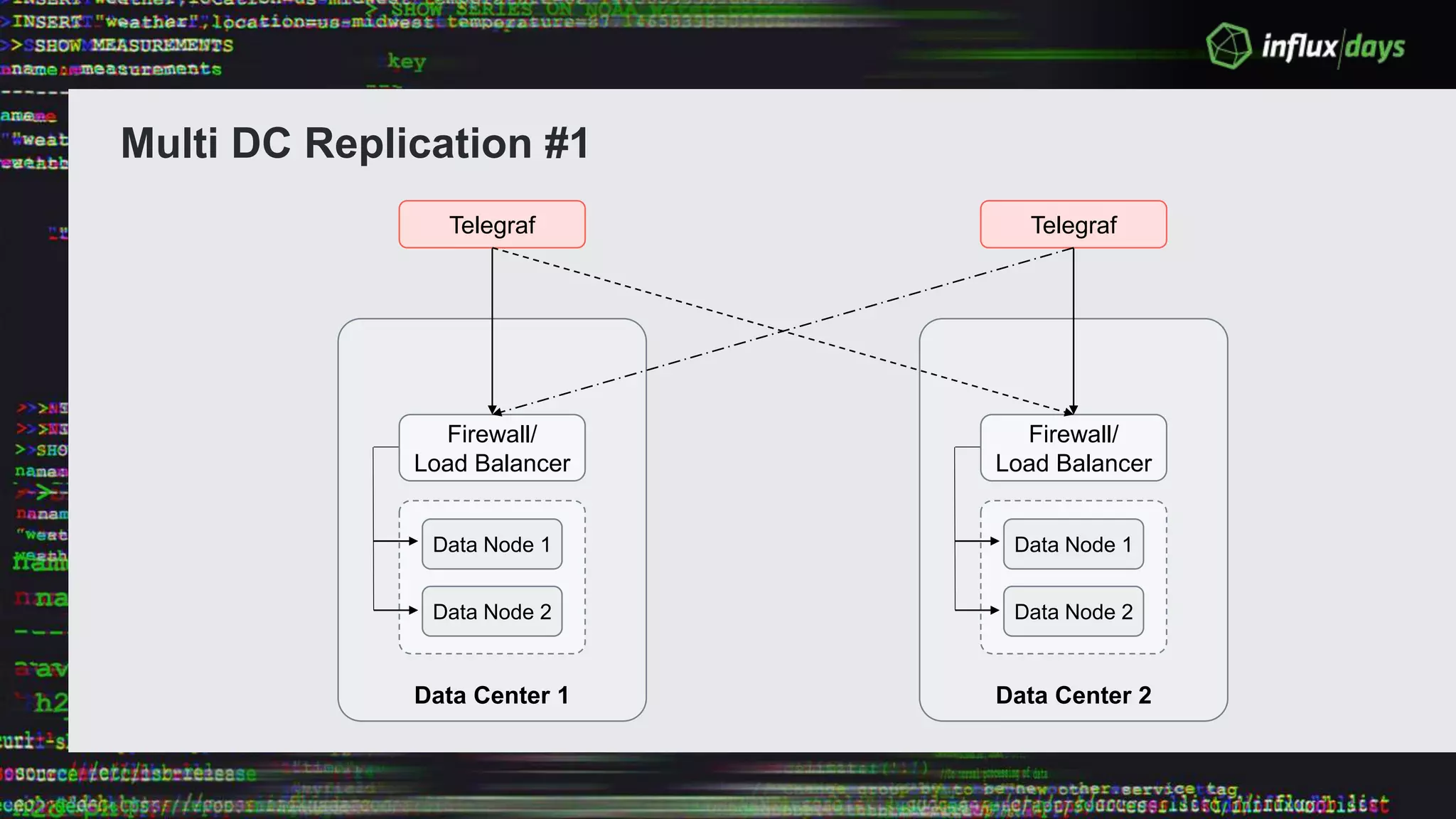
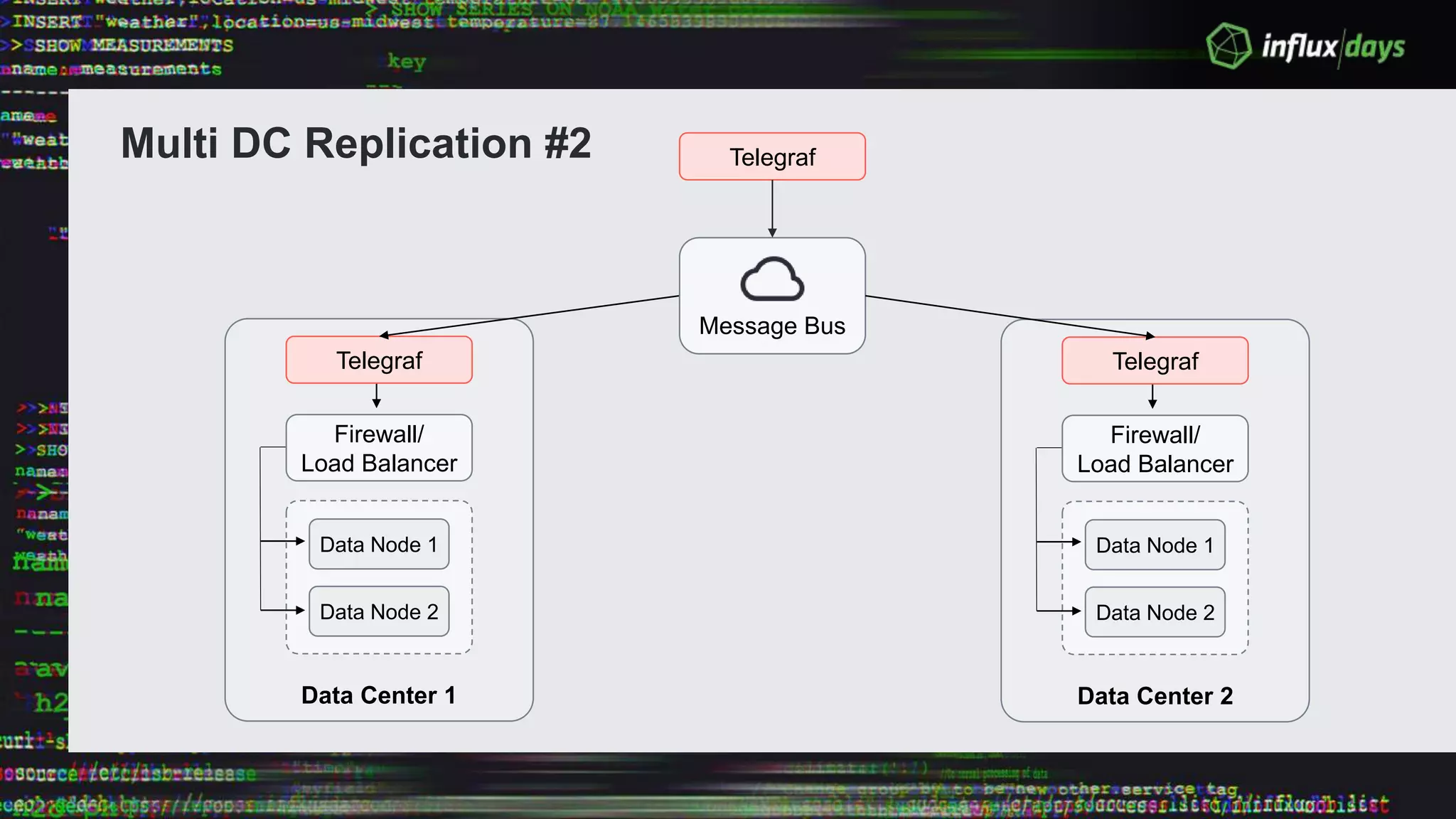
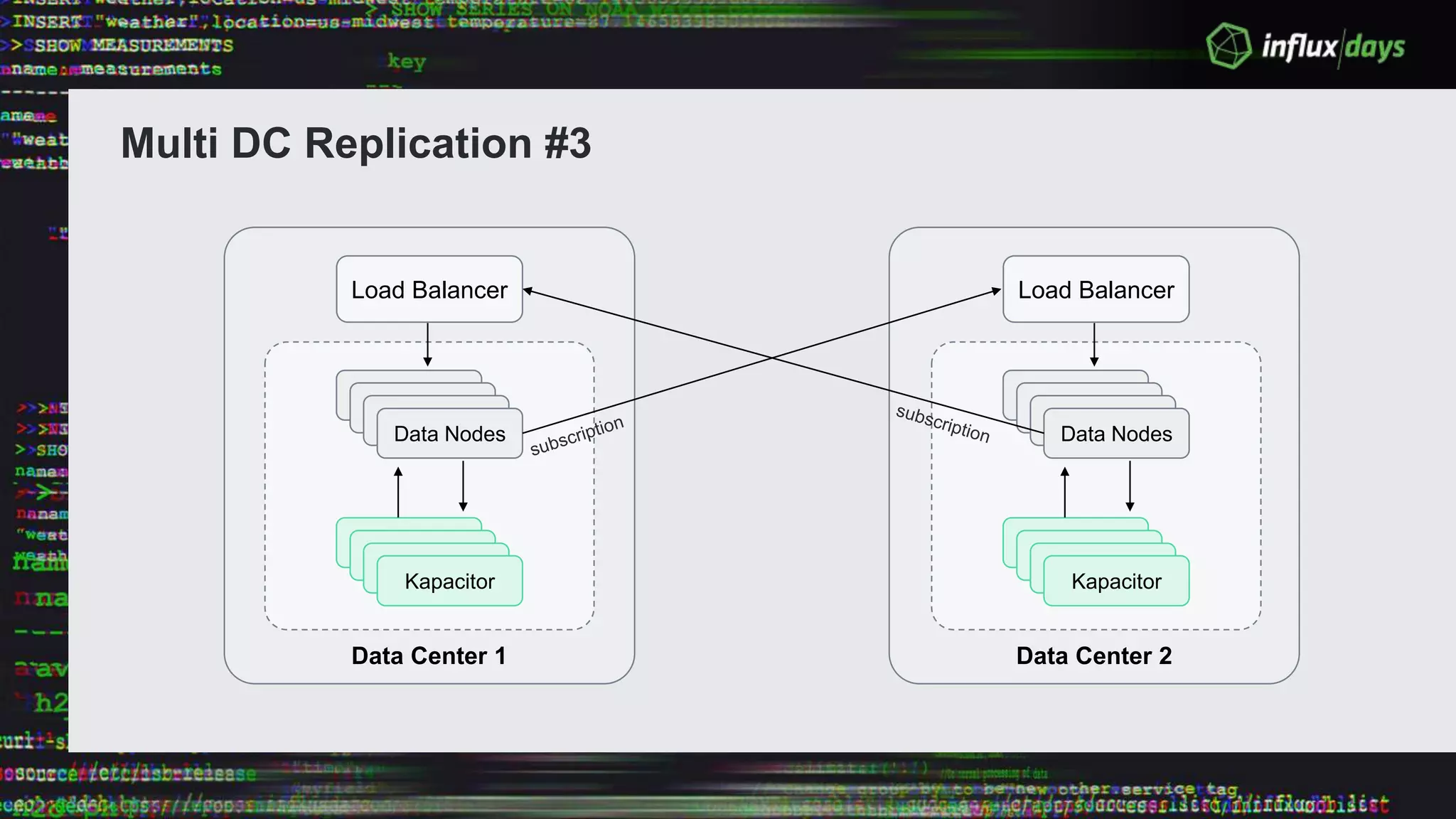
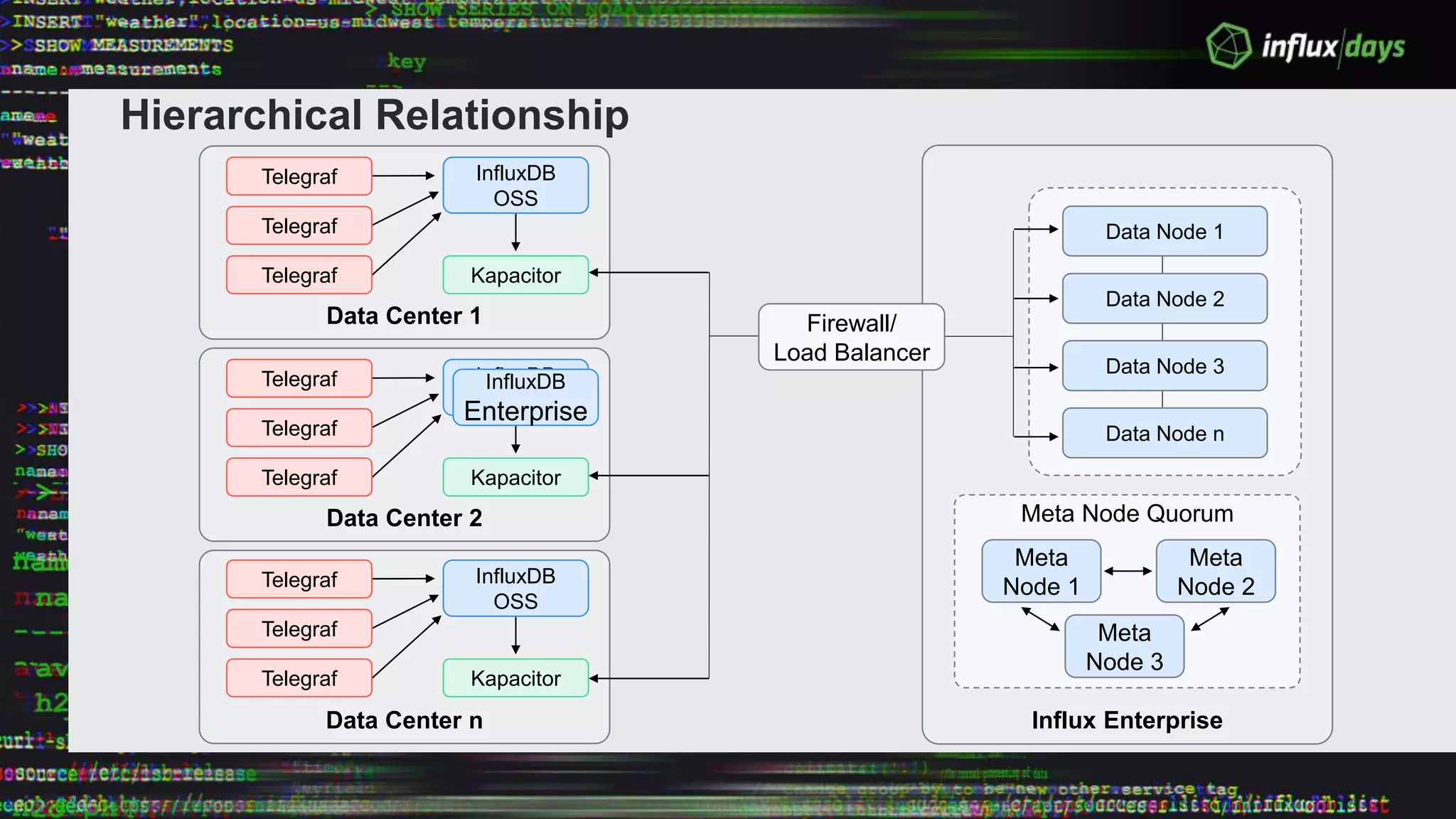
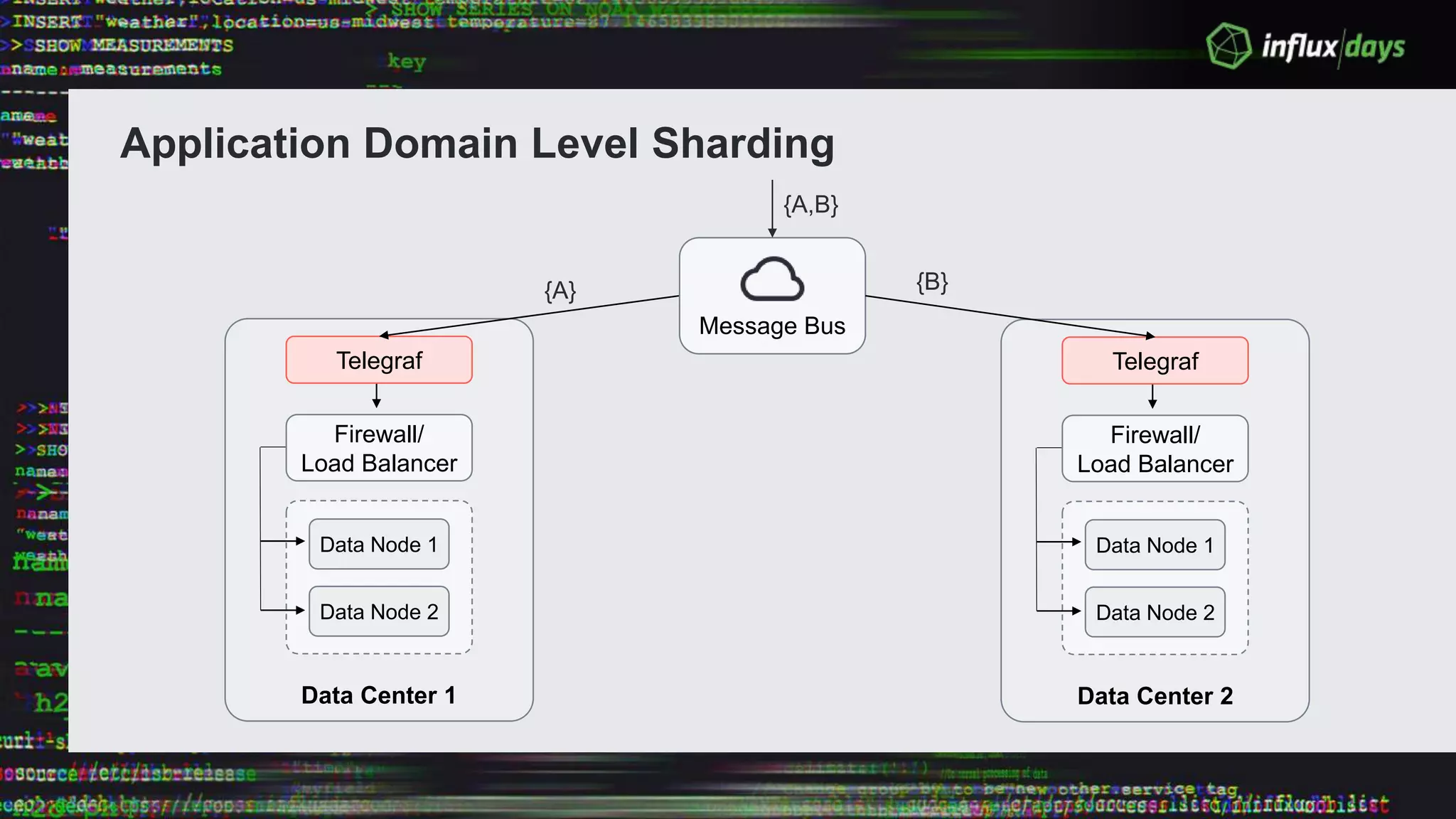
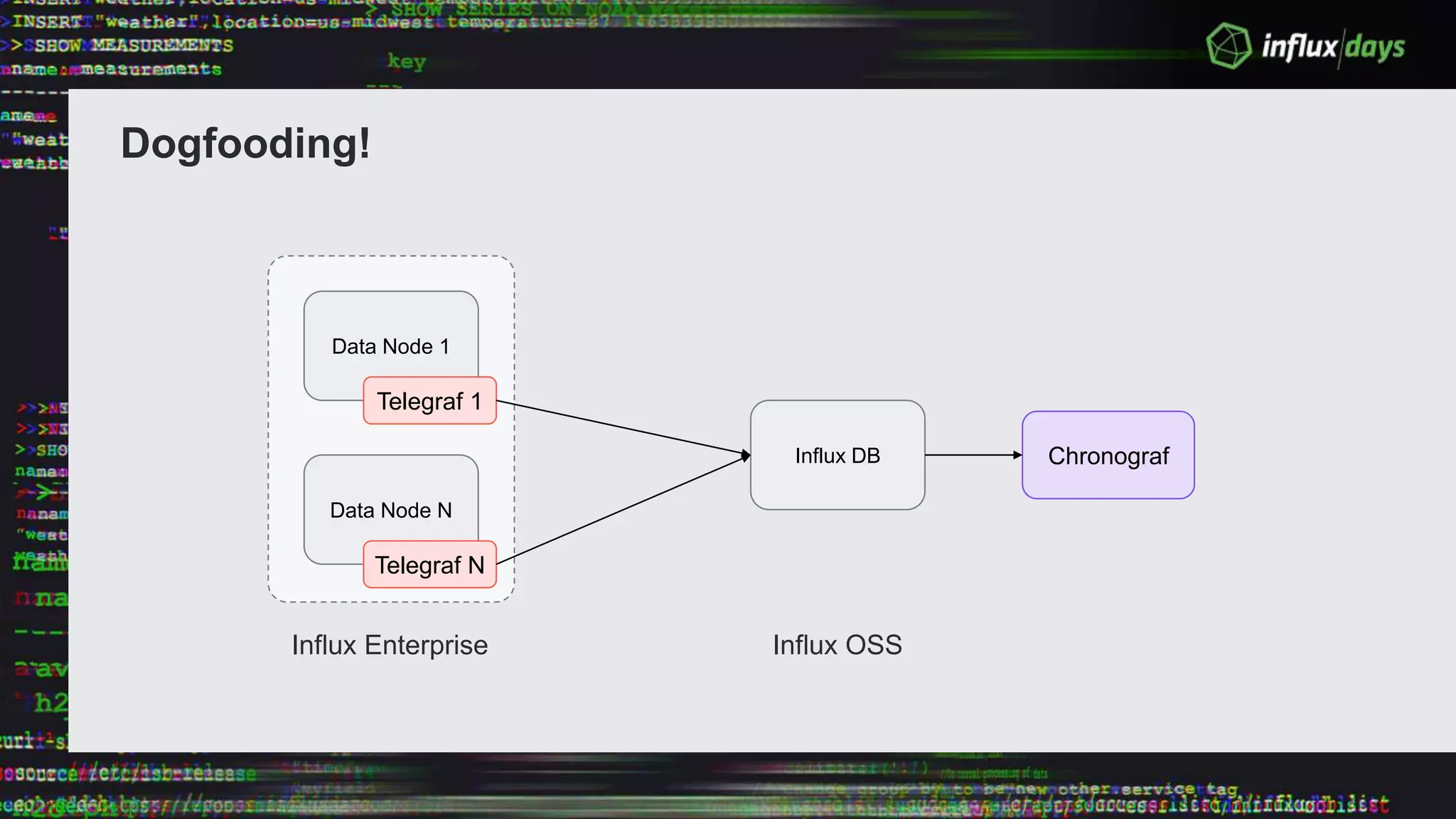
The document outlines the agenda for a workshop on the new practitioners track, including sessions on installing the Tick stack, writing queries, and optimizing InfluxEnterprise. It details the architecture of InfluxEnterprise clusters, including the roles of meta and data nodes, considerations for horizontal scalability, and deployment strategies across multiple data centers. Additionally, it discusses high availability measures and the importance of replication factors for data integrity.