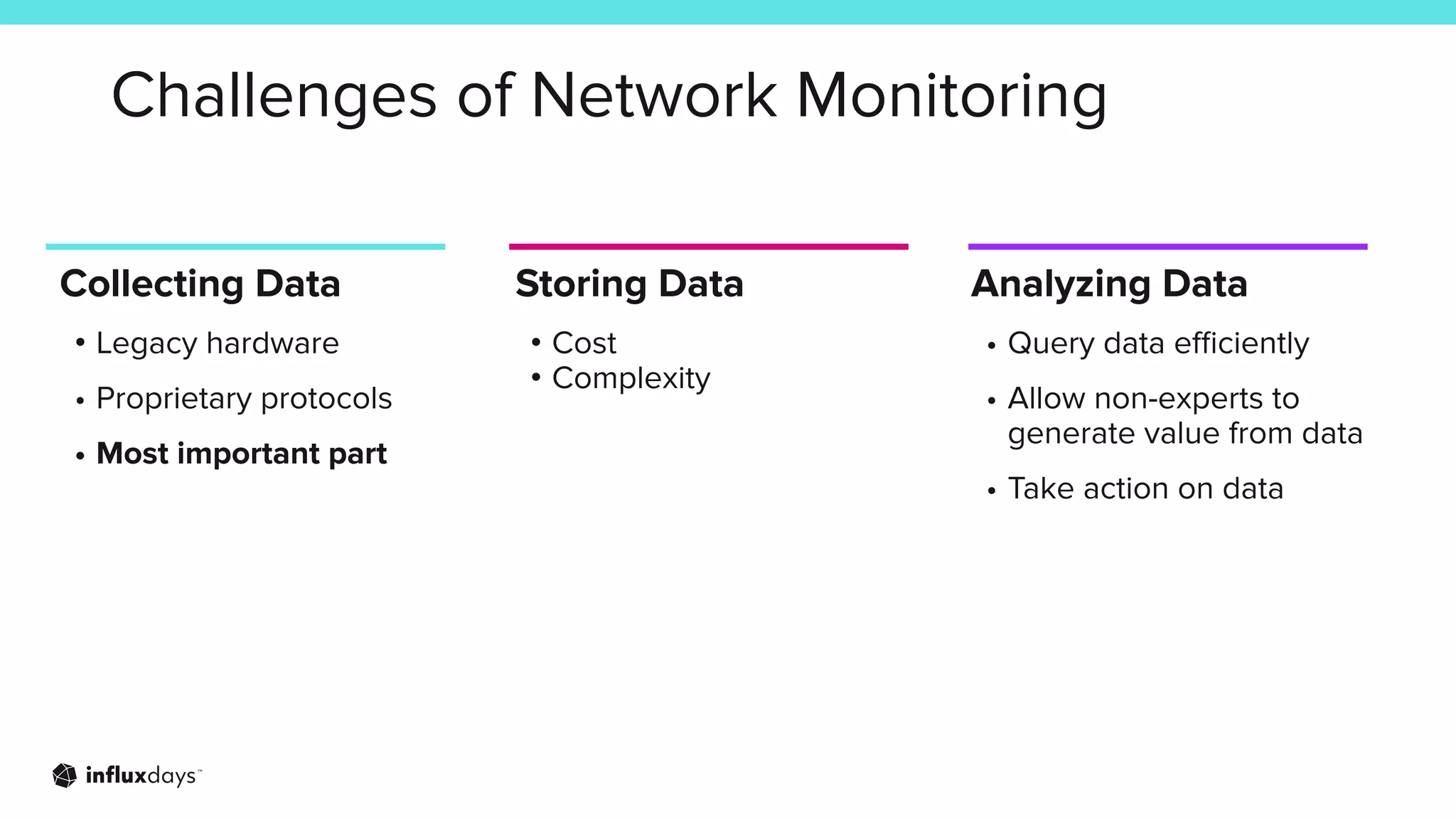
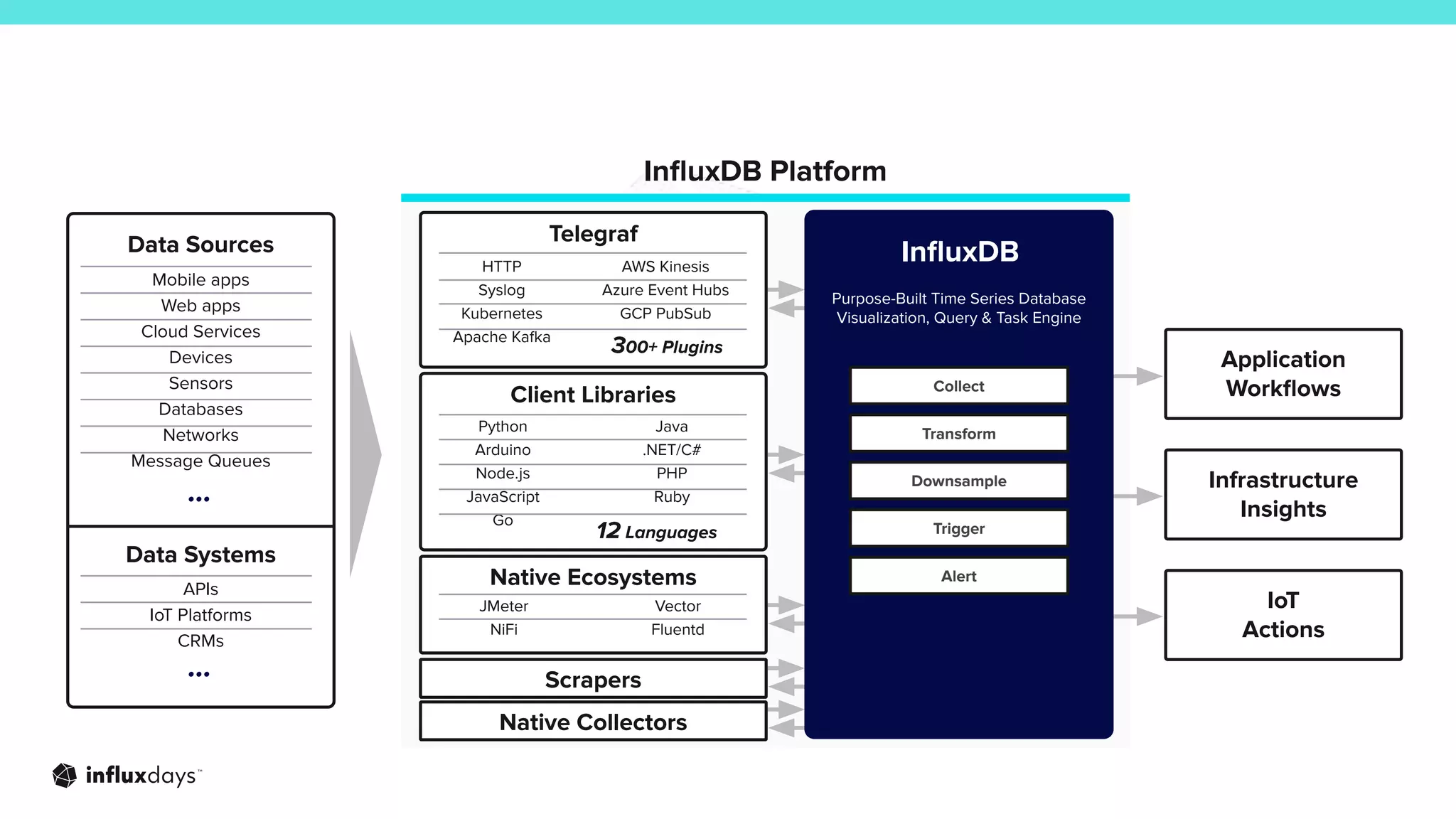
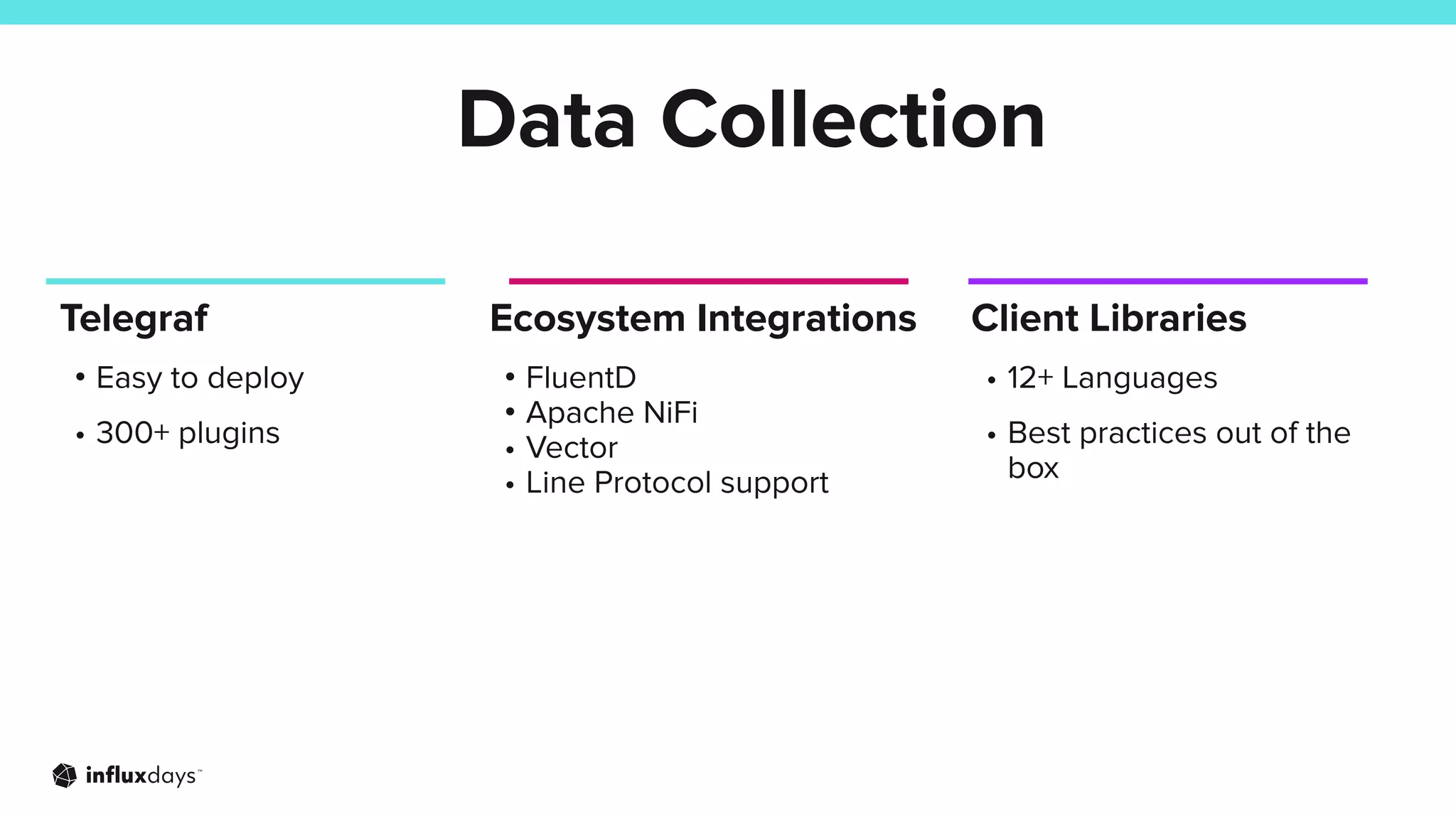
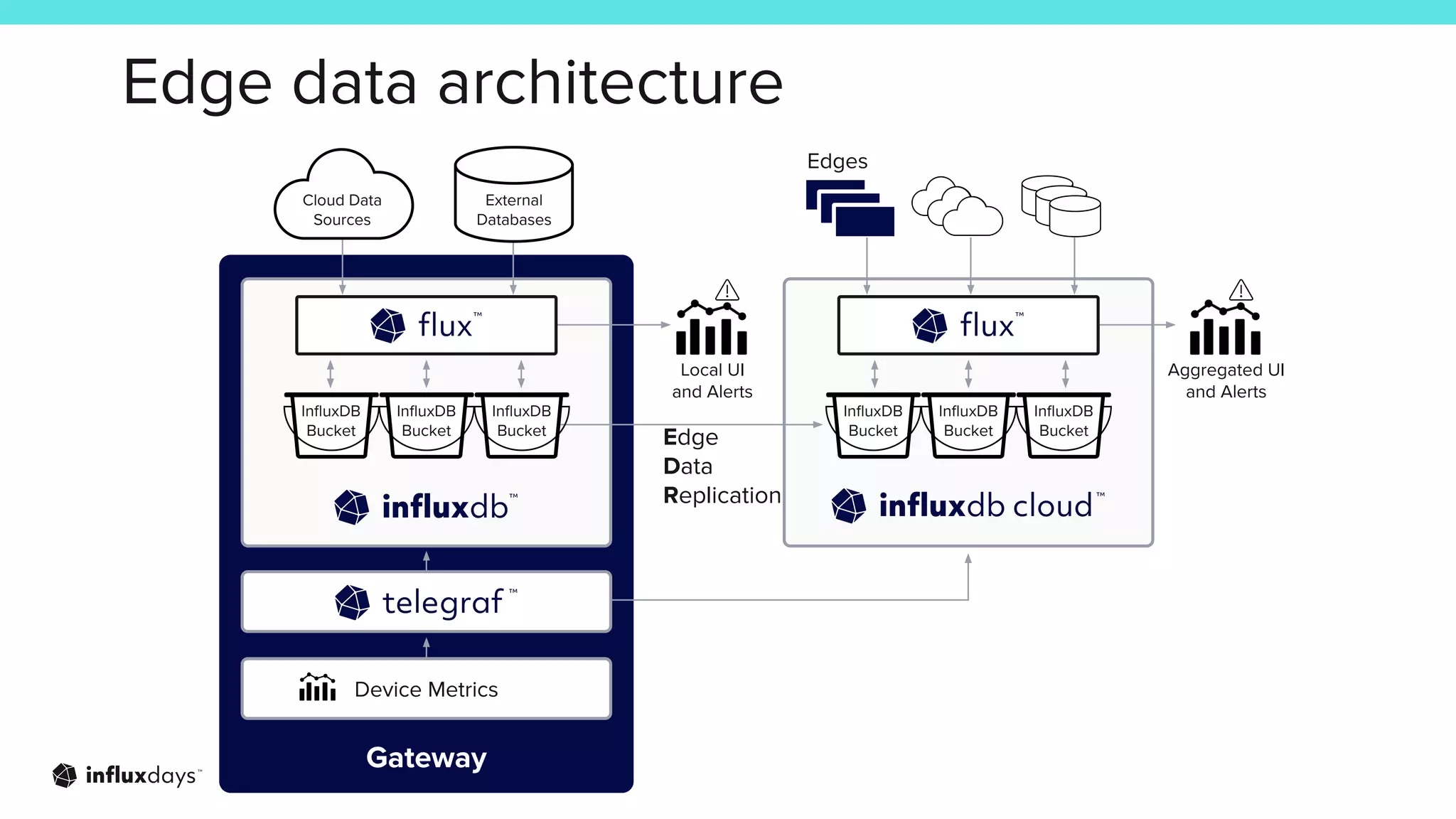
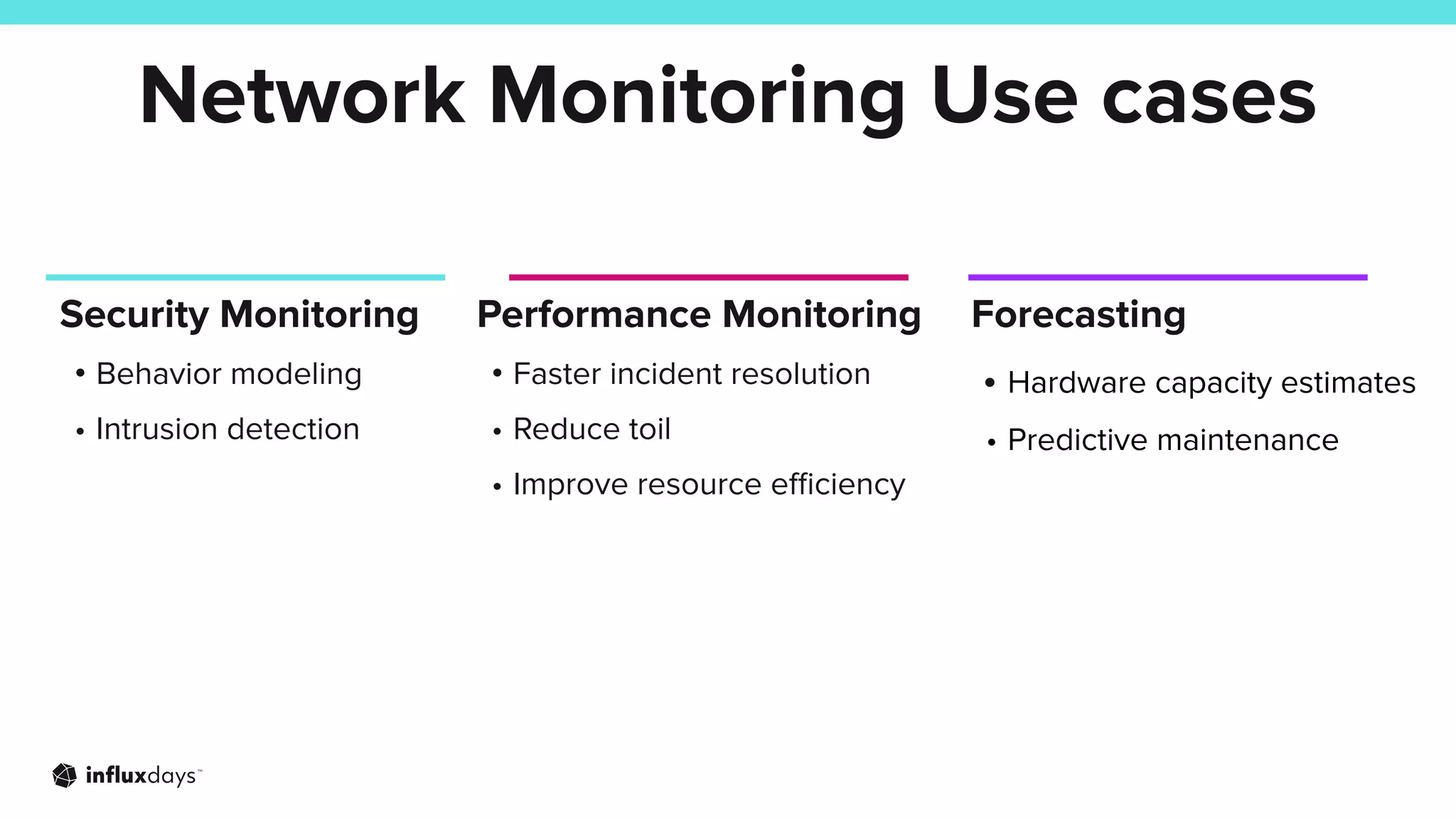
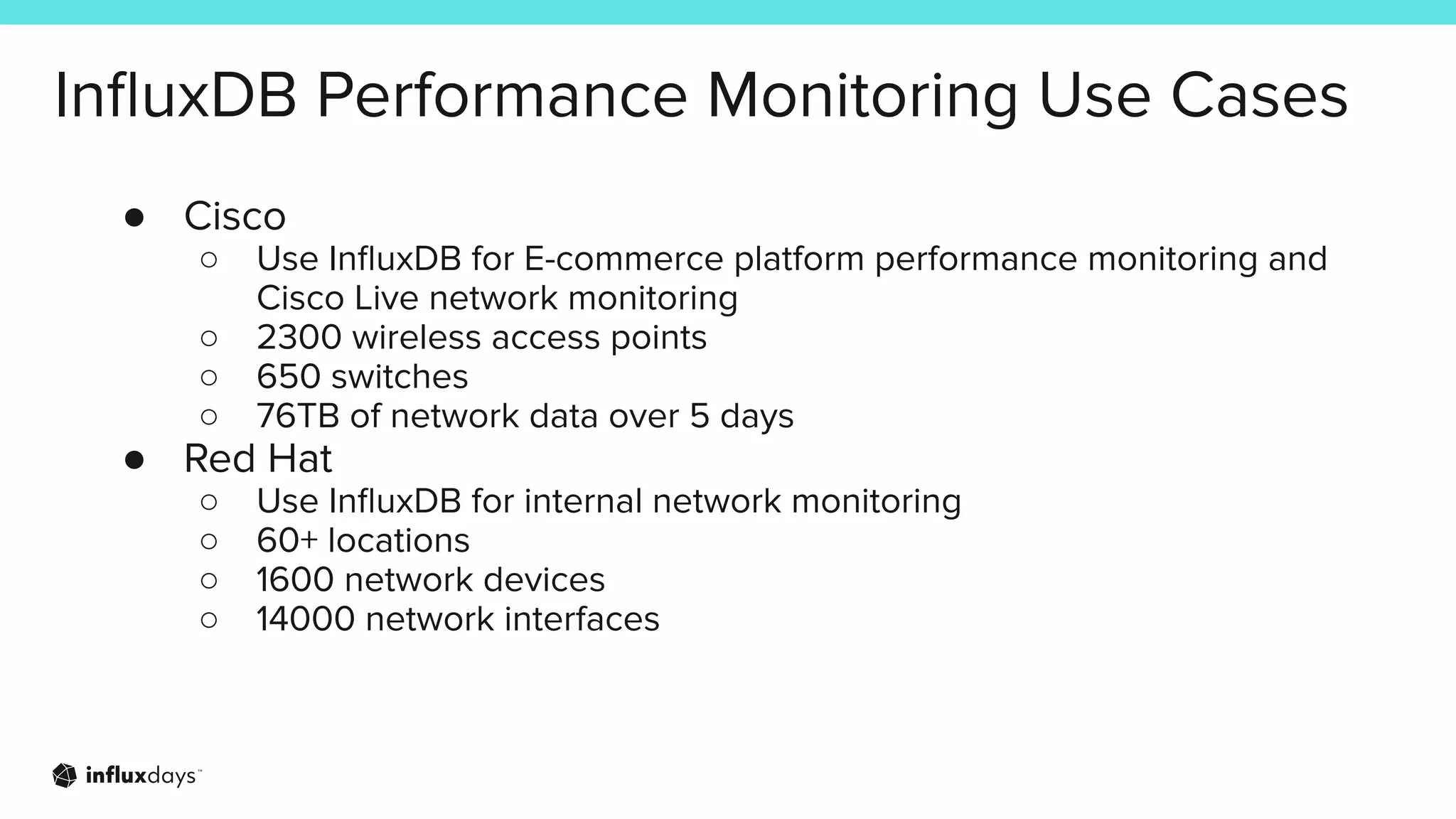
The document outlines how InfluxDB can address challenges in network monitoring, such as data collection, storage, and analysis. It highlights various use cases, including security monitoring, performance monitoring, and predictive maintenance across different industries. The session discusses the ecosystem's tools, like telegraf, and integration capabilities for effective network management.