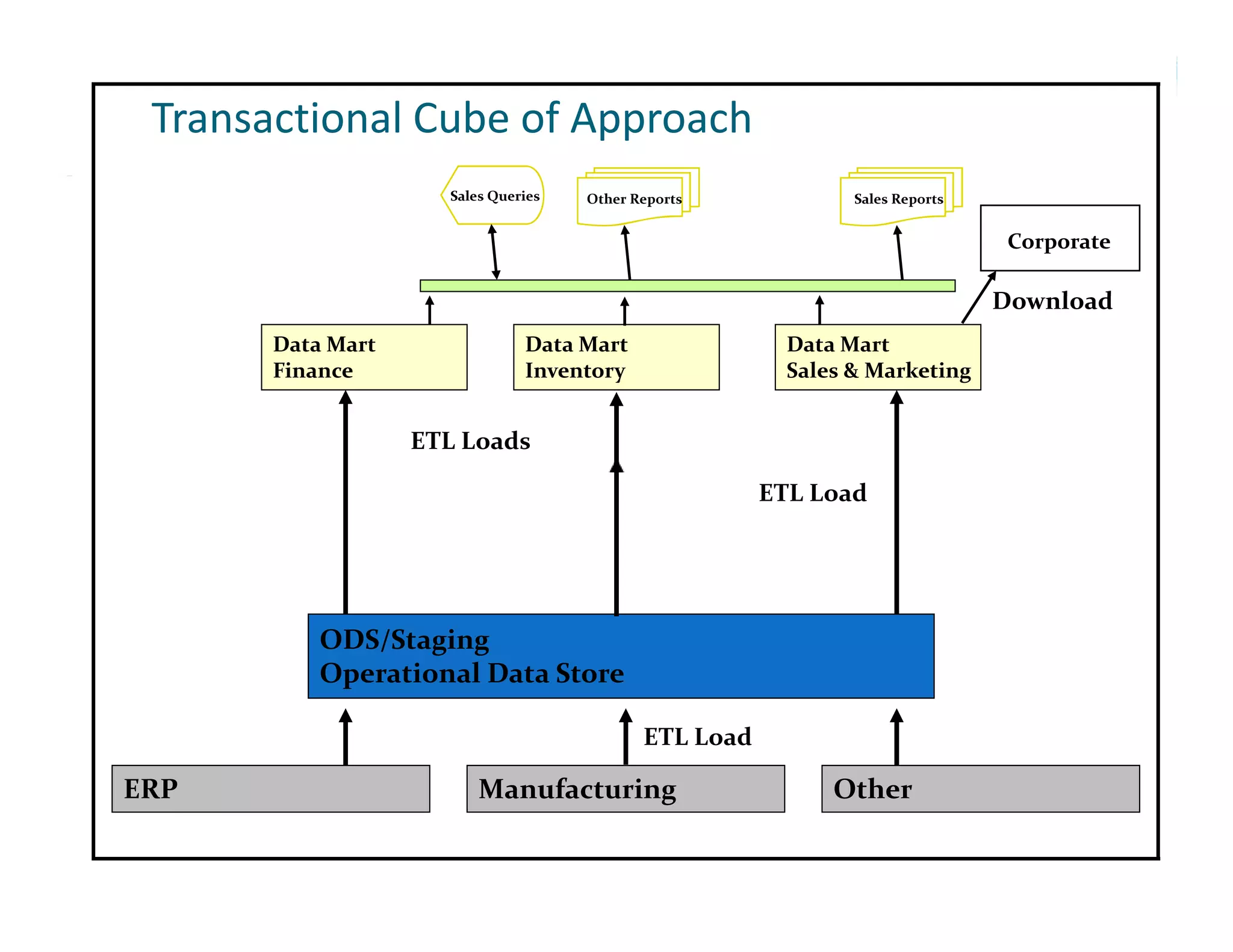
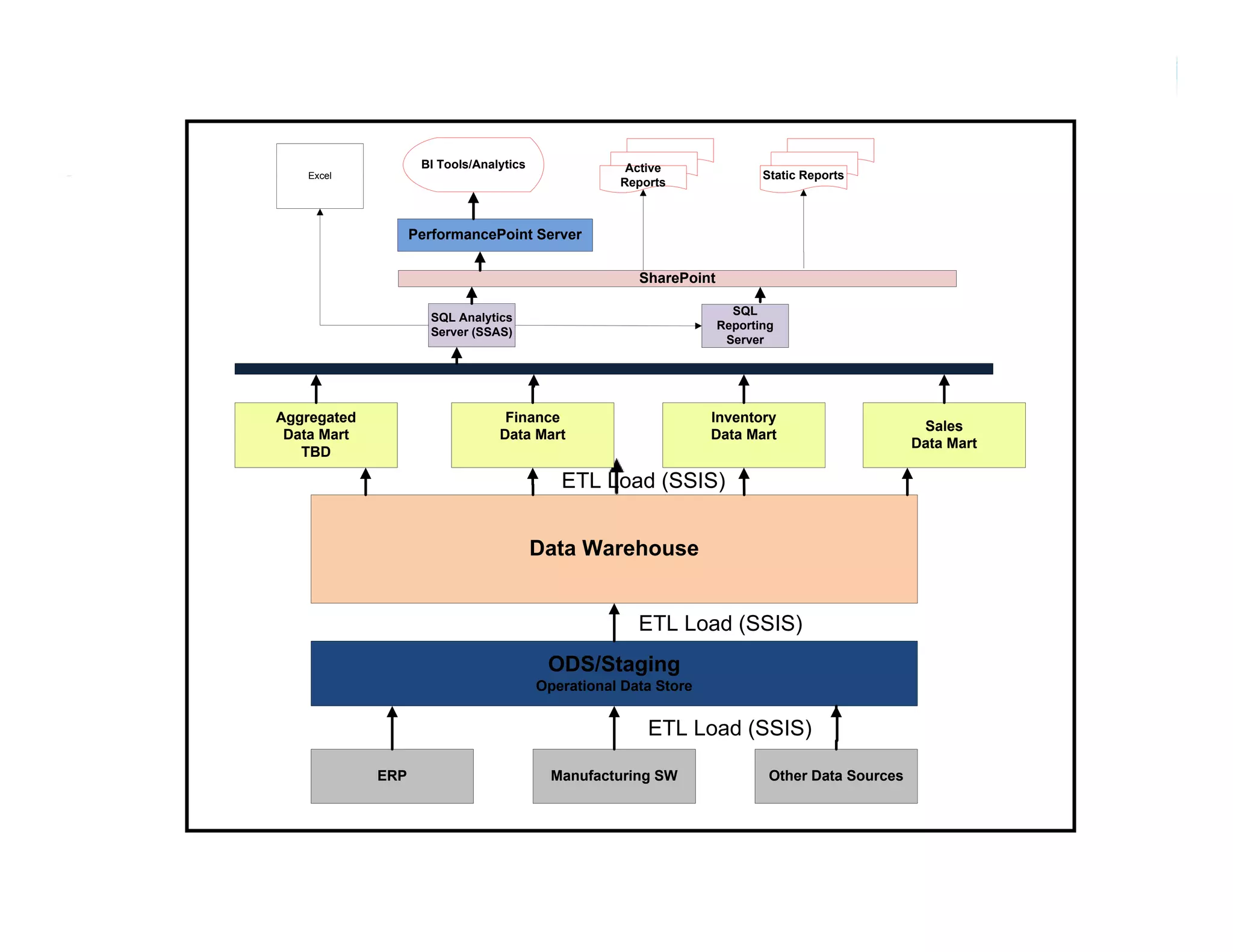
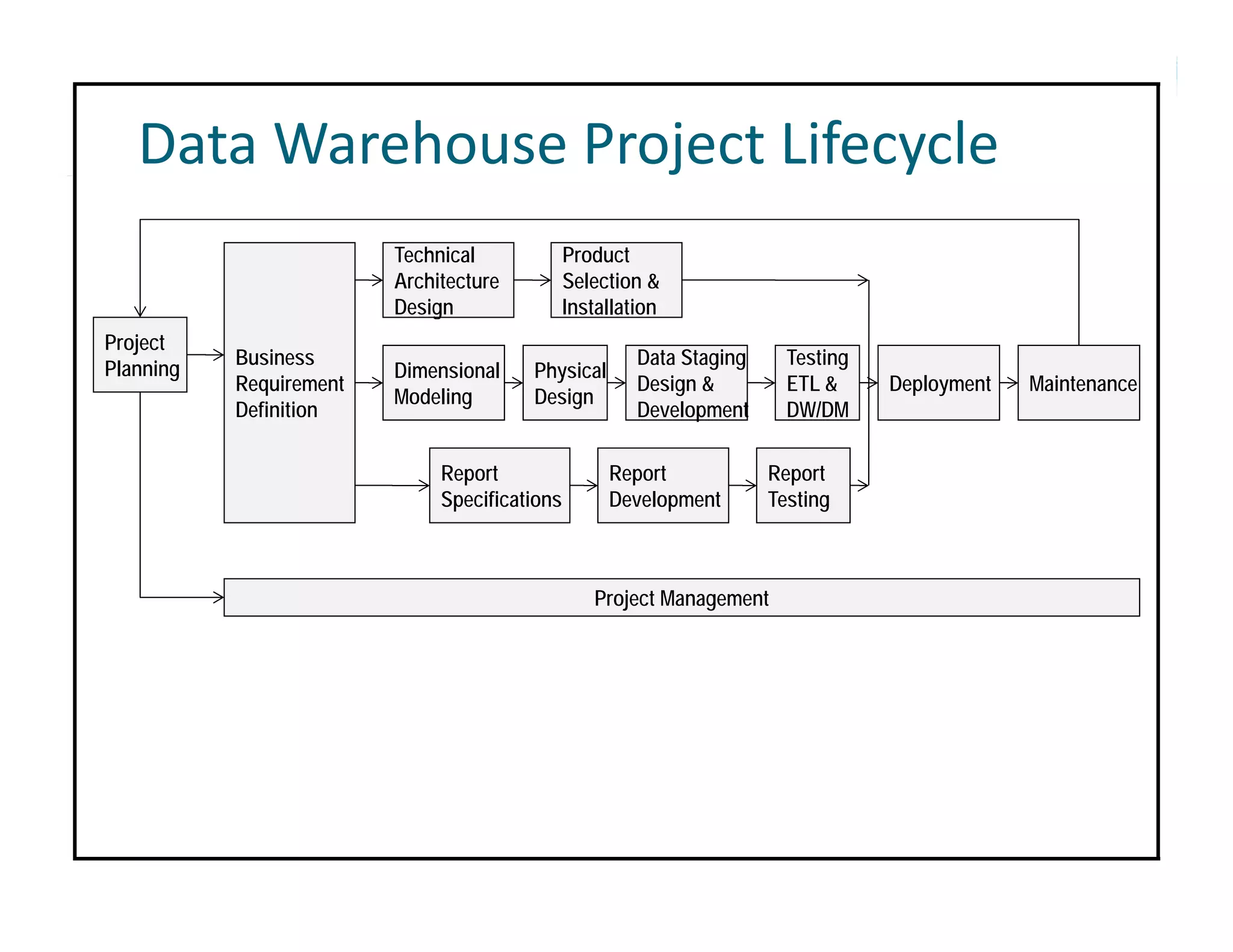
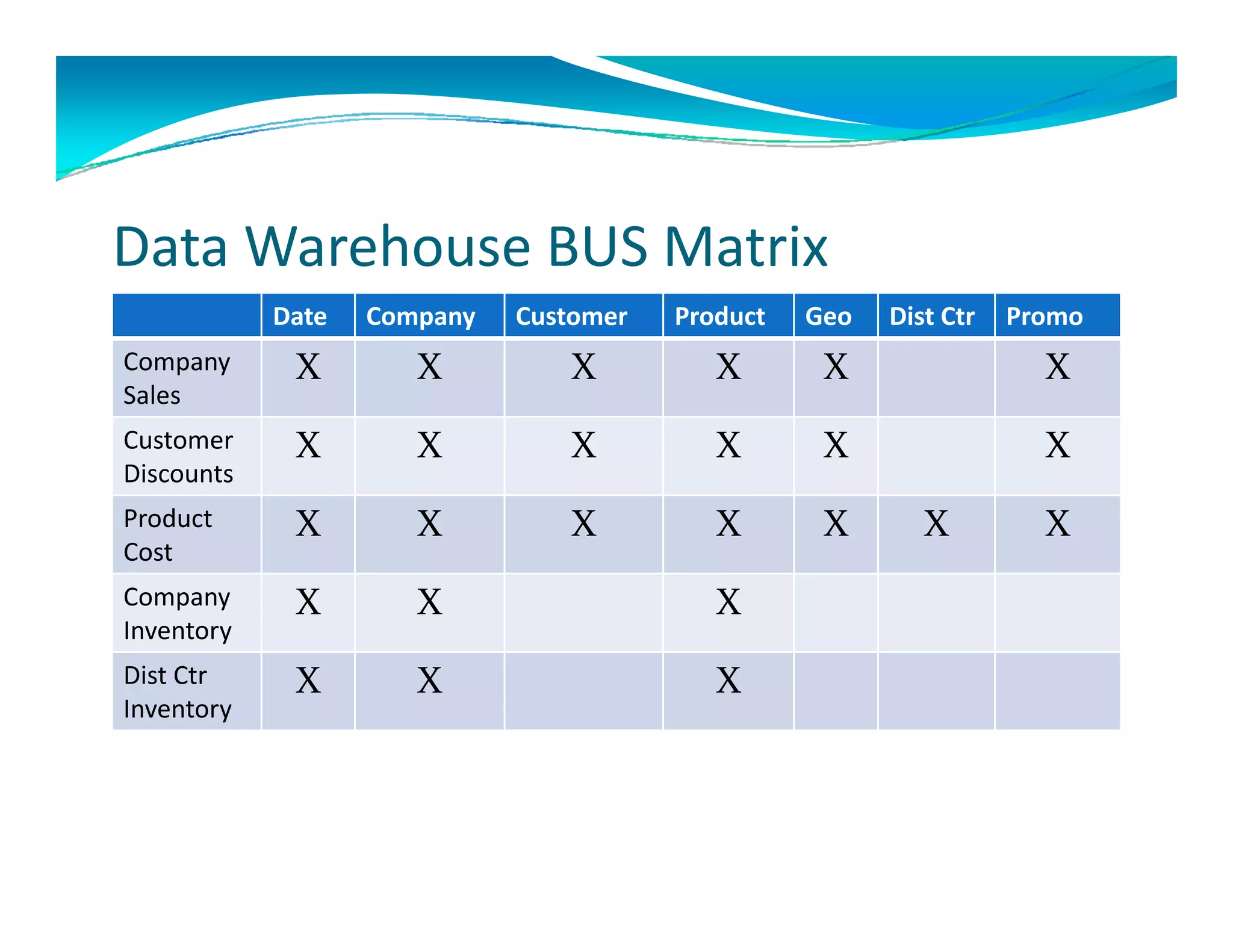
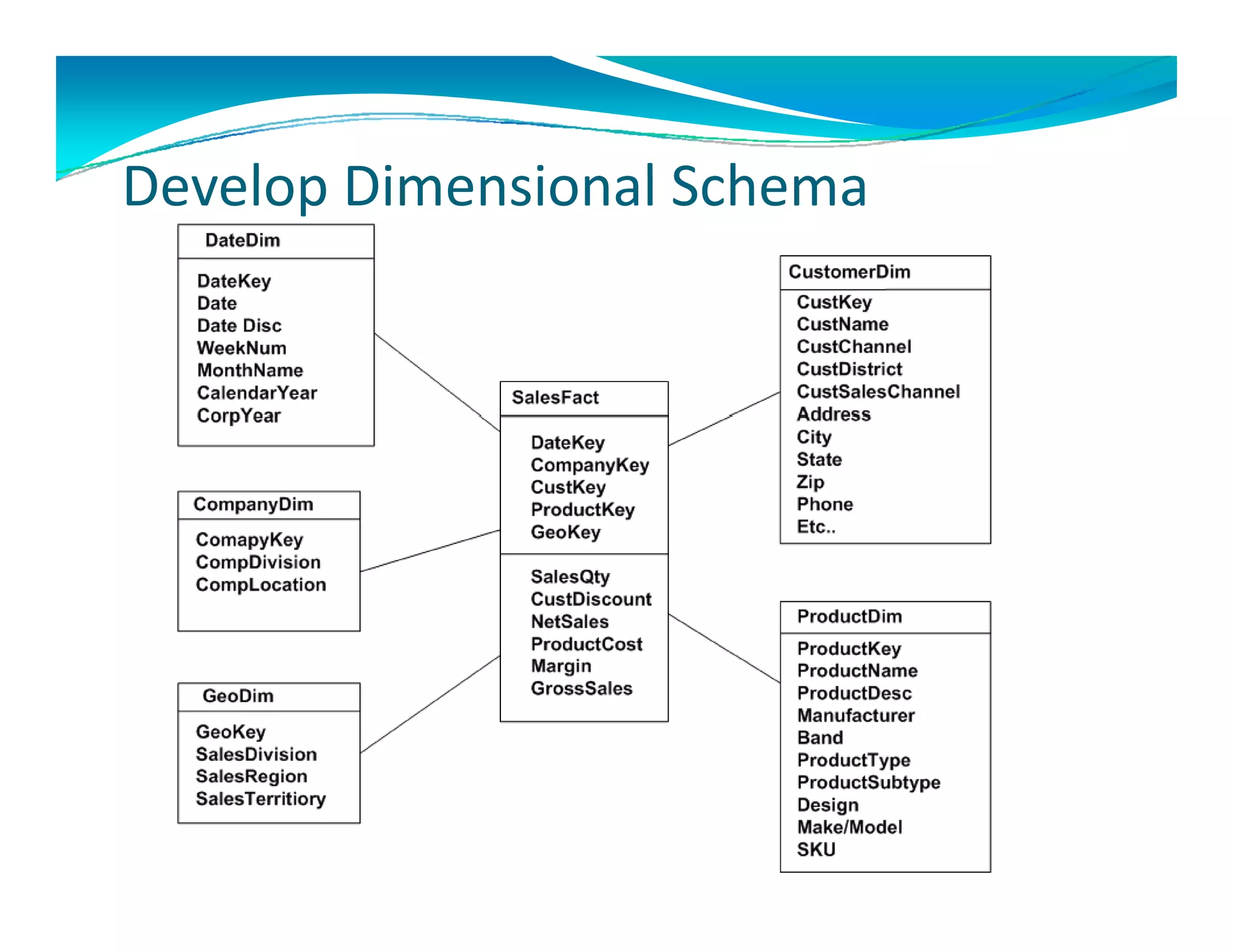
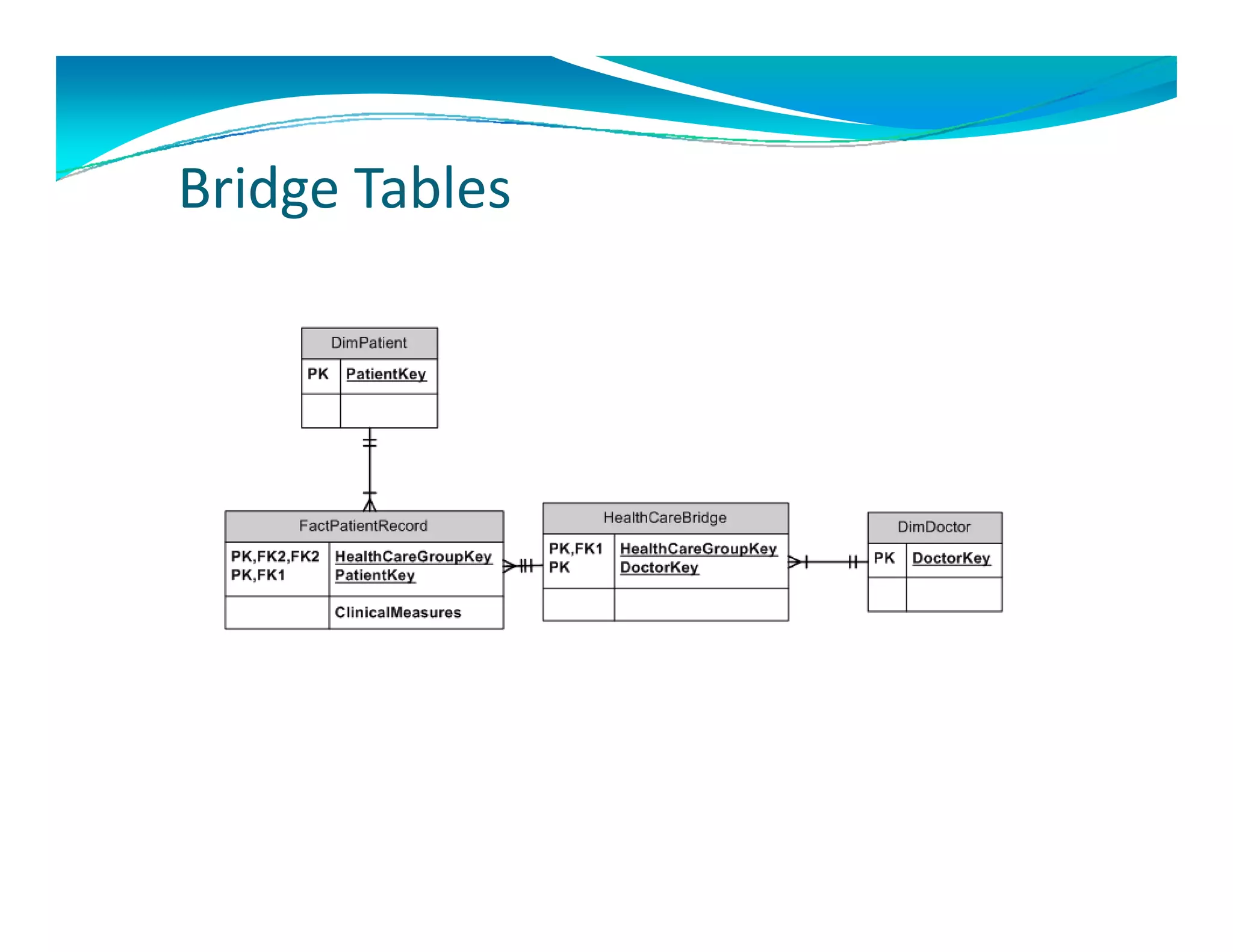
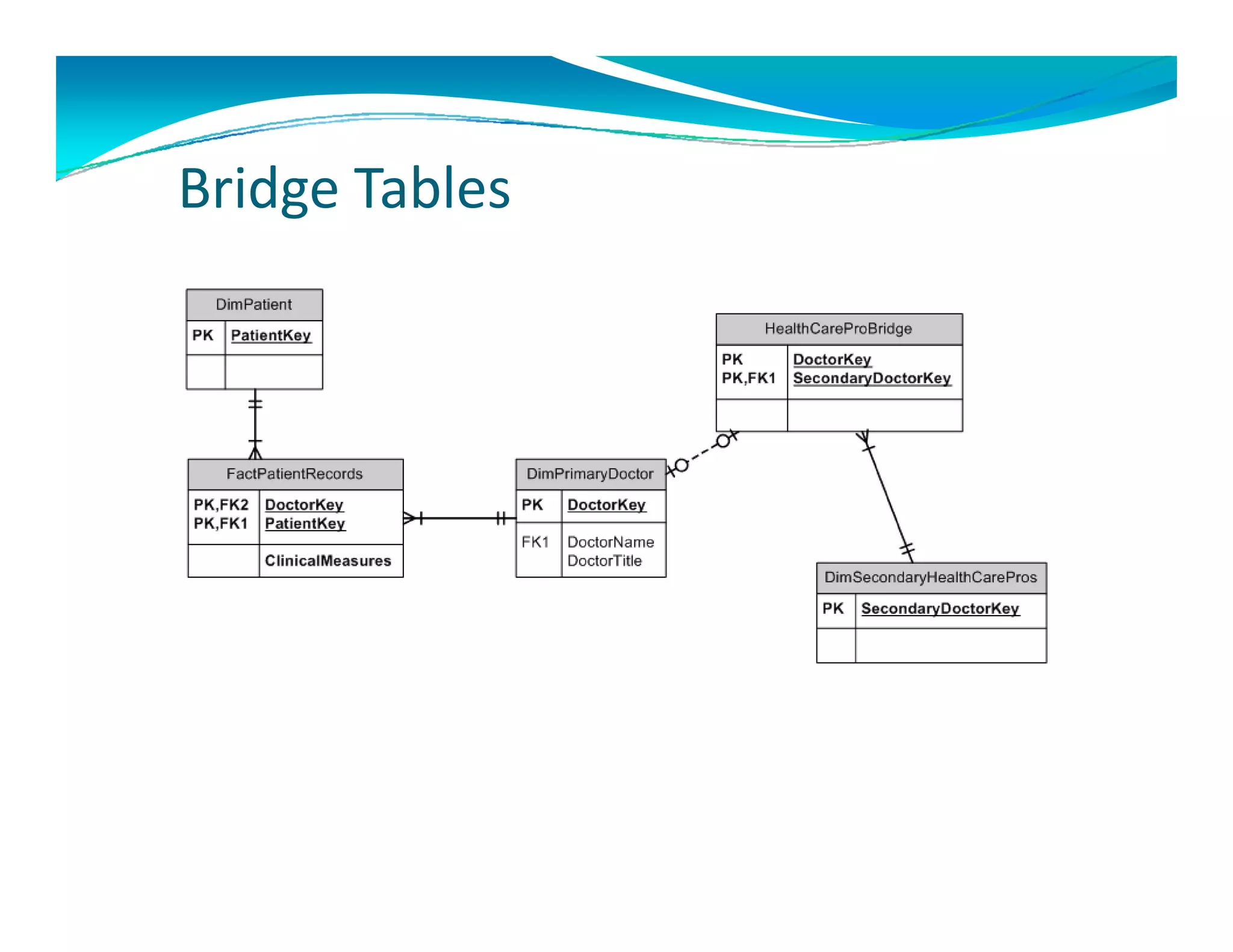
The document outlines the design and development of an enterprise data warehouse for Carl Zeiss Vision North America, emphasizing the need for consolidated and user-friendly reporting. It details the project approach, including the use of various Microsoft tools for ETL, analytics, and reporting, as well as the importance of understanding business processes and requirements. Additionally, it highlights the significance of dimensional design and the creation of star schemas for data management and analytics.