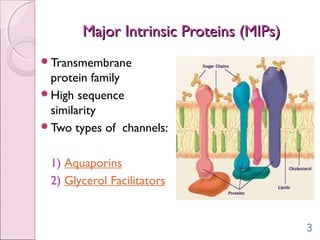
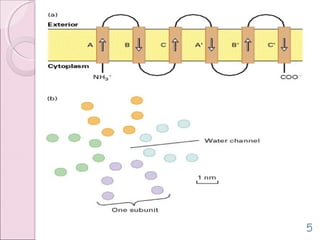
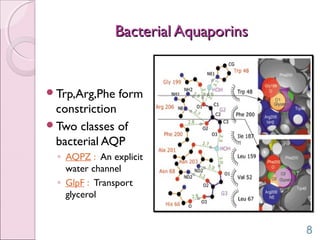
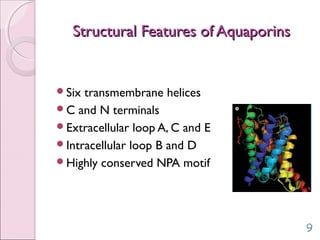
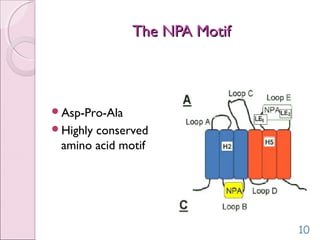
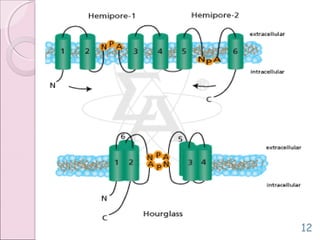
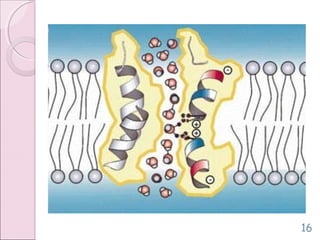
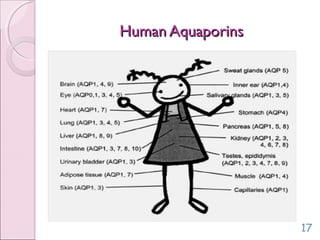
This document discusses aquaporins, which are membrane channel proteins that facilitate the efficient transport of water across cell membranes. It outlines the key structural features of aquaporins, including their six transmembrane helices and hourglass shape. The document also notes that aquaporins are found across life forms and help transport water in critical biological functions like plant water transport and bacterial water movement. Finally, it briefly discusses some human aquaporins and their roles in diseases like nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.