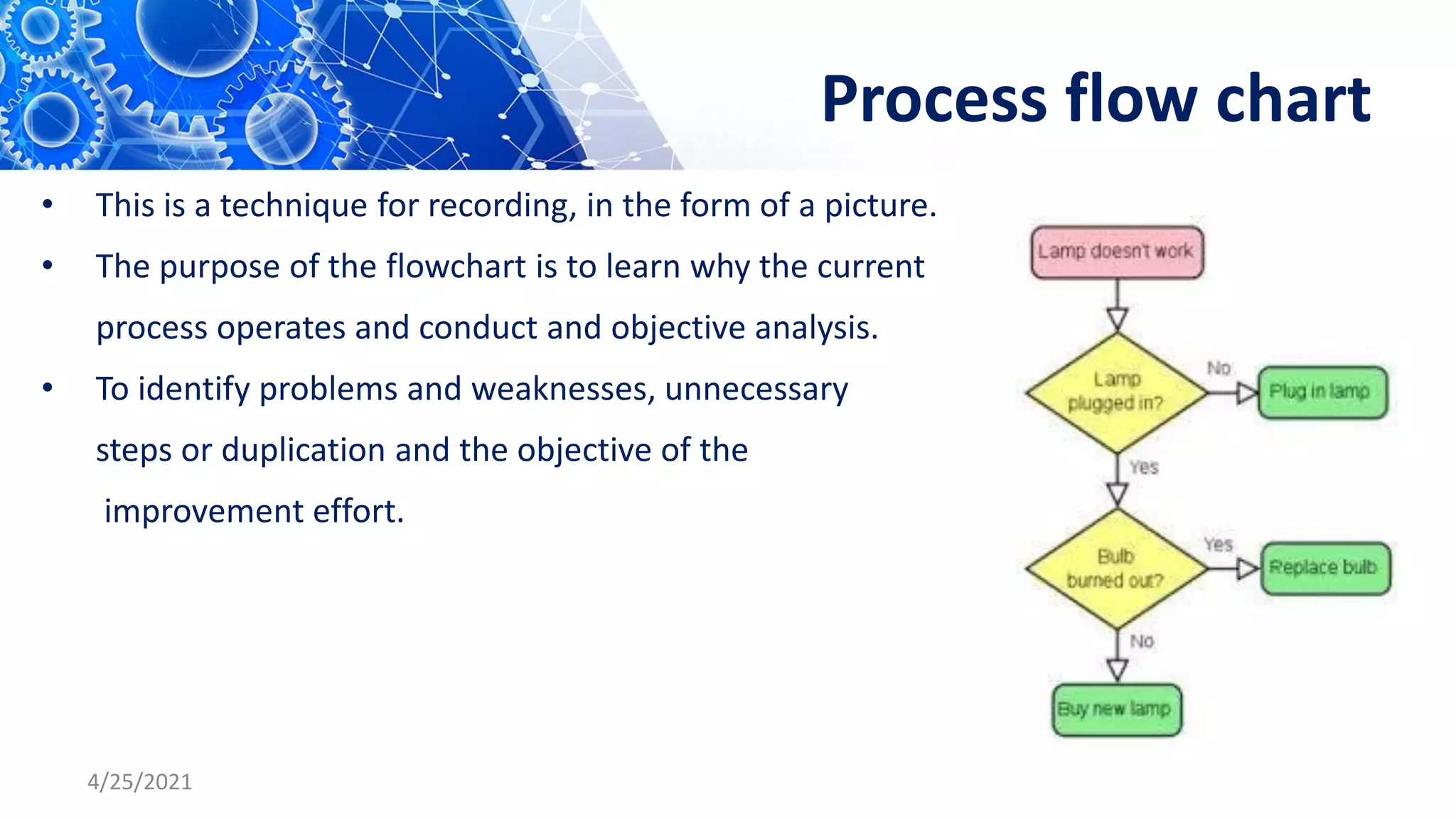
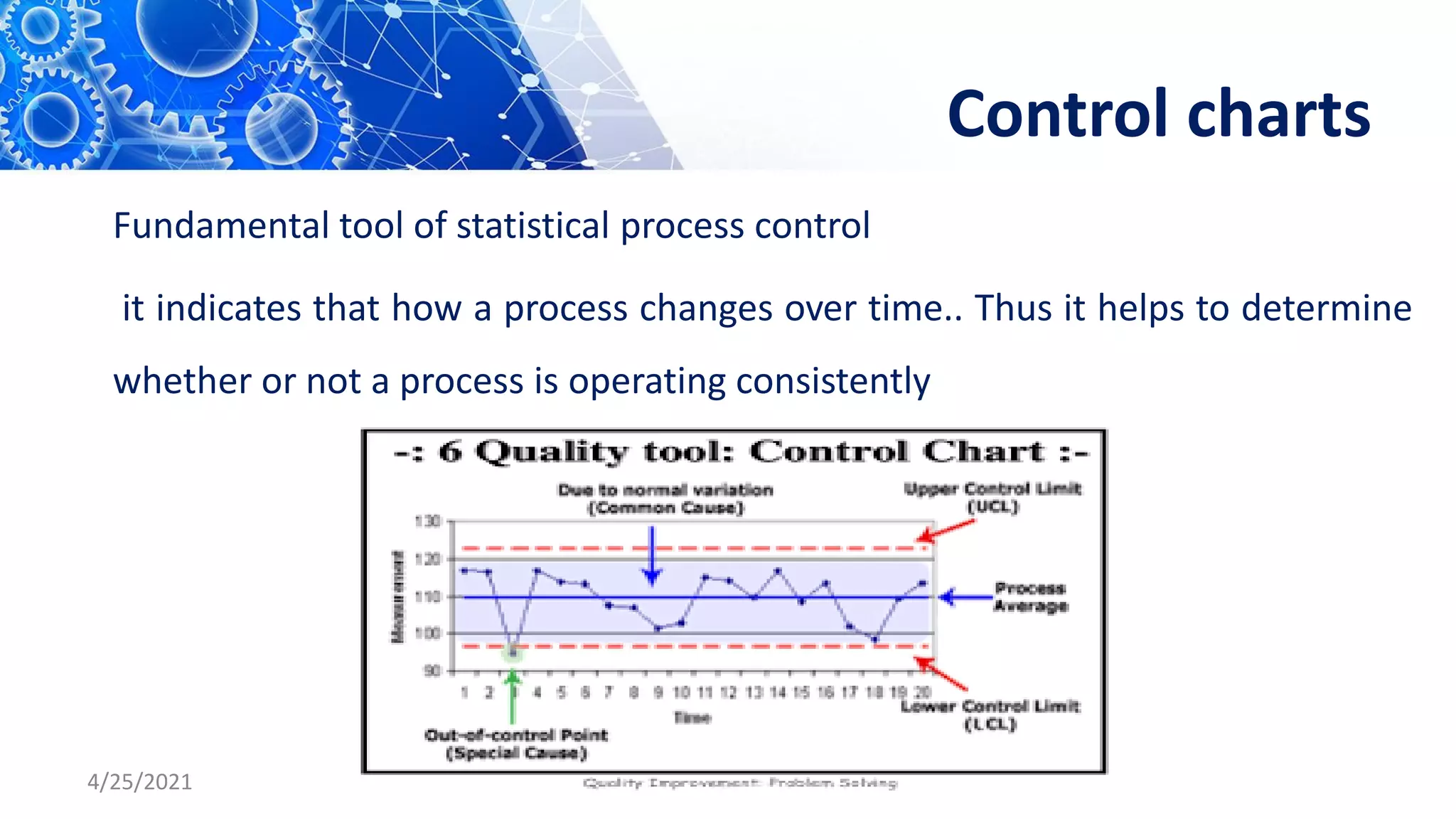
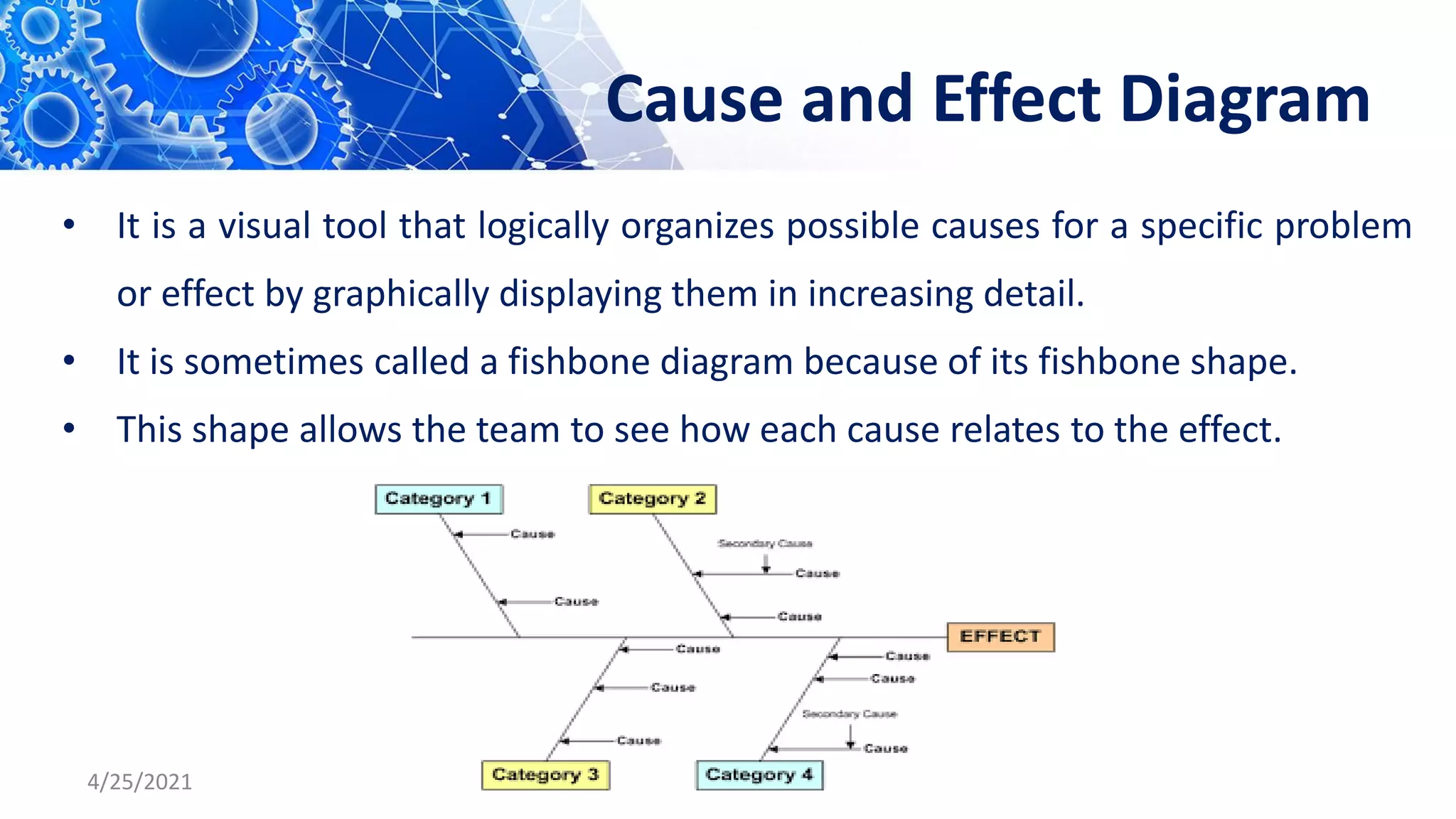
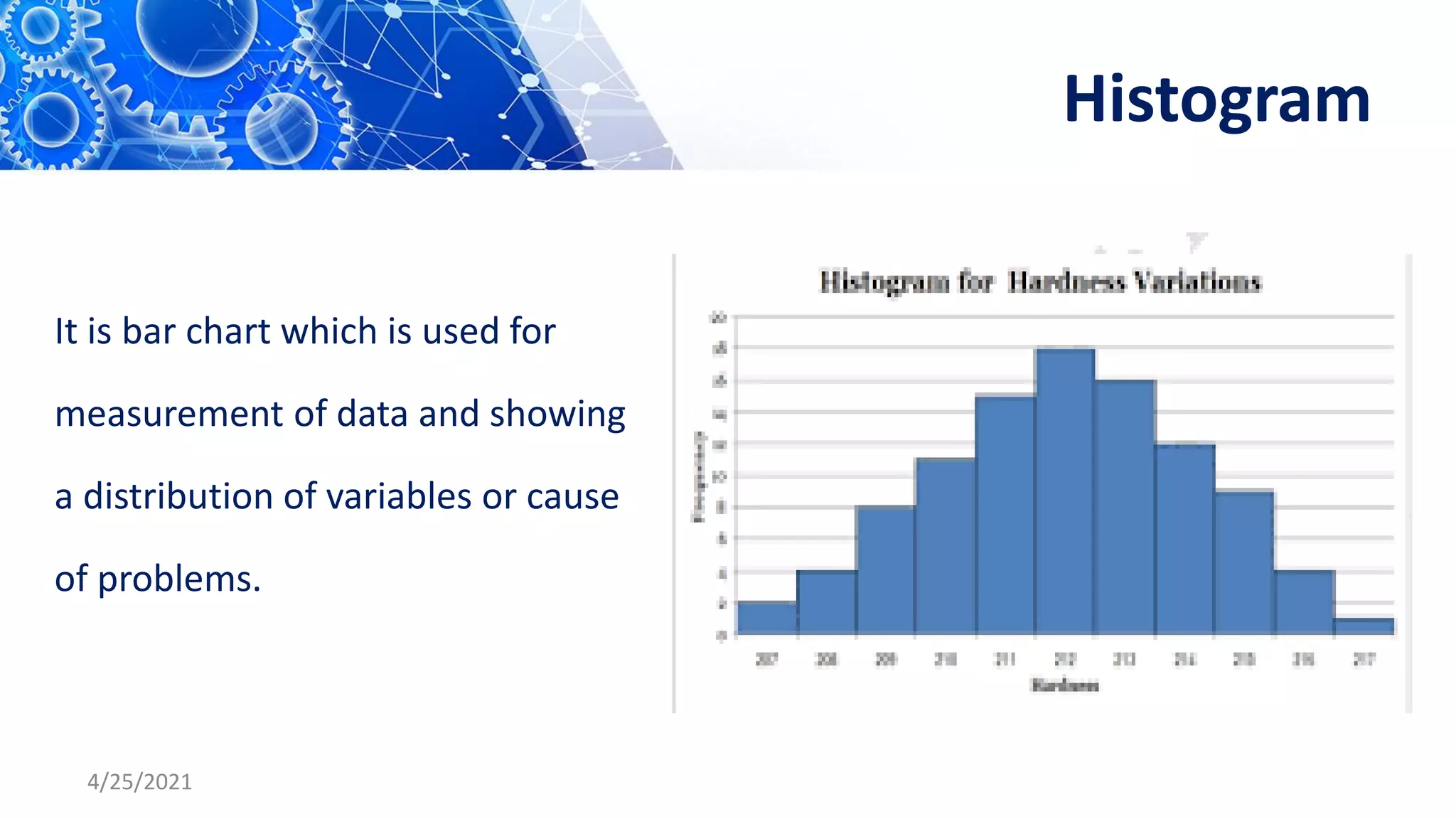
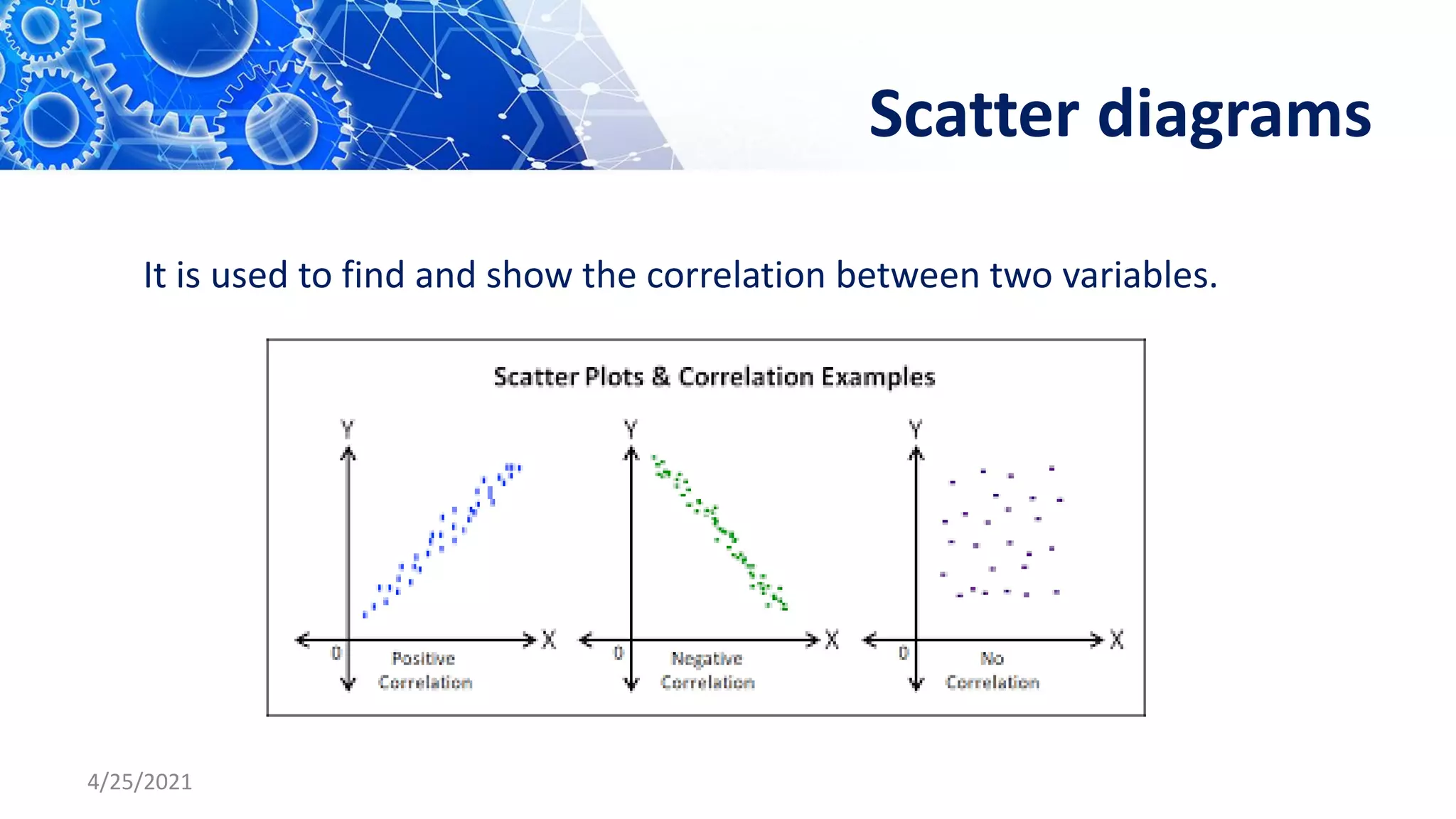
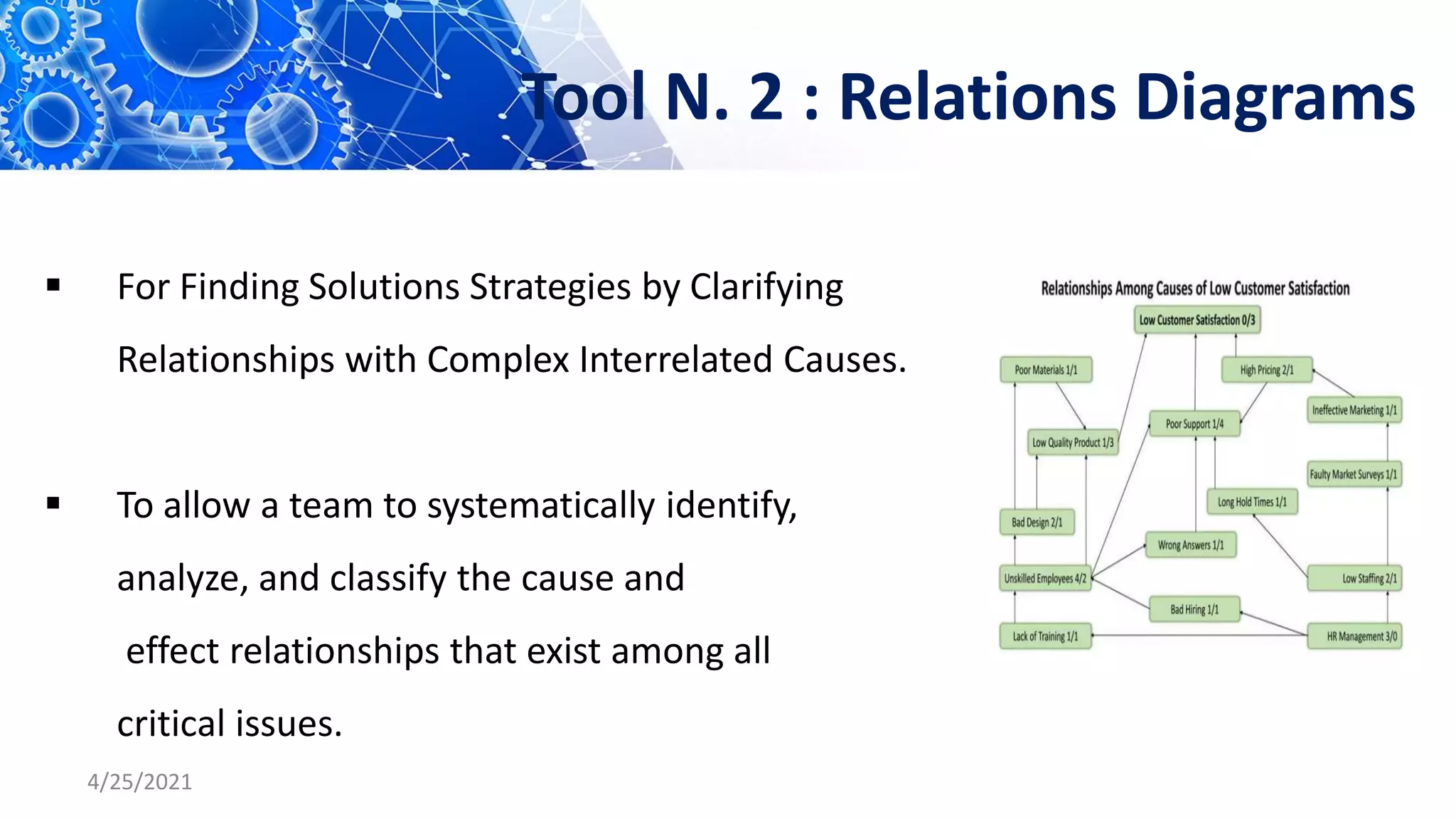
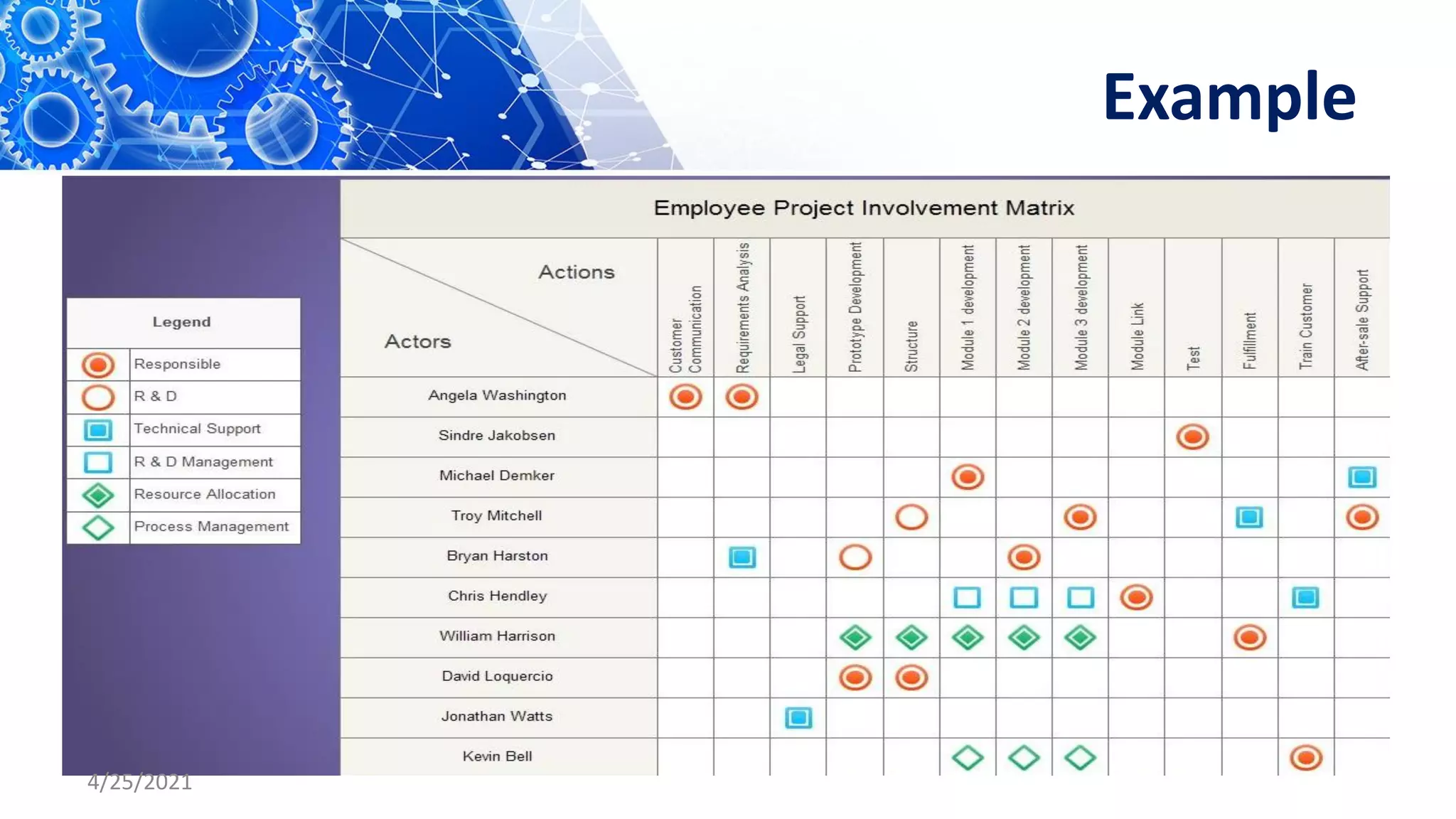
The document discusses quality control tools and techniques. It provides an overview of several commonly used tools, including check sheets, process flow charts, control charts, cause and effect diagrams, histograms, Pareto analysis, and scatter diagrams. It then describes the seven new quality control tools: affinity diagrams, relations diagrams, tree diagrams, matrix diagrams, arrow diagrams, process decision program charts, and prioritization matrices. The benefits of using these quality control tools include improving process performance, production efficiency, reducing costs and defects, and enhancing customer satisfaction.