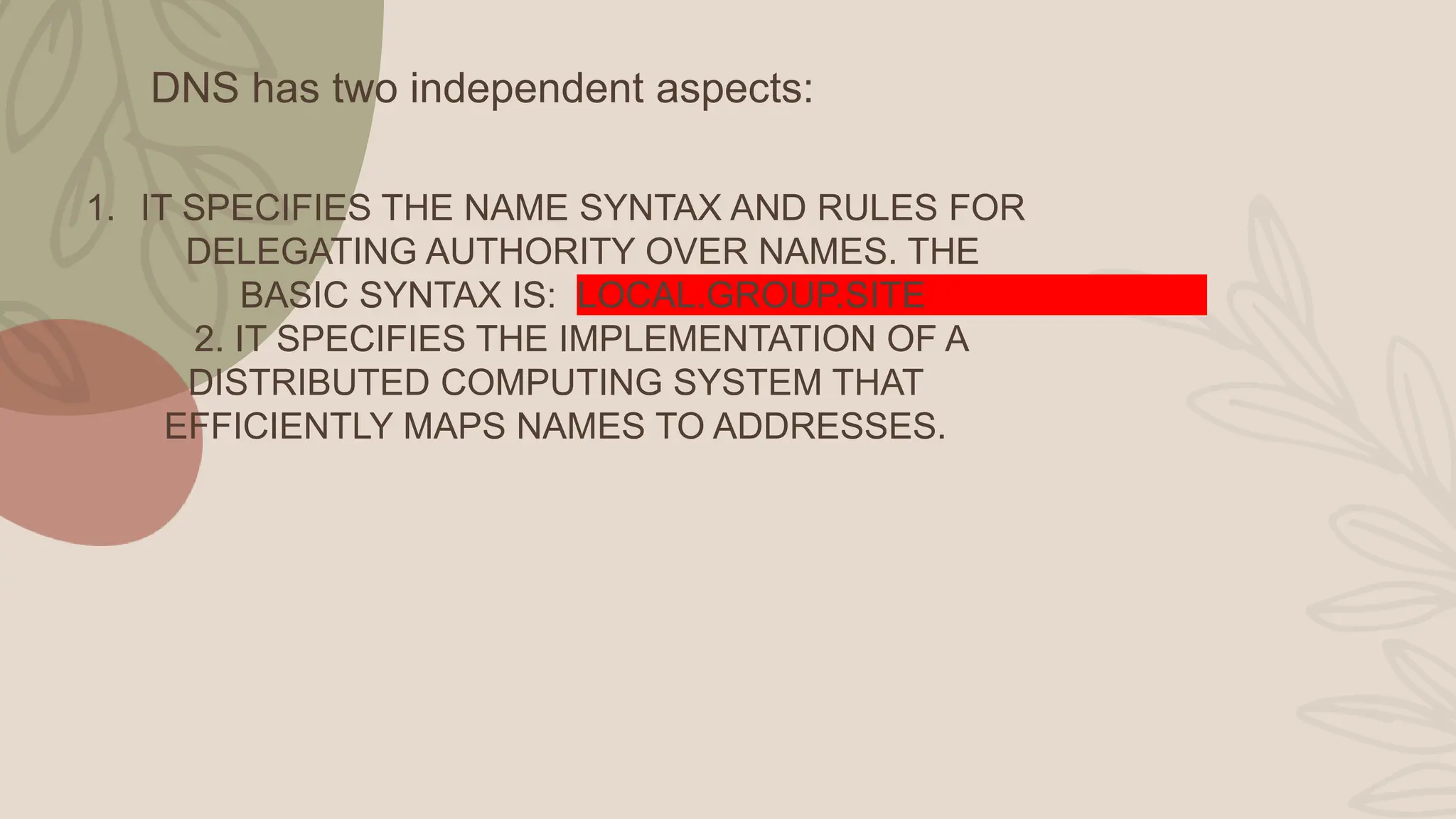
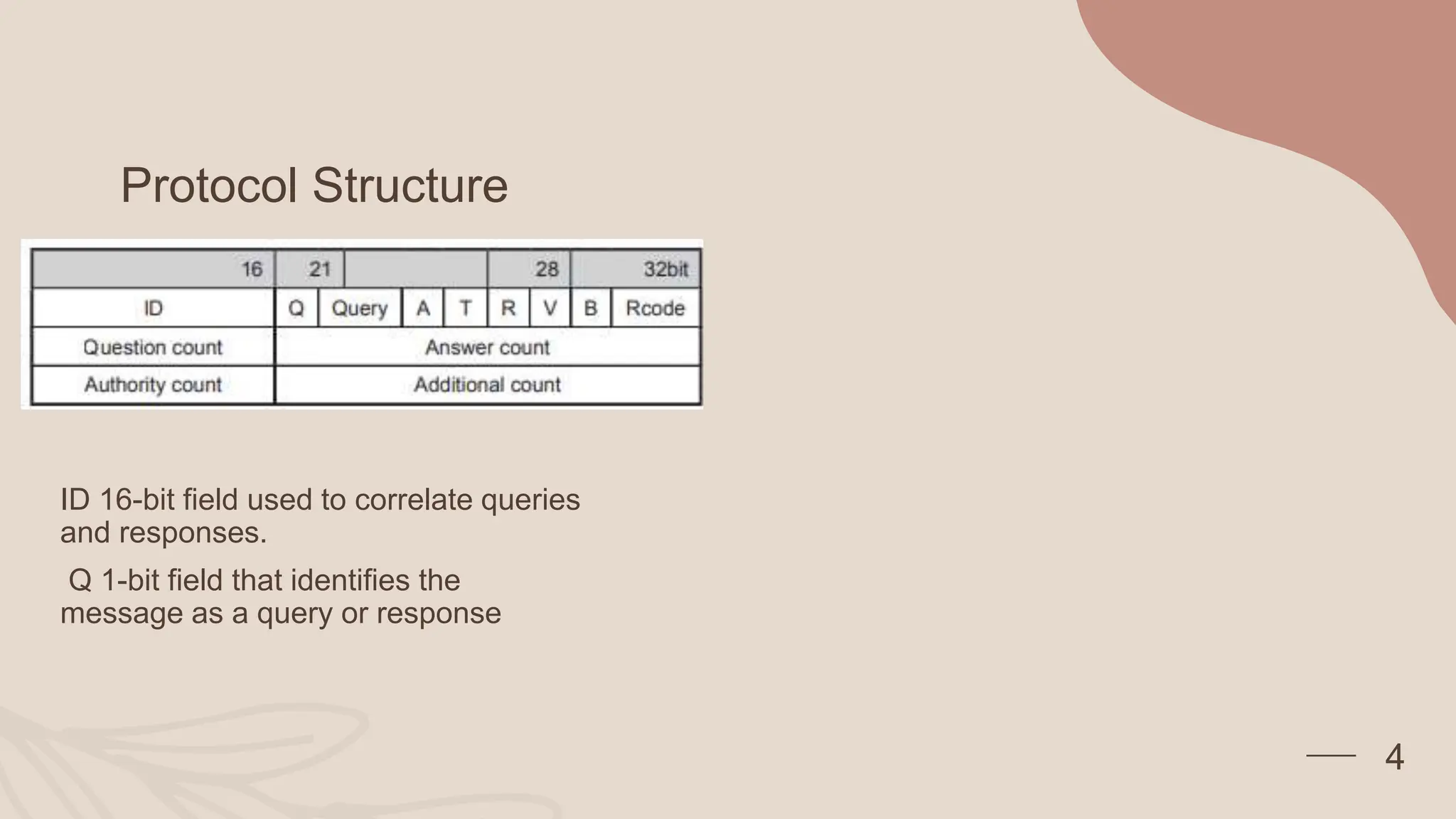
The document describes essential application layer protocols, focusing on the Domain Name System (DNS) and File Transfer Protocol (FTP). DNS functions as a distributed internet directory service, facilitating the translation of domain names to IP addresses, while FTP enables file sharing between hosts through TCP connections. Key features of FTP include promoting file sharing, indirect use of remote computers, and efficiently transferring data.