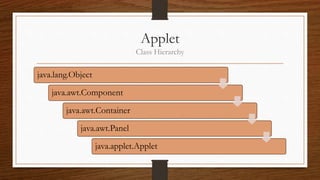
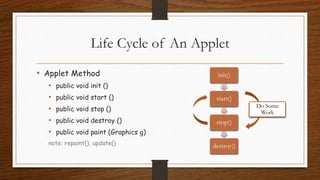
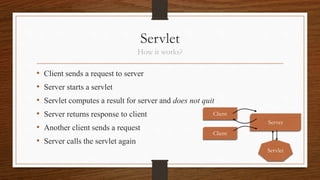
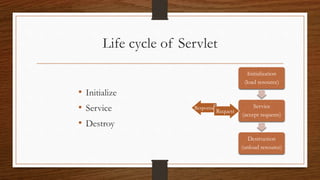
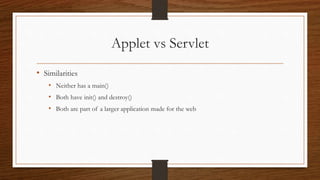
This document provides an overview of applets and servlets, comparing their key differences. It defines applets as small Java programs embedded in web pages that provide interactive content in browsers using the Java interpreter. Servlets are server-side Java programs that dynamically generate content in response to client requests, allowing servers to handle multiple clients concurrently. The document outlines the lifecycles of applets and servlets, including their initialization, processing, and destruction methods. It concludes that the main differences are that applets run on clients while servlets run on servers, and servlets handle HTTP requests to dynamically generate pages rather than provide static content like applets.