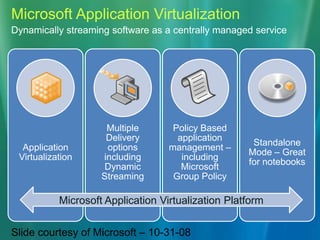
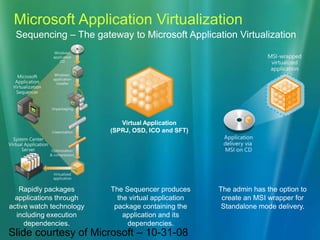
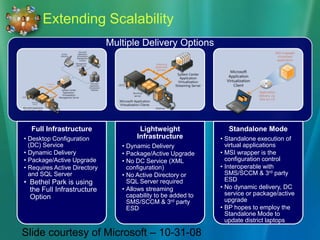
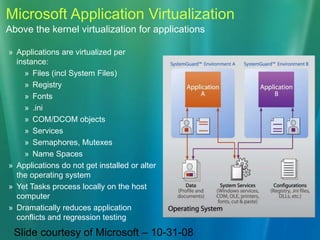
This document discusses the concept of application virtualization, particularly focusing on Microsoft's solution for deploying applications without traditional installations. It outlines the benefits and challenges of using Microsoft Application Virtualization, including cost and licensing details, as well as compatibility with various operating systems. Additionally, it highlights the sequencer's role in packaging applications for virtualization and the potential impact on application management in educational settings.


![What is Application Virtualization?According to Wikipedia: “Application virtualization is an umbrella term that describes software technologies that improve portability, manageability and compatibility of applications by encapsulating them from the underlying operating system on which they are executed. A fully virtualized application is not installed in the traditional sense [1], although it is still executed as if it is. The application is fooled at runtime into believing that it is directly interfacing with the original operating system and all the resources managed by it, when in reality it is not. Application virtualization differs from operating system virtualization in that in the latter case, the whole operating system is virtualized rather than only specific applications.“ Ardence is an example of operating system virtualization](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appv-12621496885514-phpapp01/85/App-V-3-320.jpg)