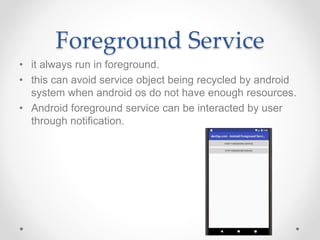
- Foreground services run in the foreground and can avoid being recycled by the Android system when low on resources. They can be interacted with by the user through notifications.
- Started services run indefinitely in the background until stopped or destroyed by the system. They are launched by other app components like activities or broadcast receivers.
- Bound services can return results and interact with the component that started them, unlike started services. They allow sending data to the launching component.
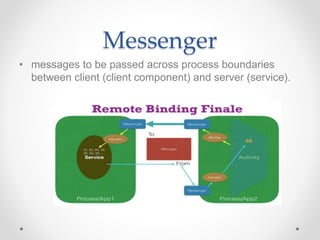
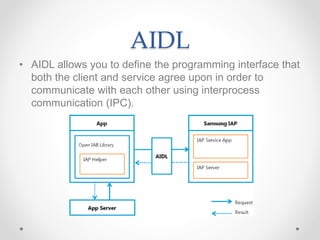
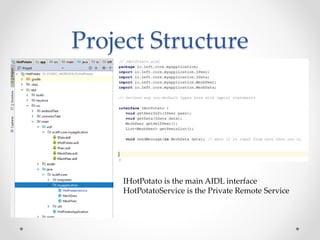
- IPC allows two processes or apps to communicate by passing data. On Android, processes cannot access each other's memory directly, so IPC provides channels for communication using messengers or AIDL.