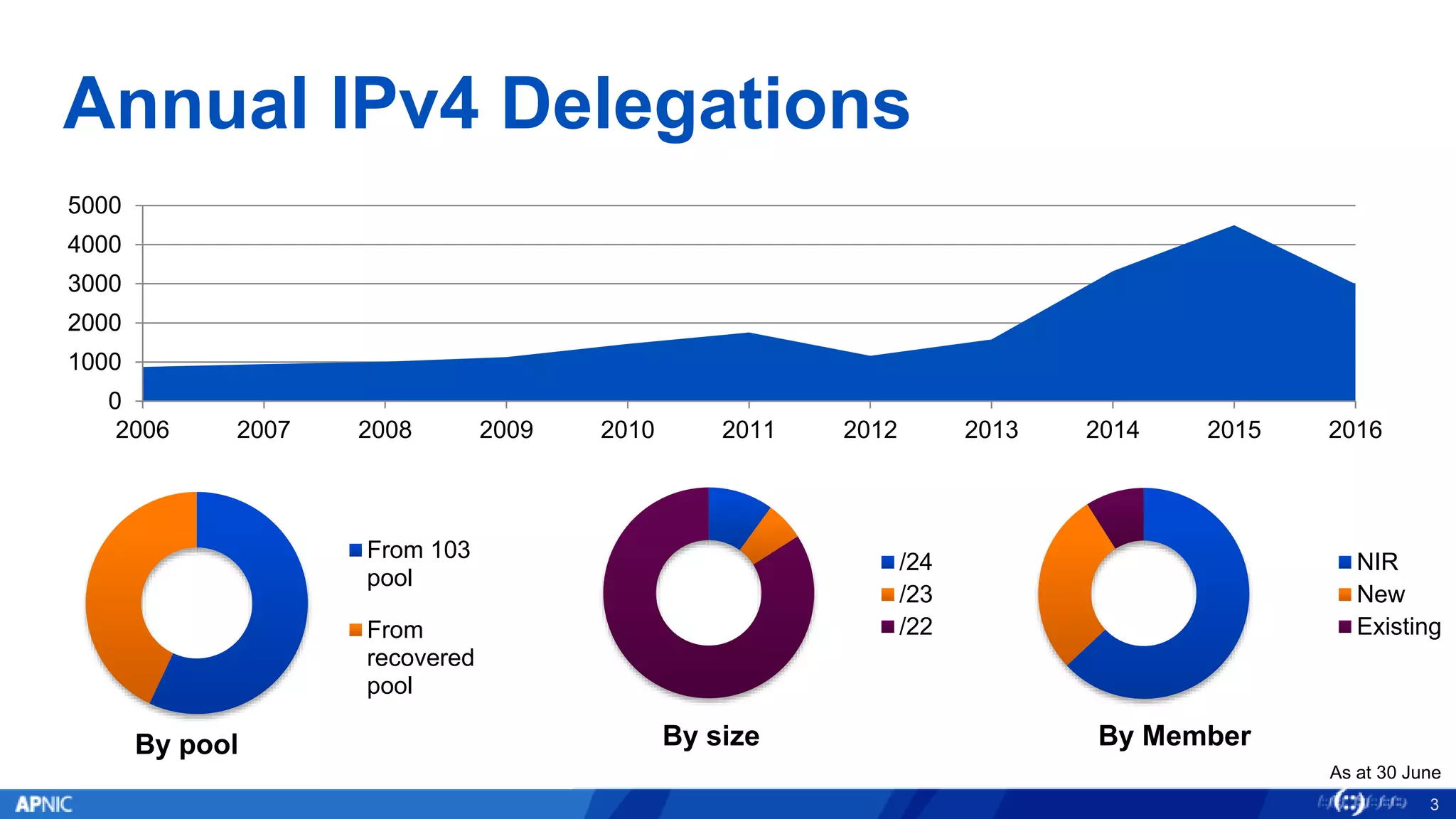
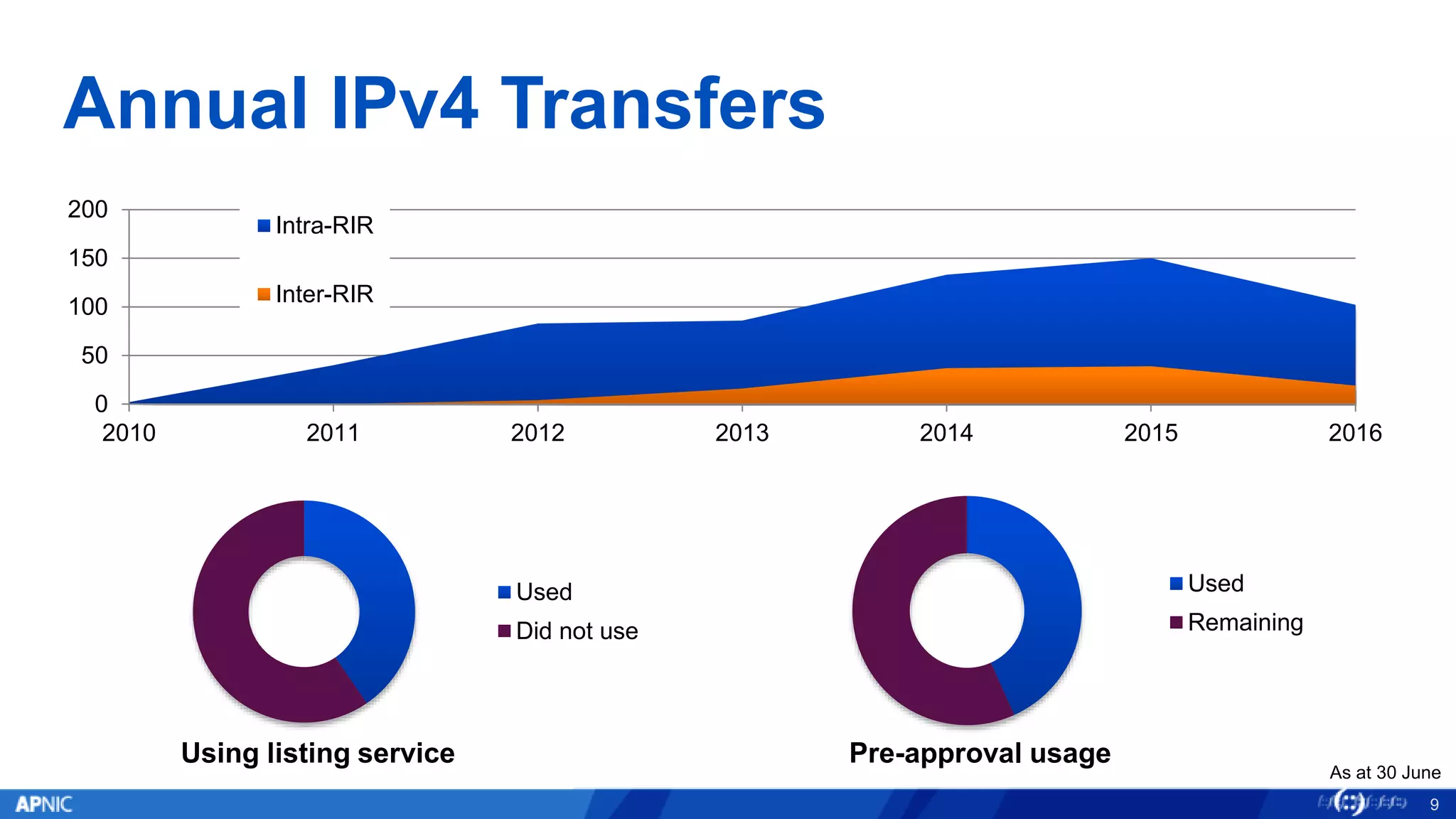
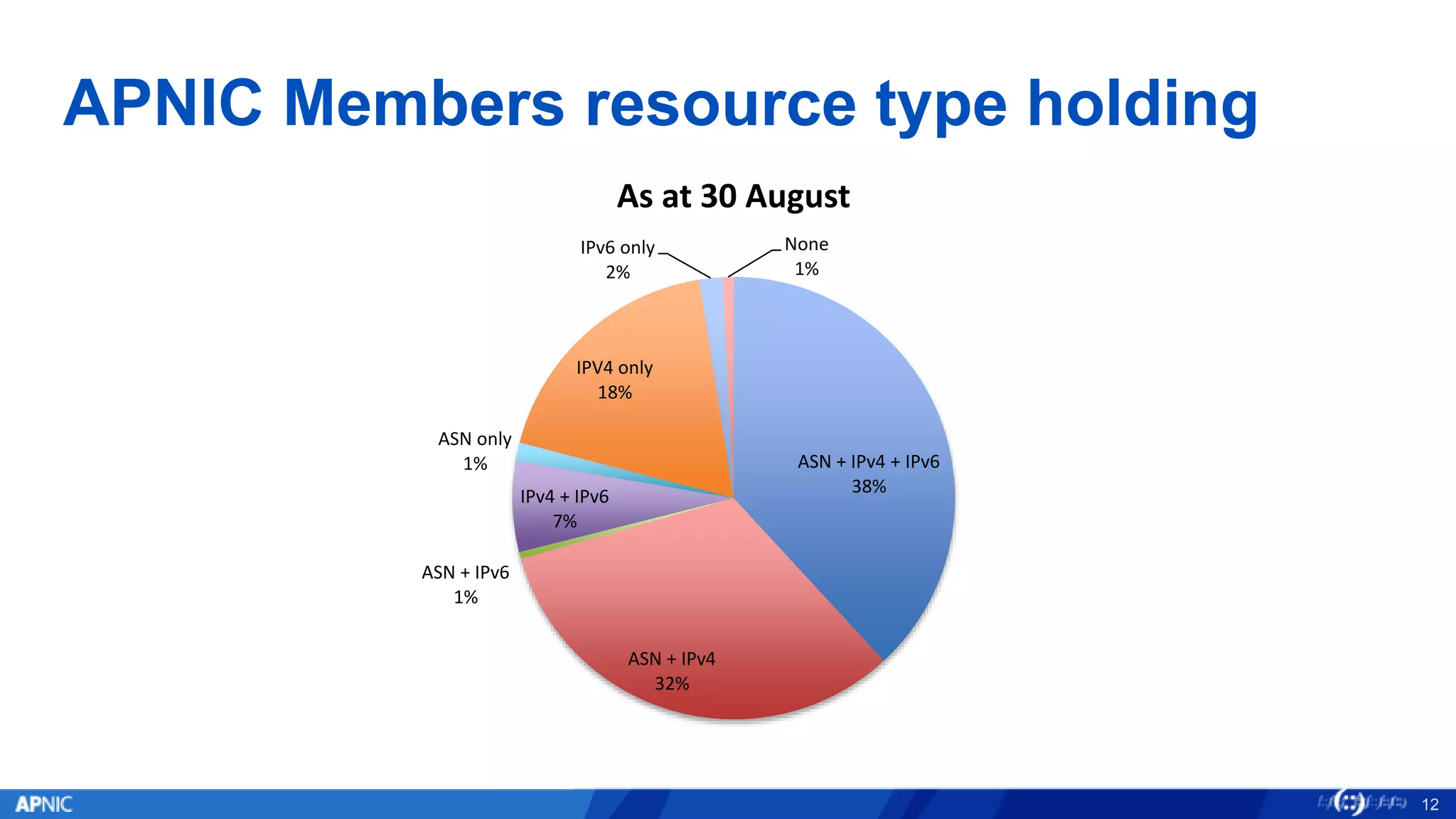
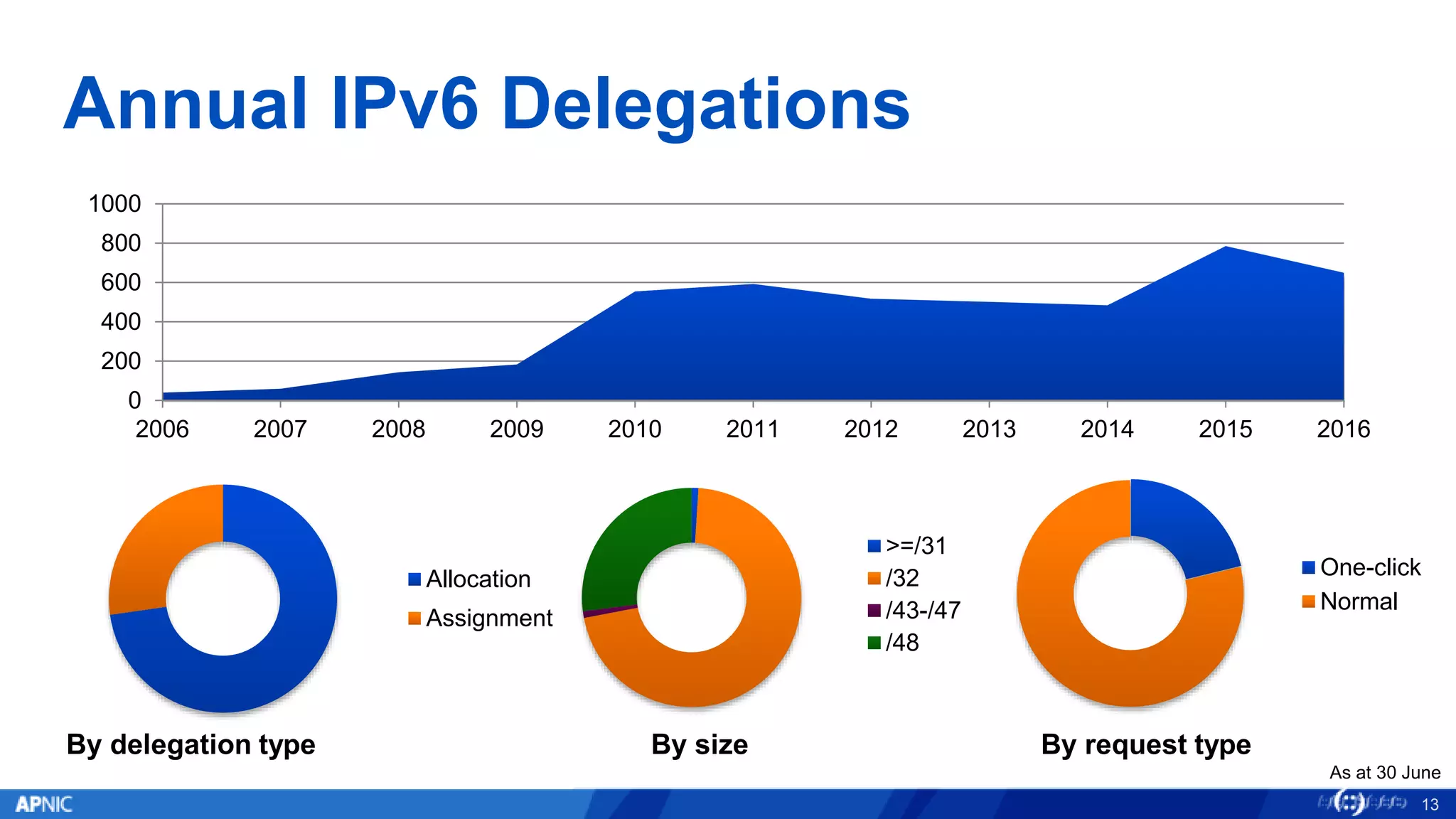
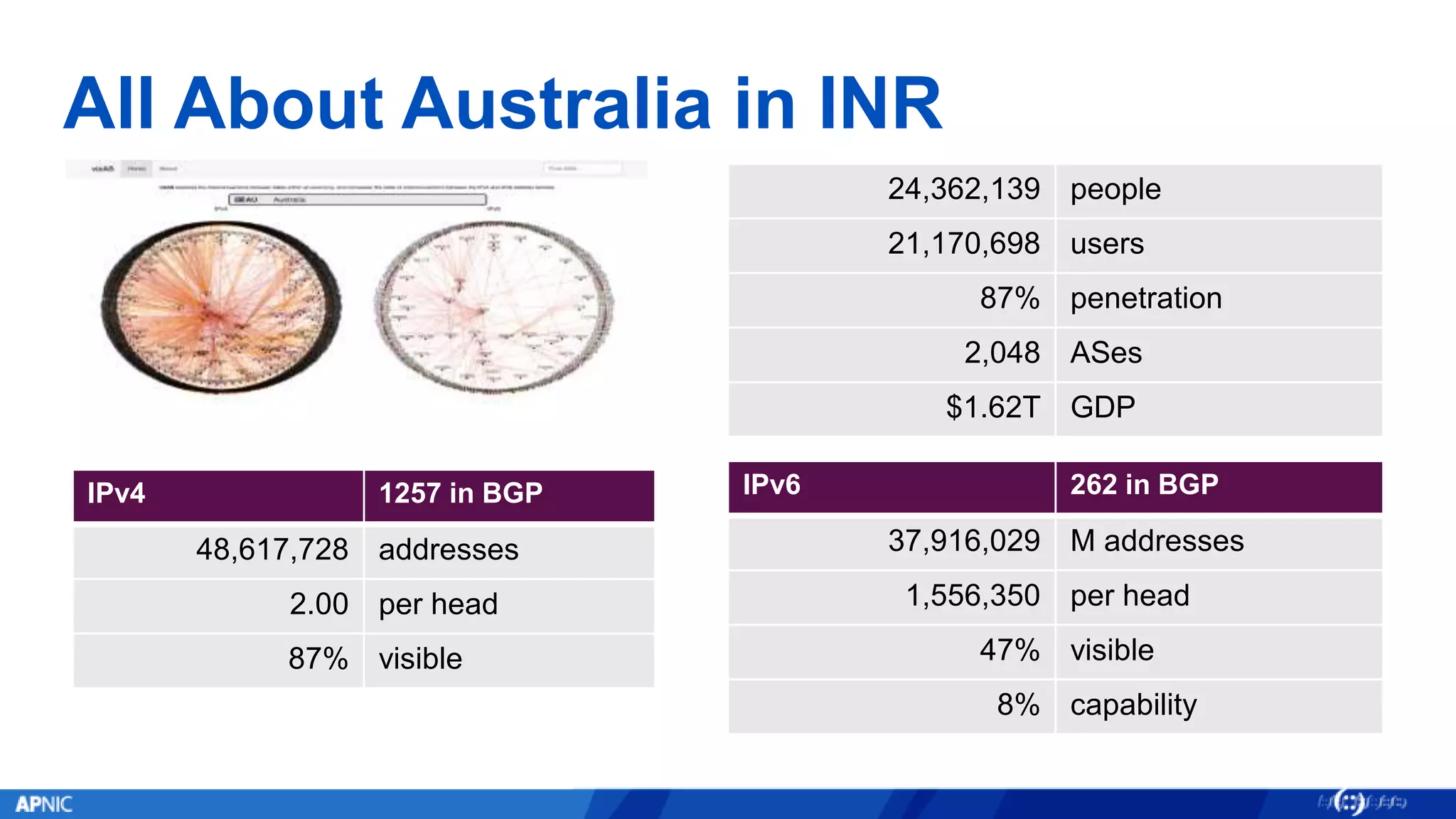
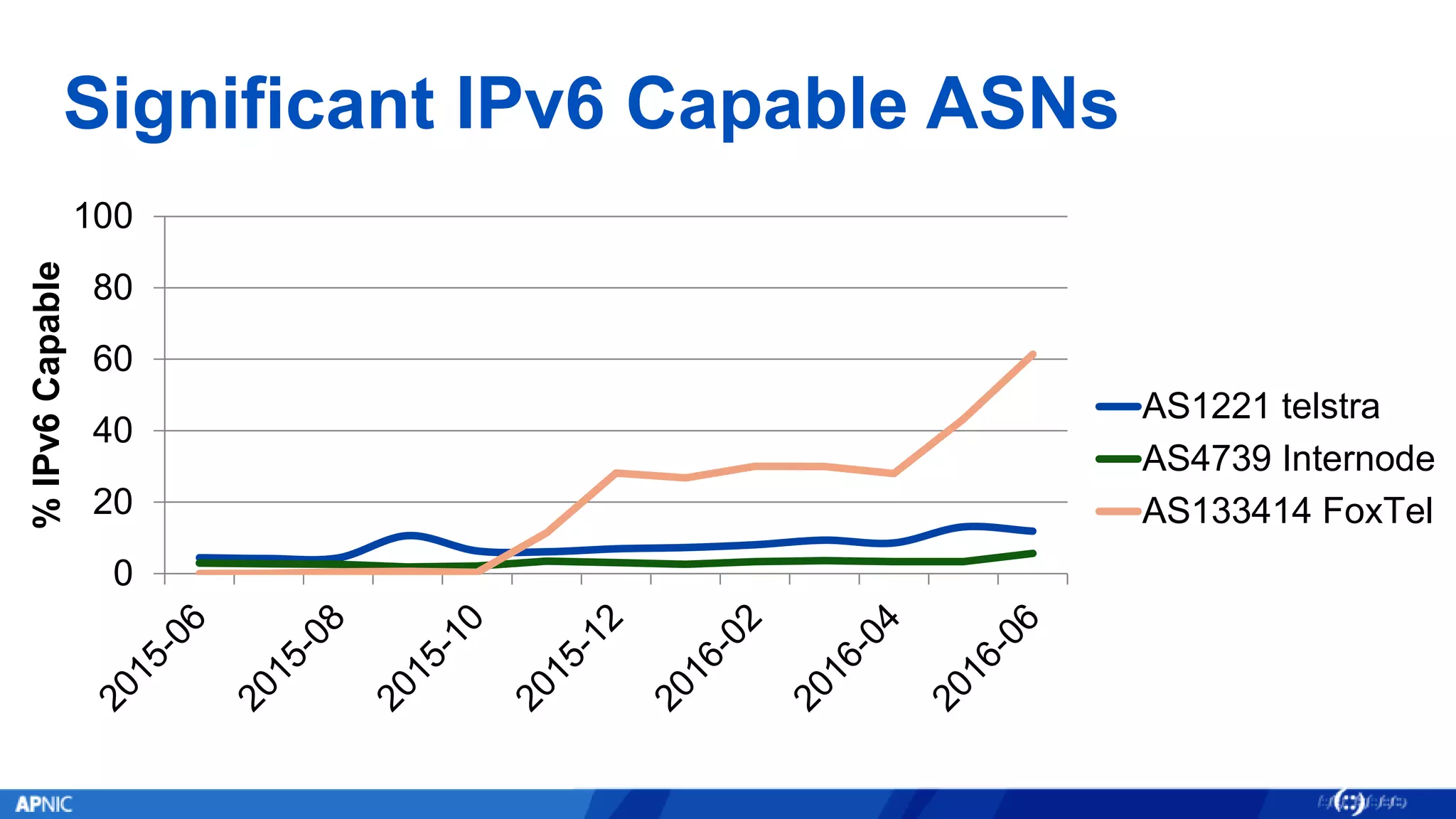
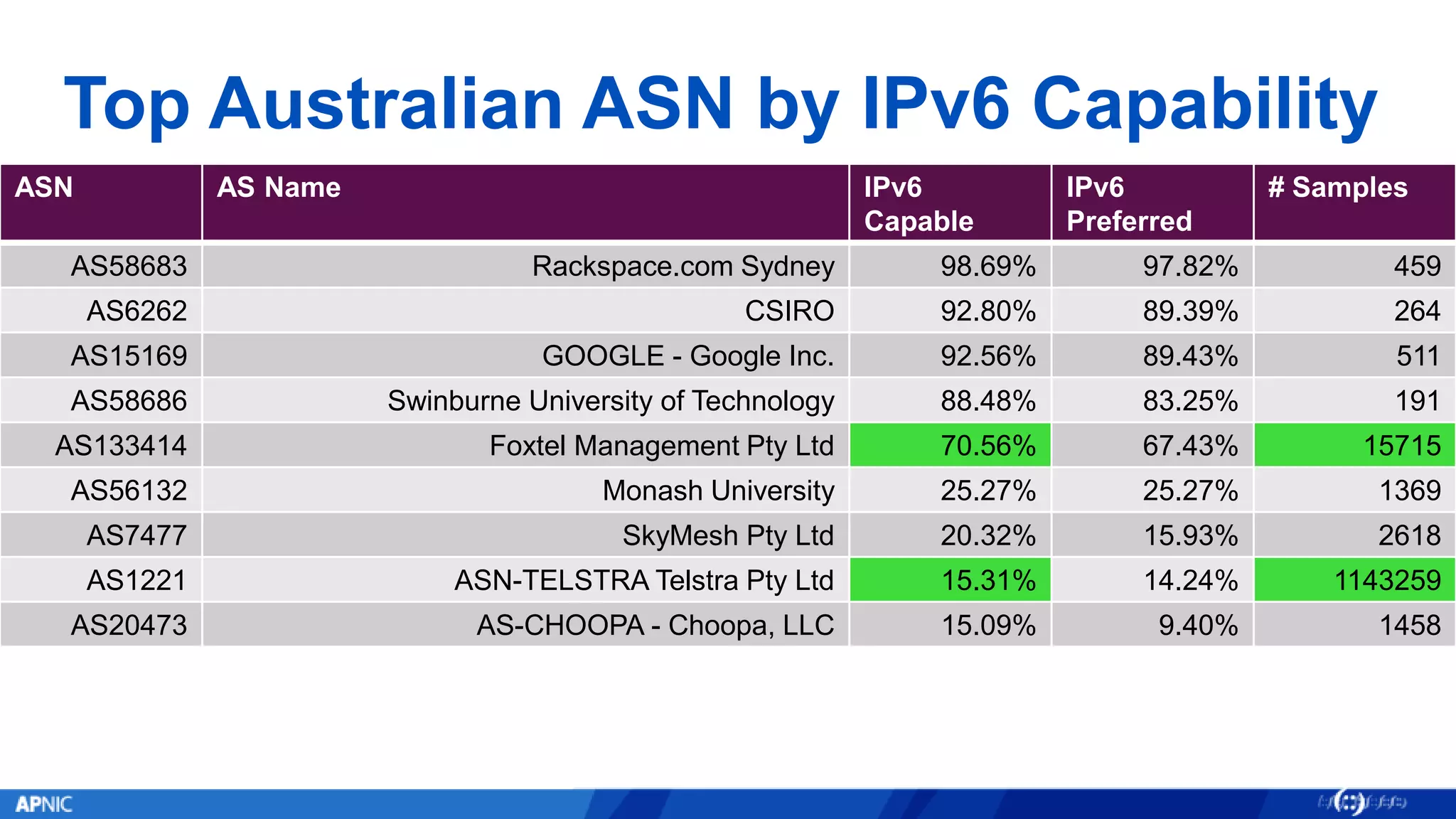
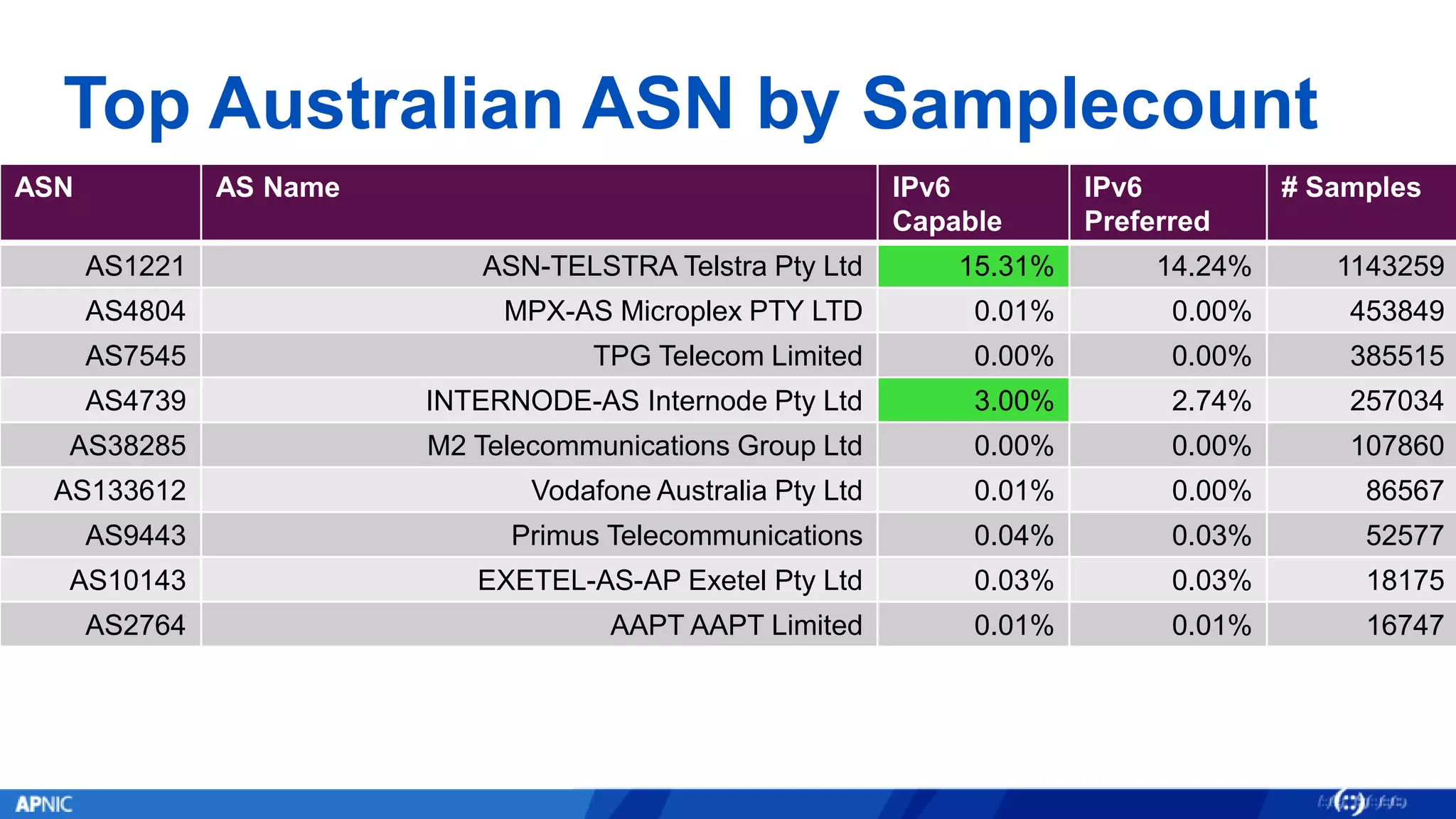
The document outlines the trends in IPv4 delegations and the introduction of an IPv4 waiting list due to the exhaustion of the IPv4 address supply. Various regional internet registries have different policies regarding IPv4 allocations and waiting lists, with the document illustrating how requests are processed. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of transitioning to IPv6 as the only viable option for accommodating the growing demand for internet addresses.