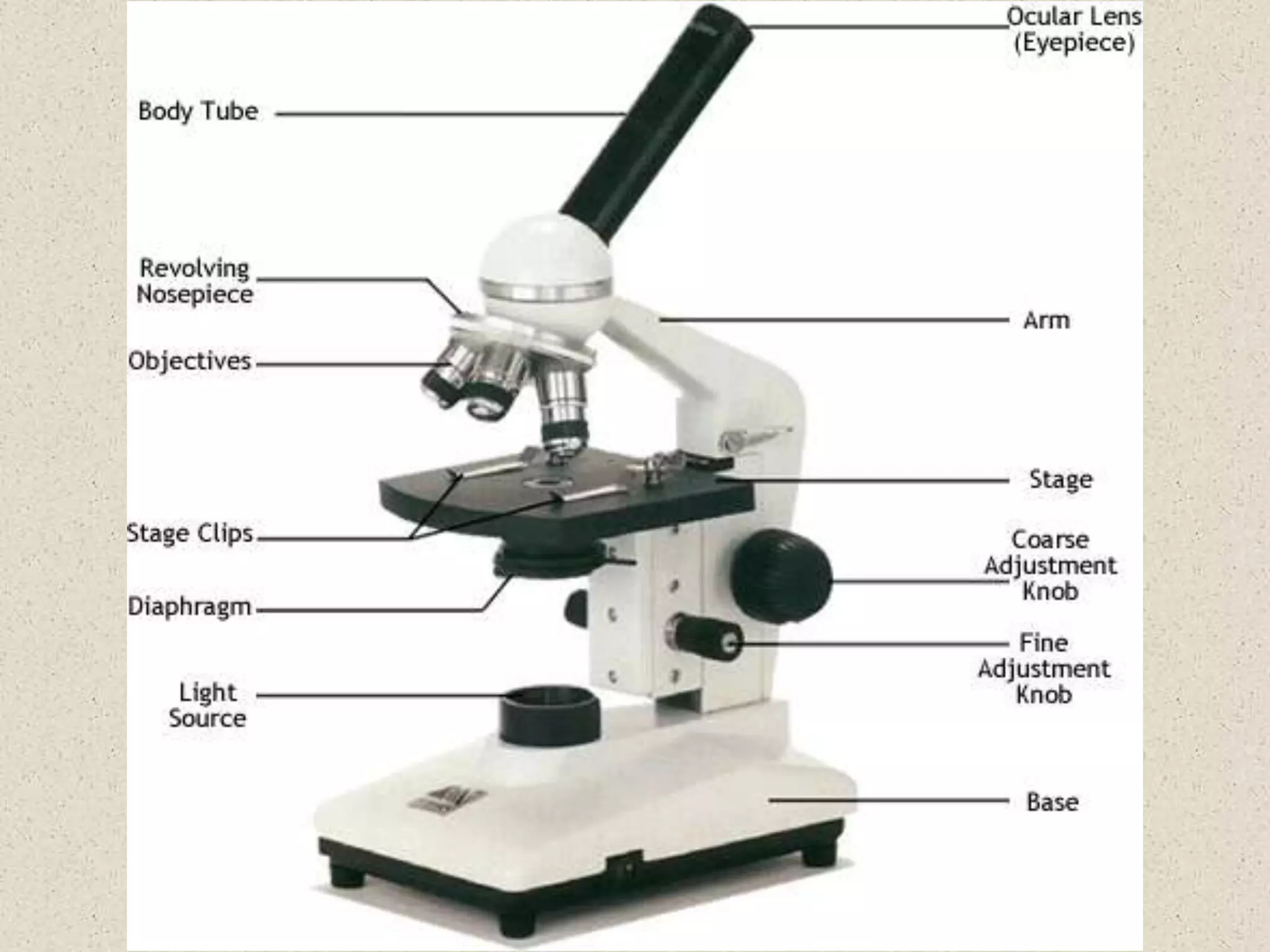
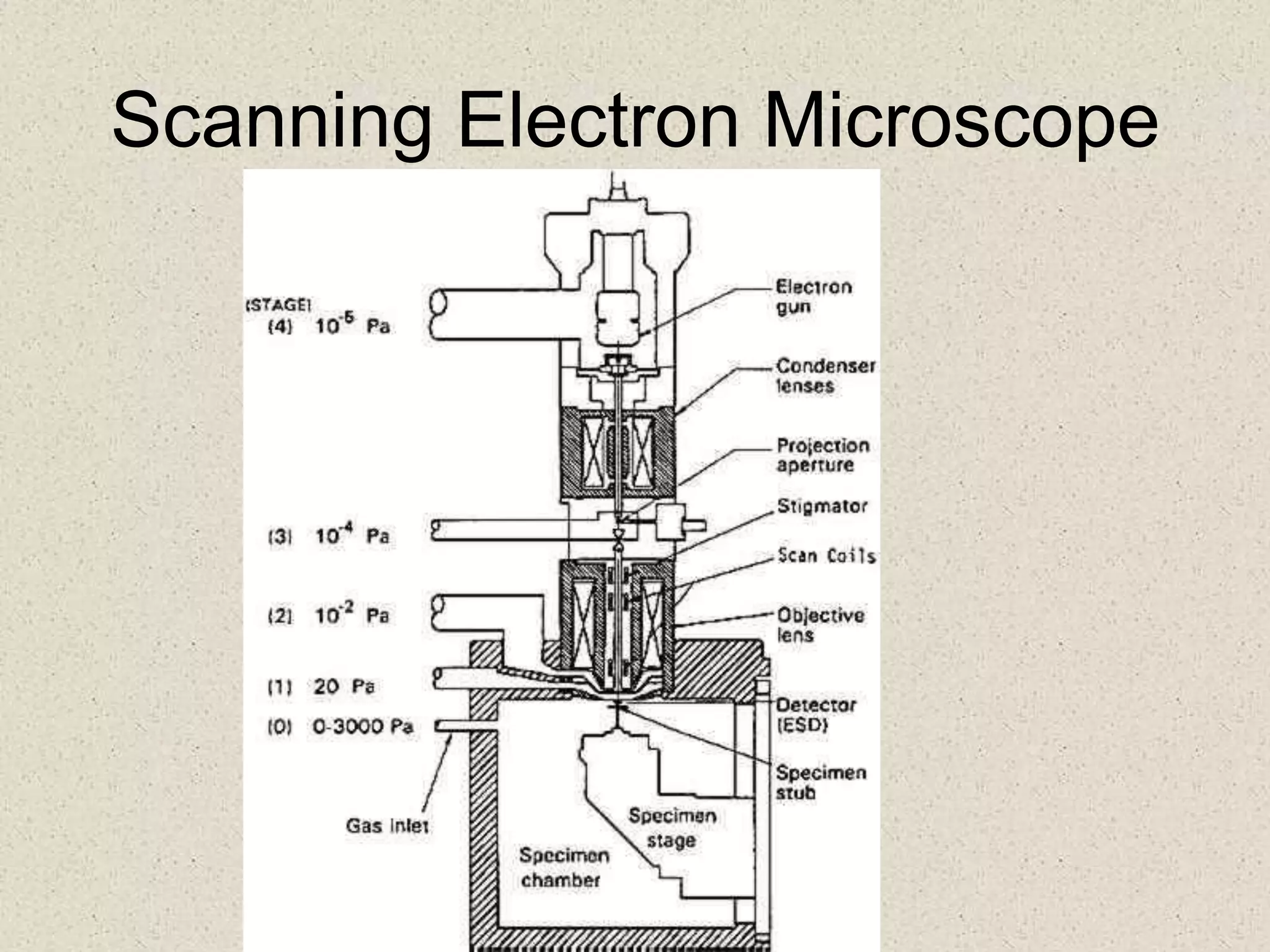
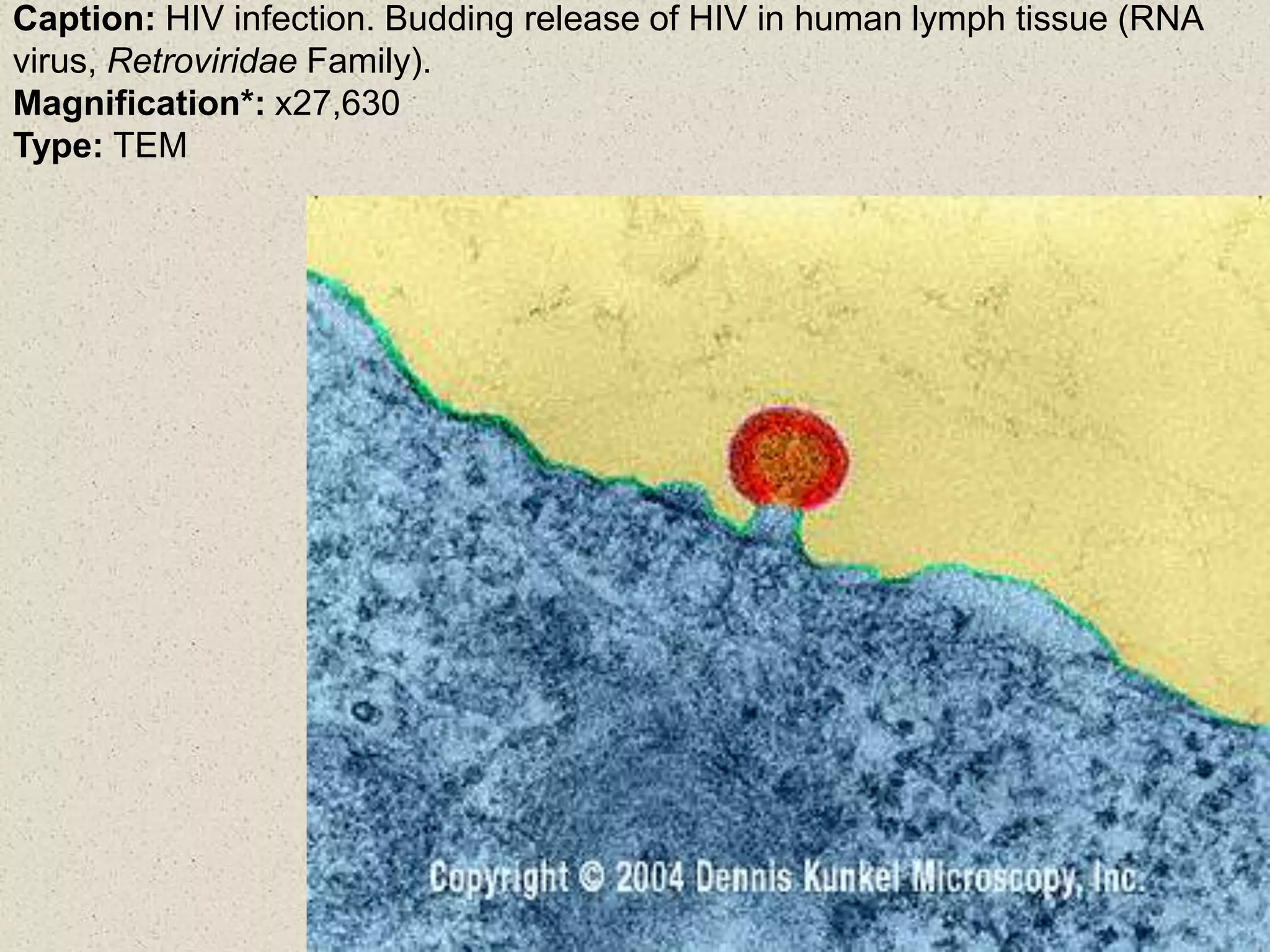
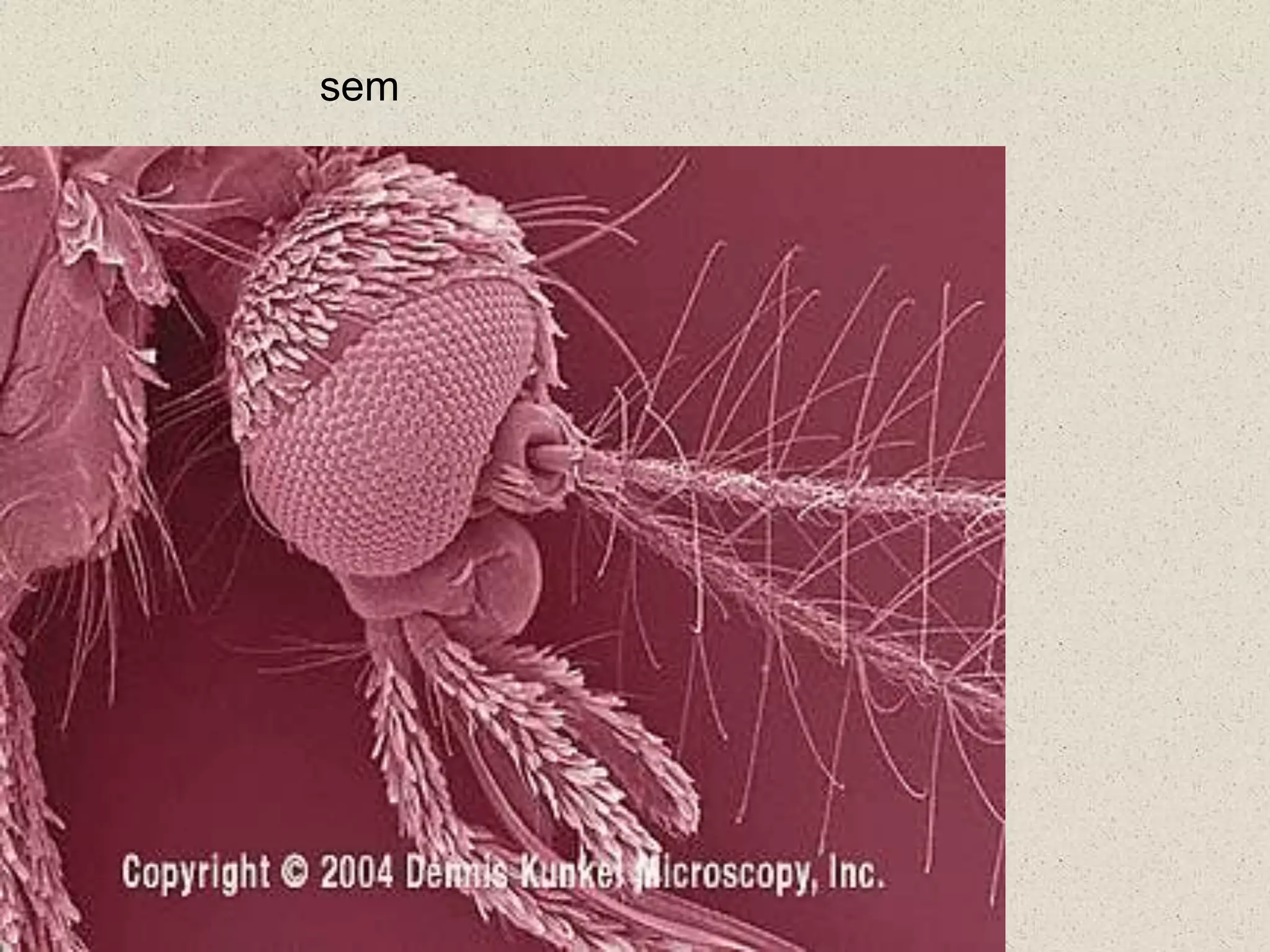
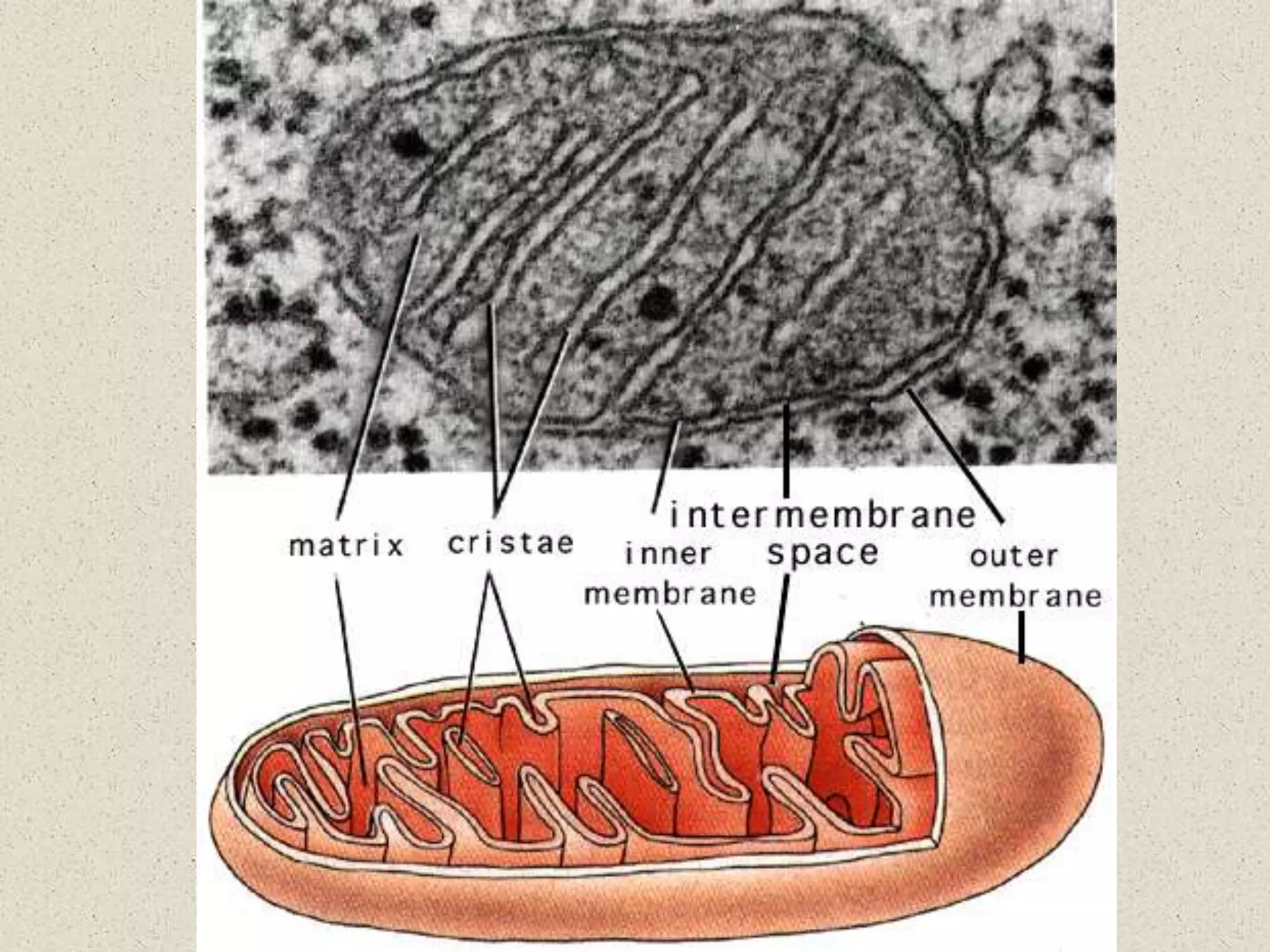
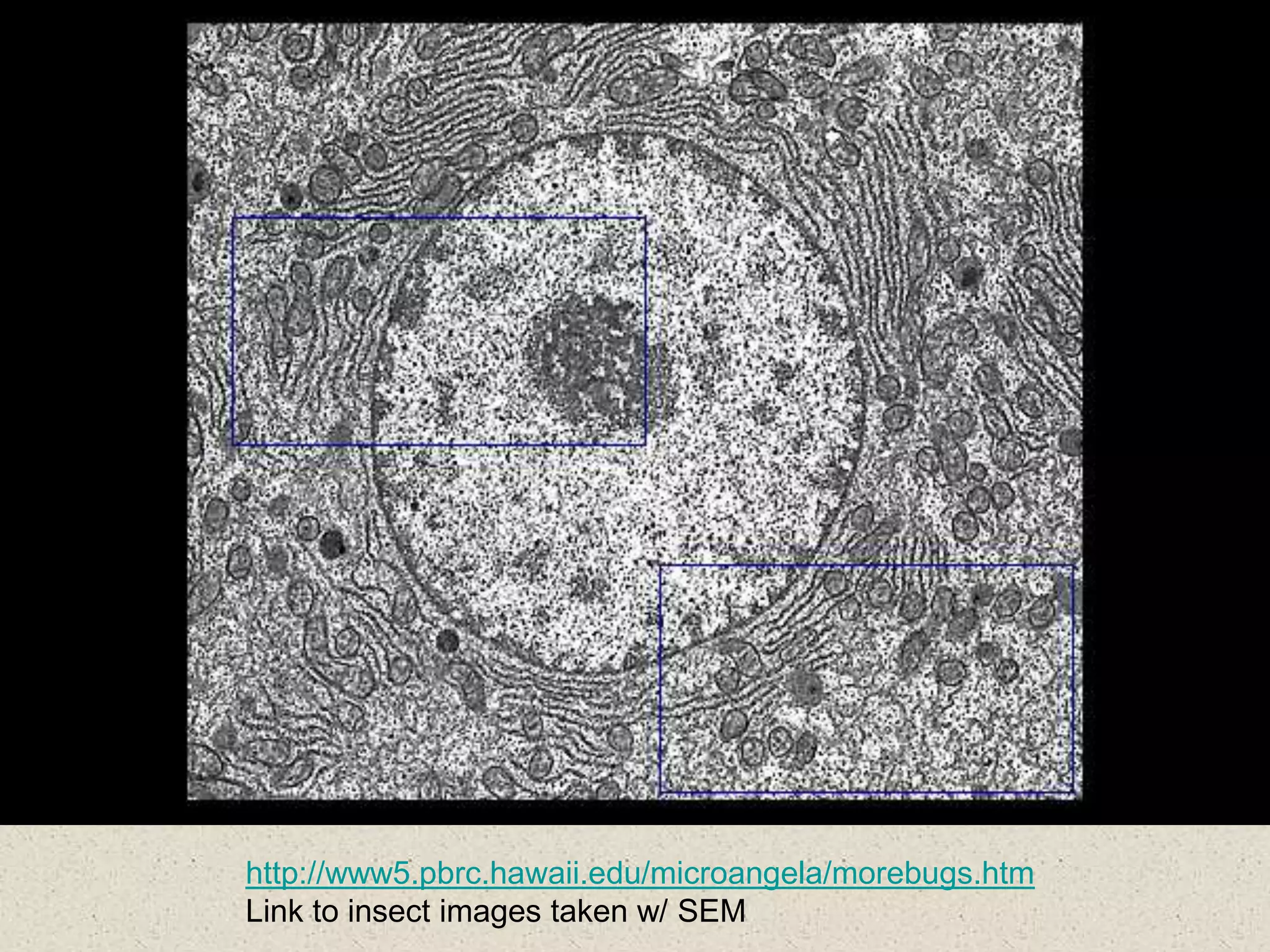
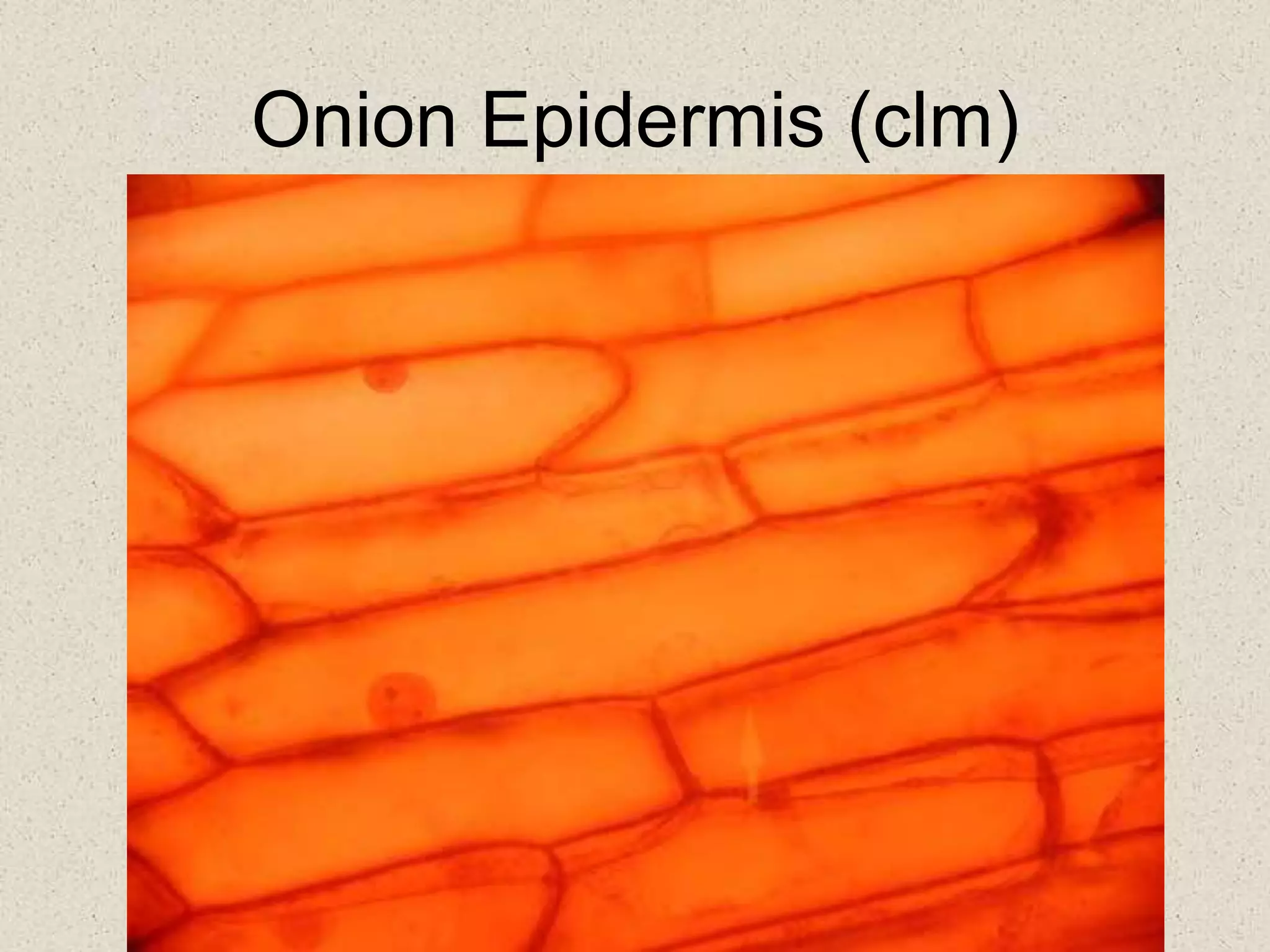
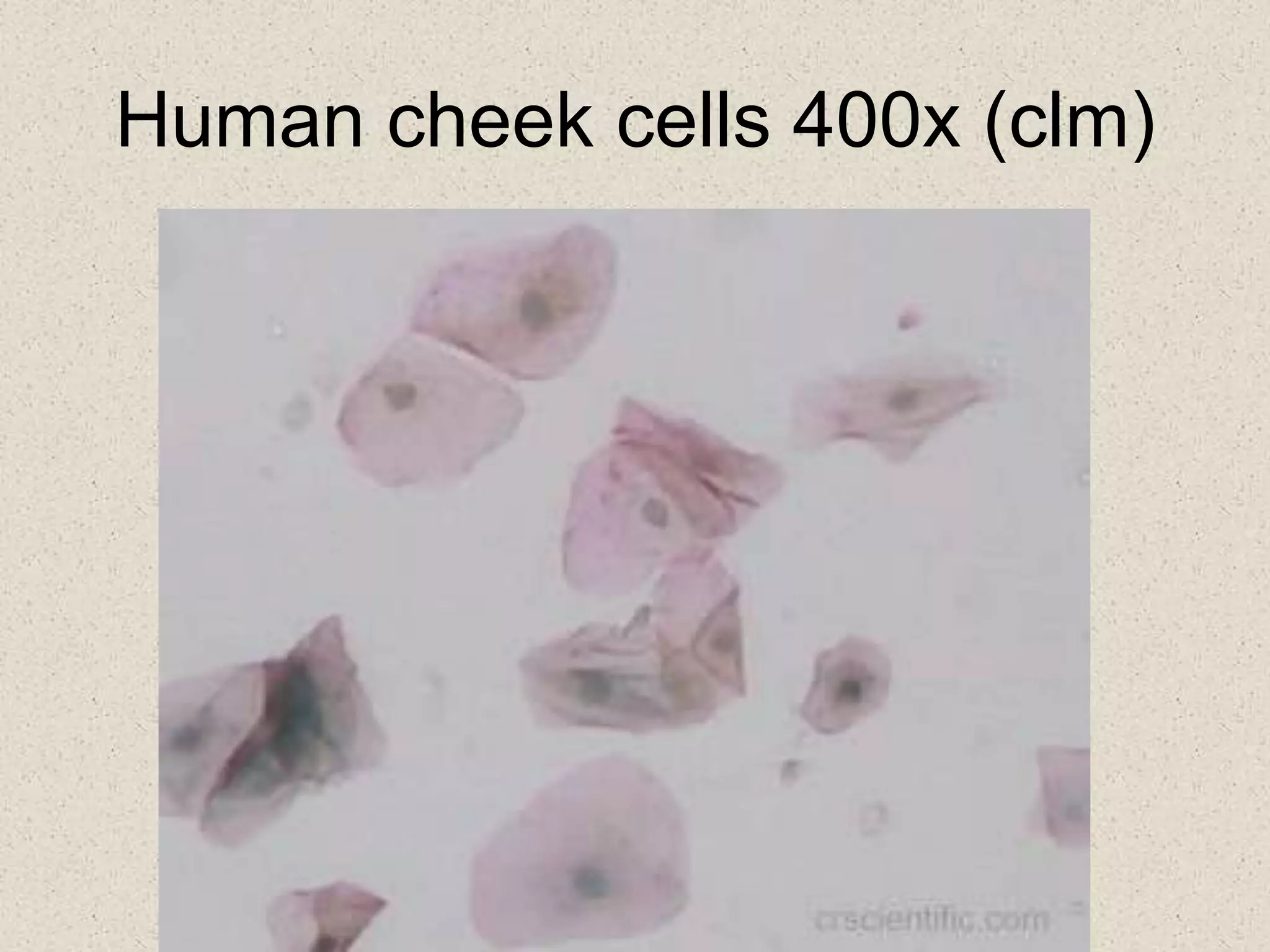
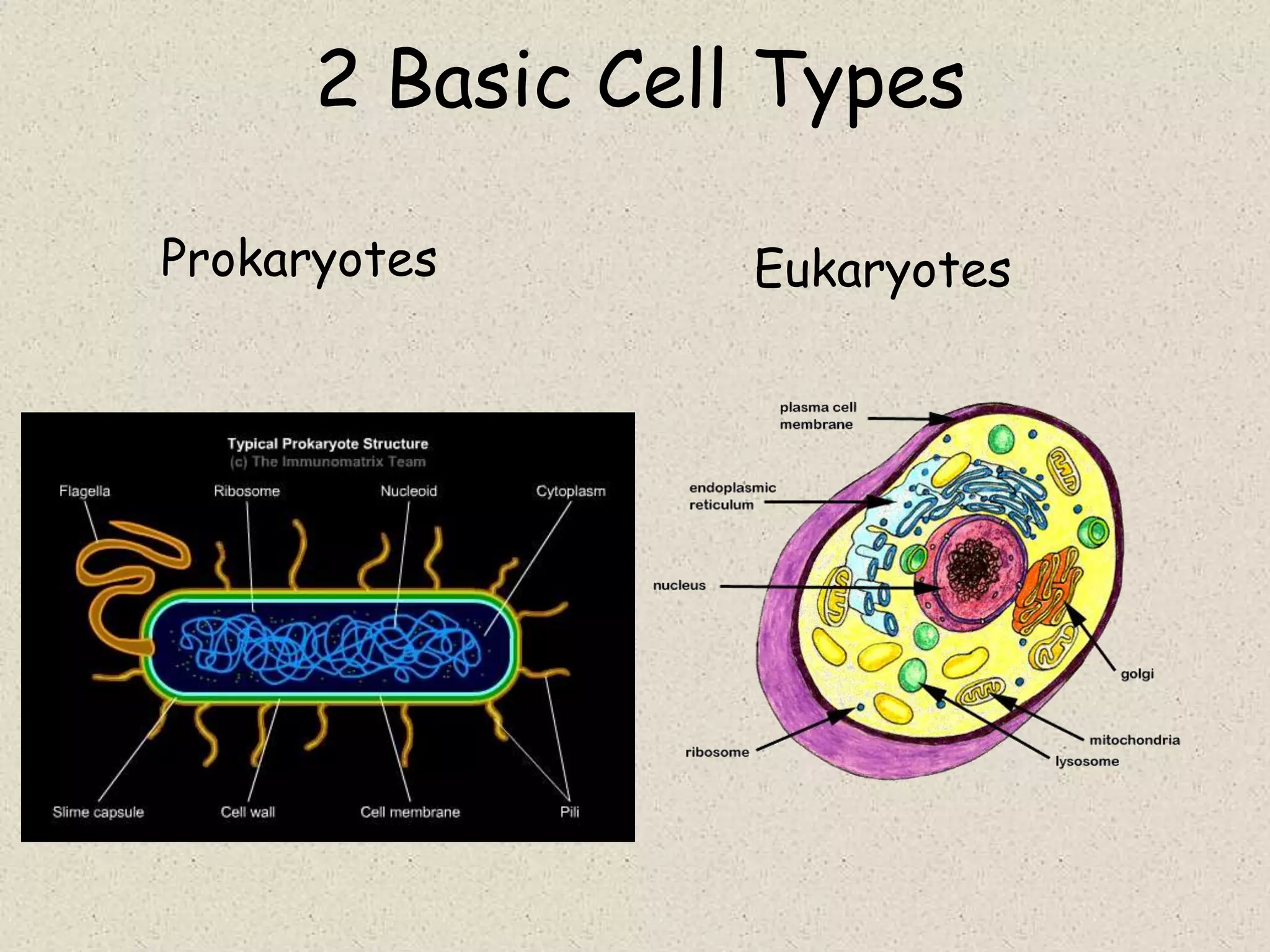
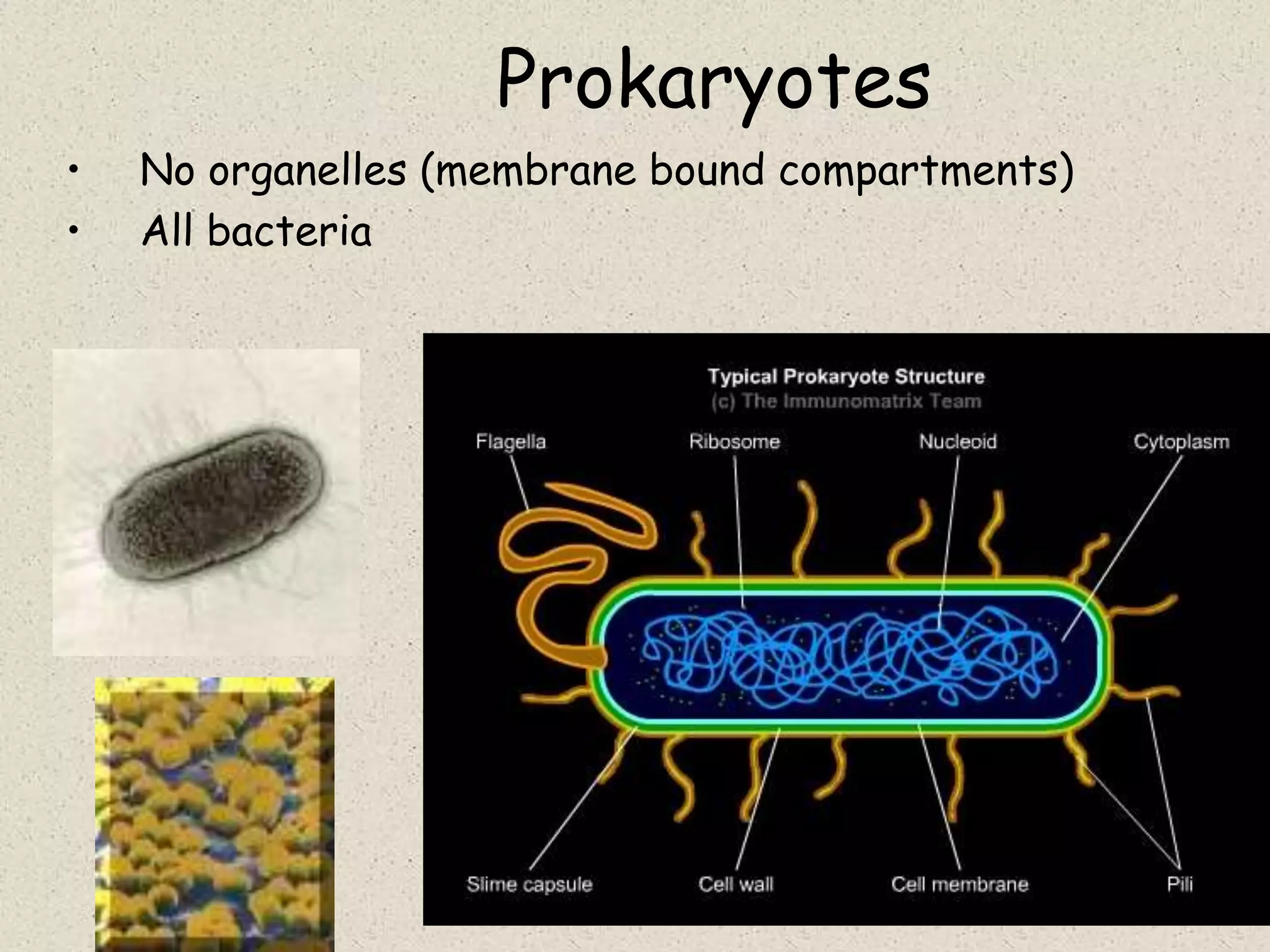
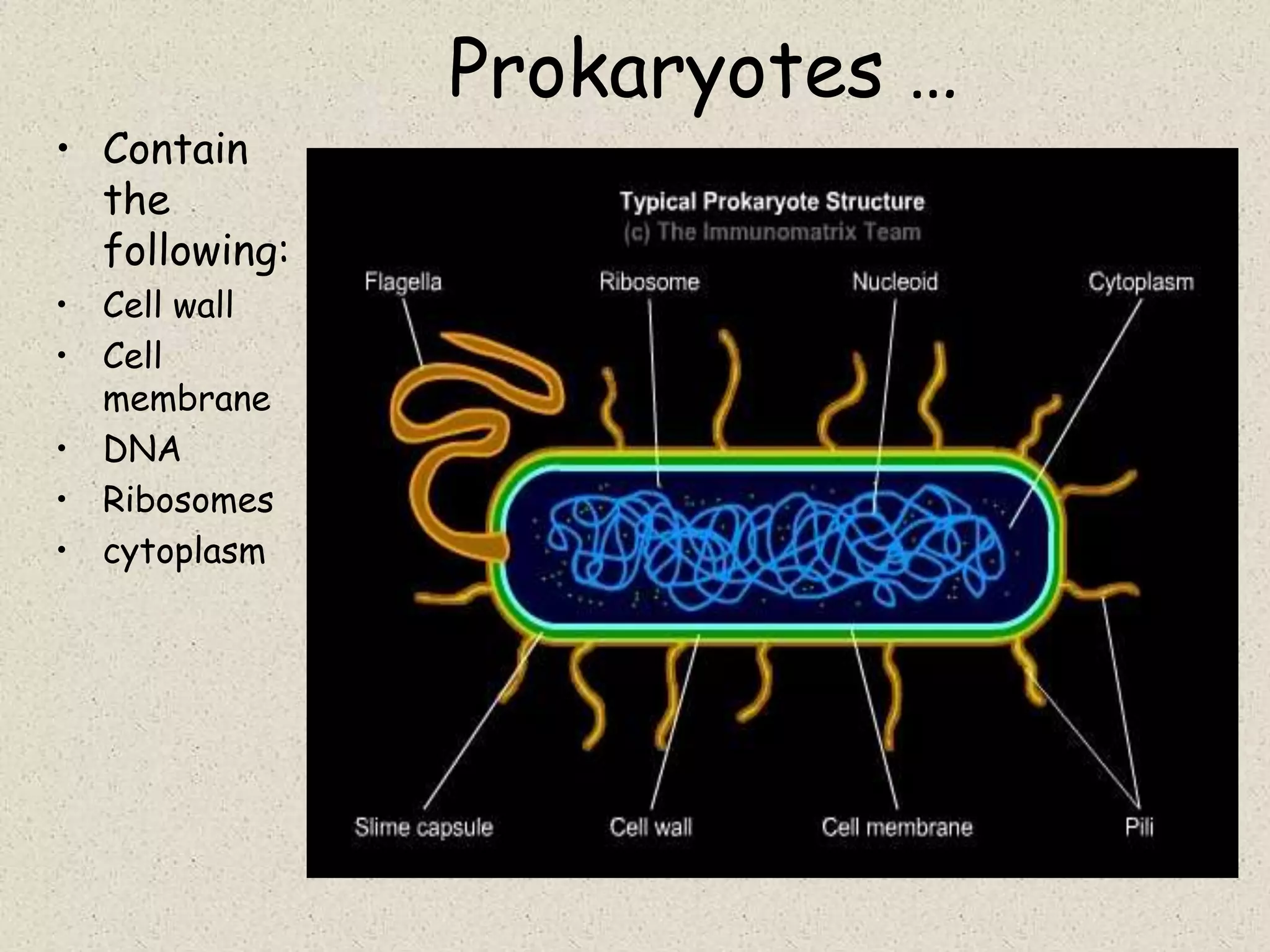
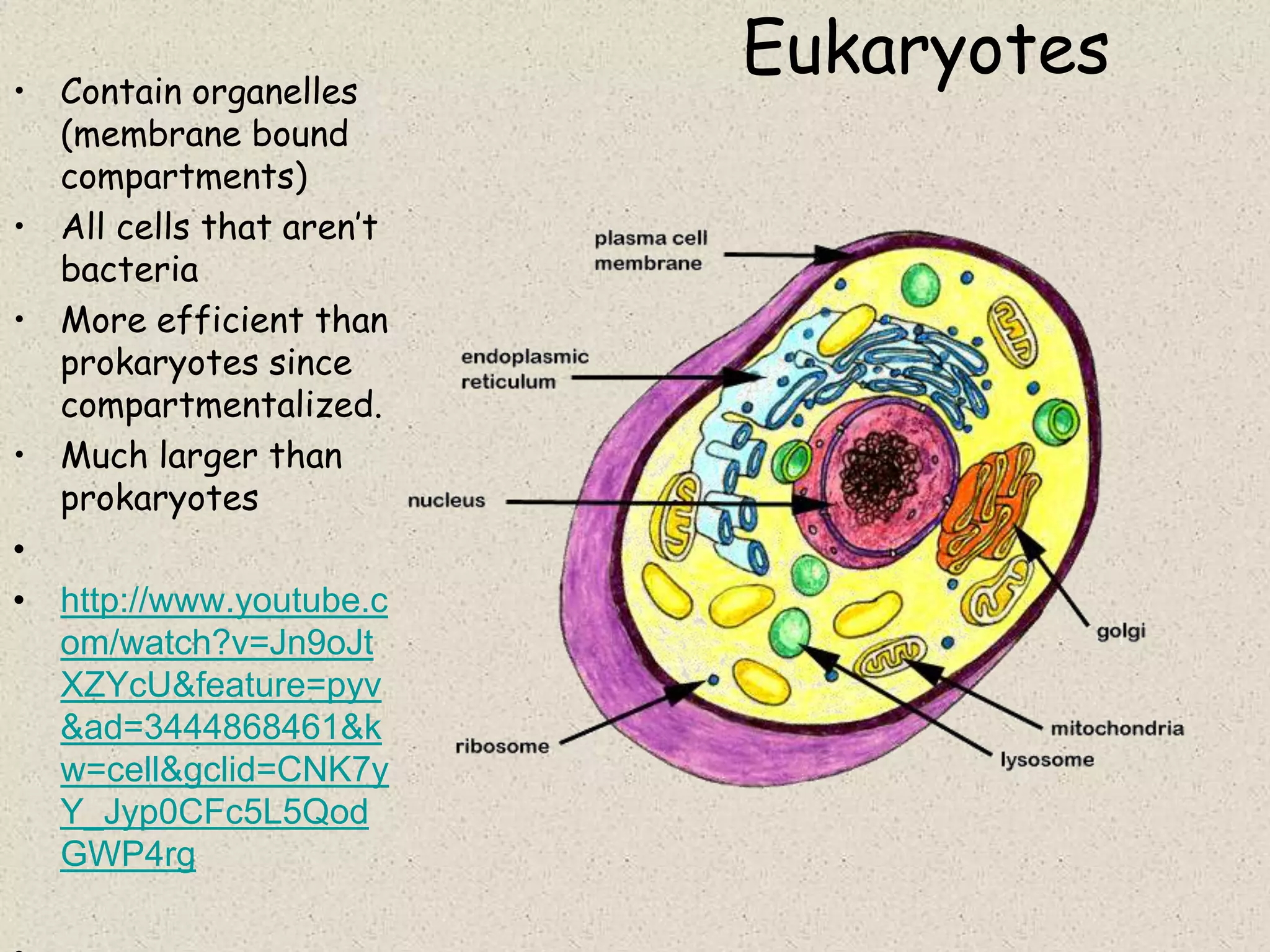
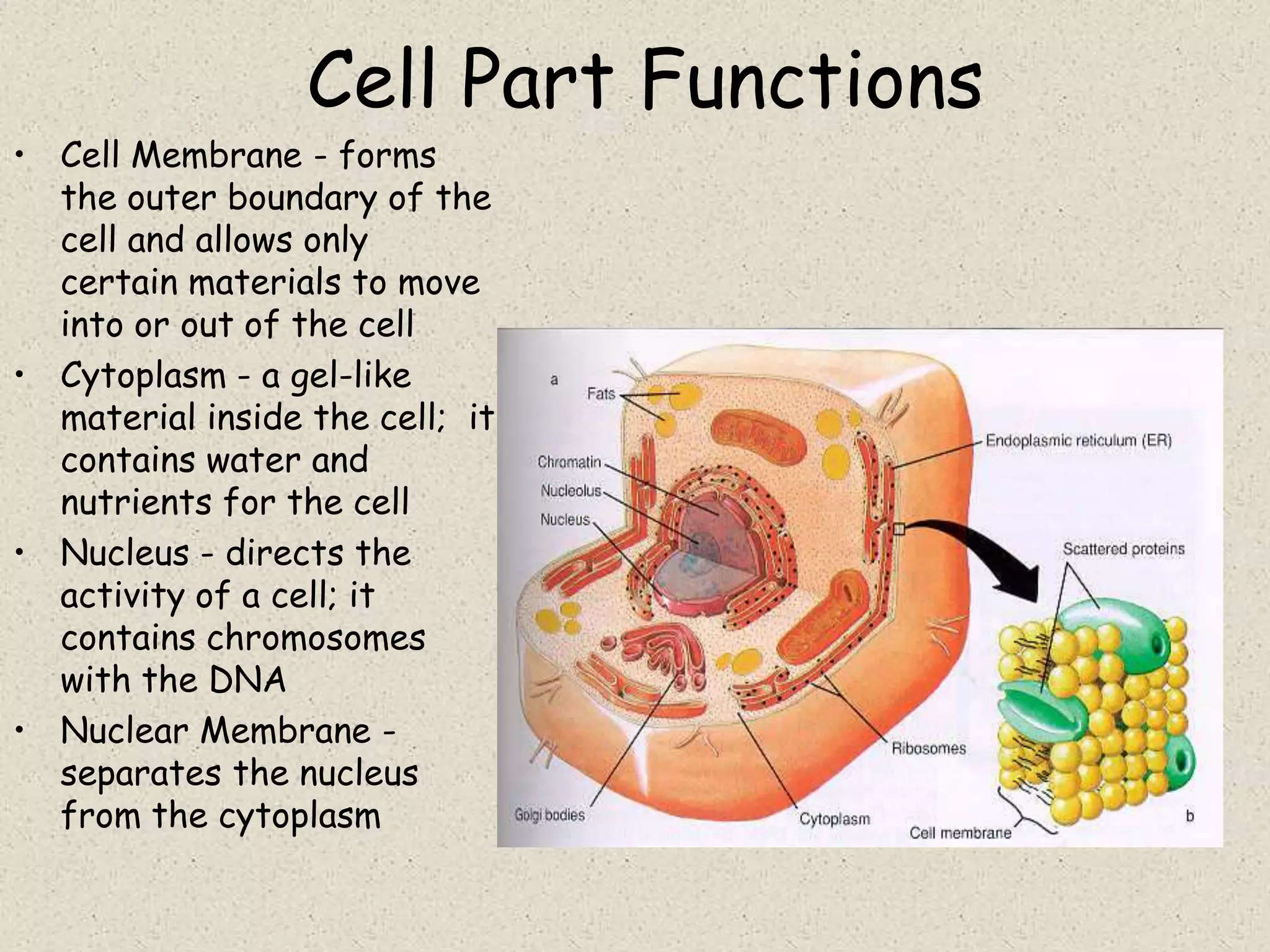
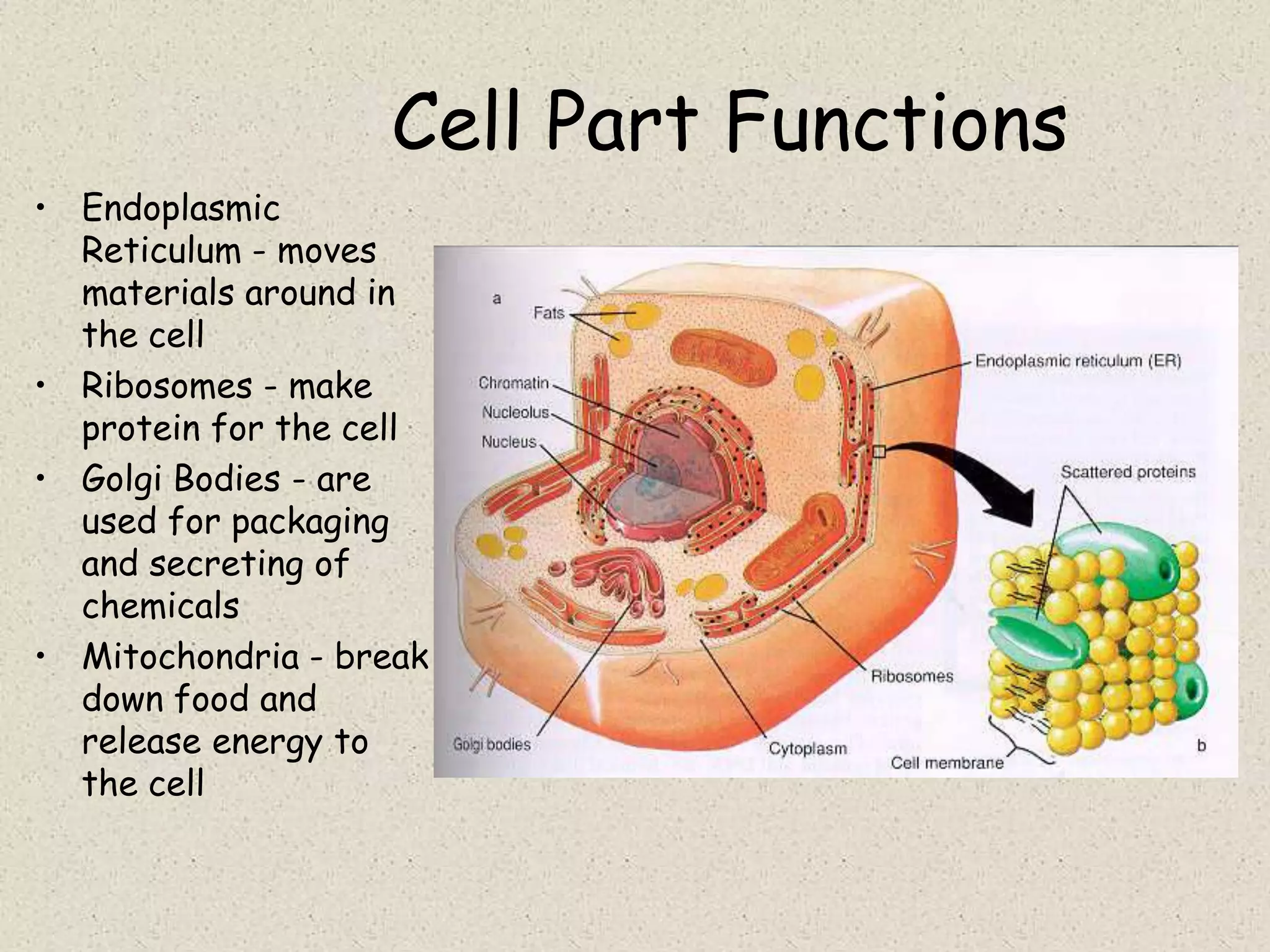
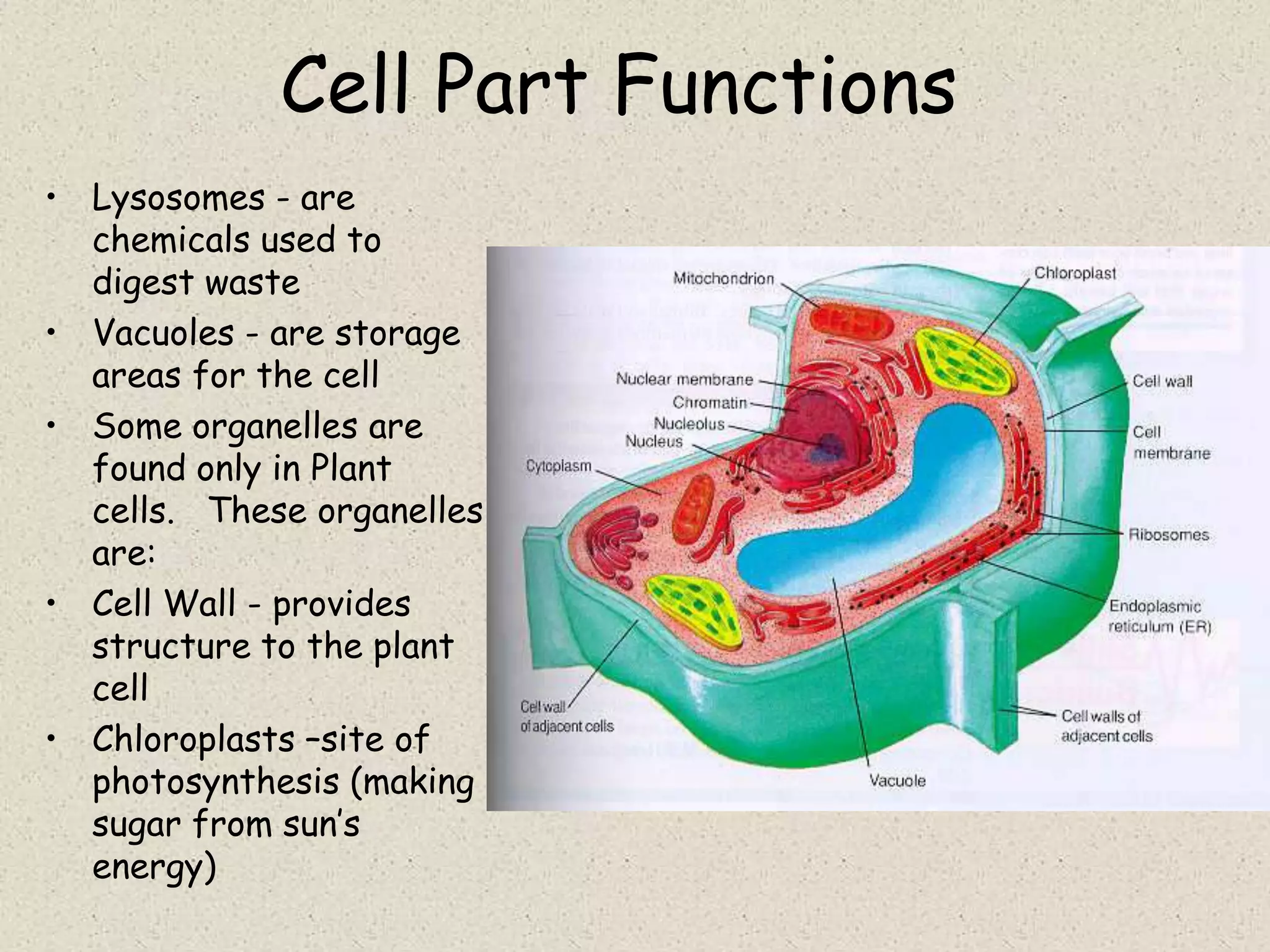
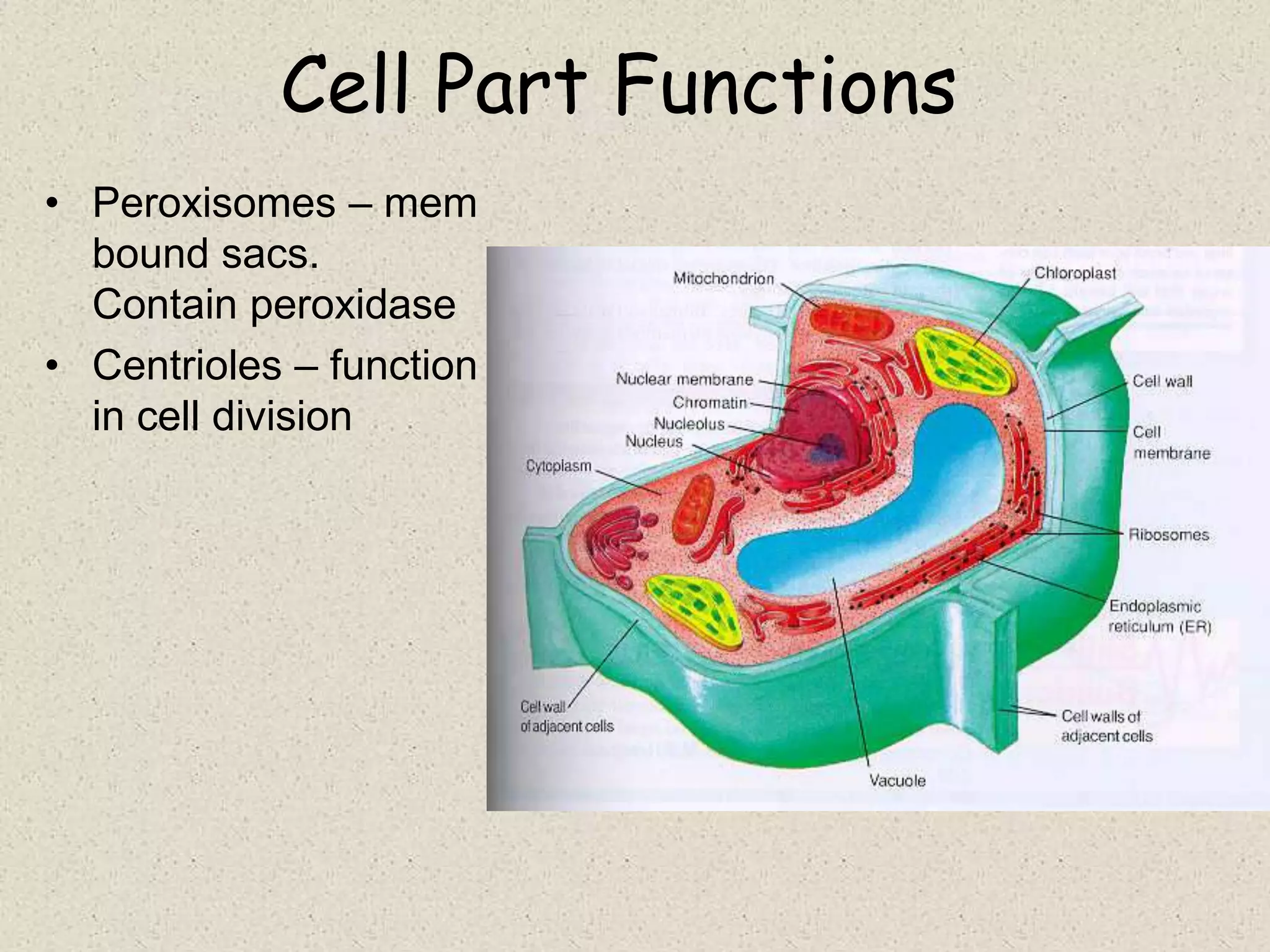
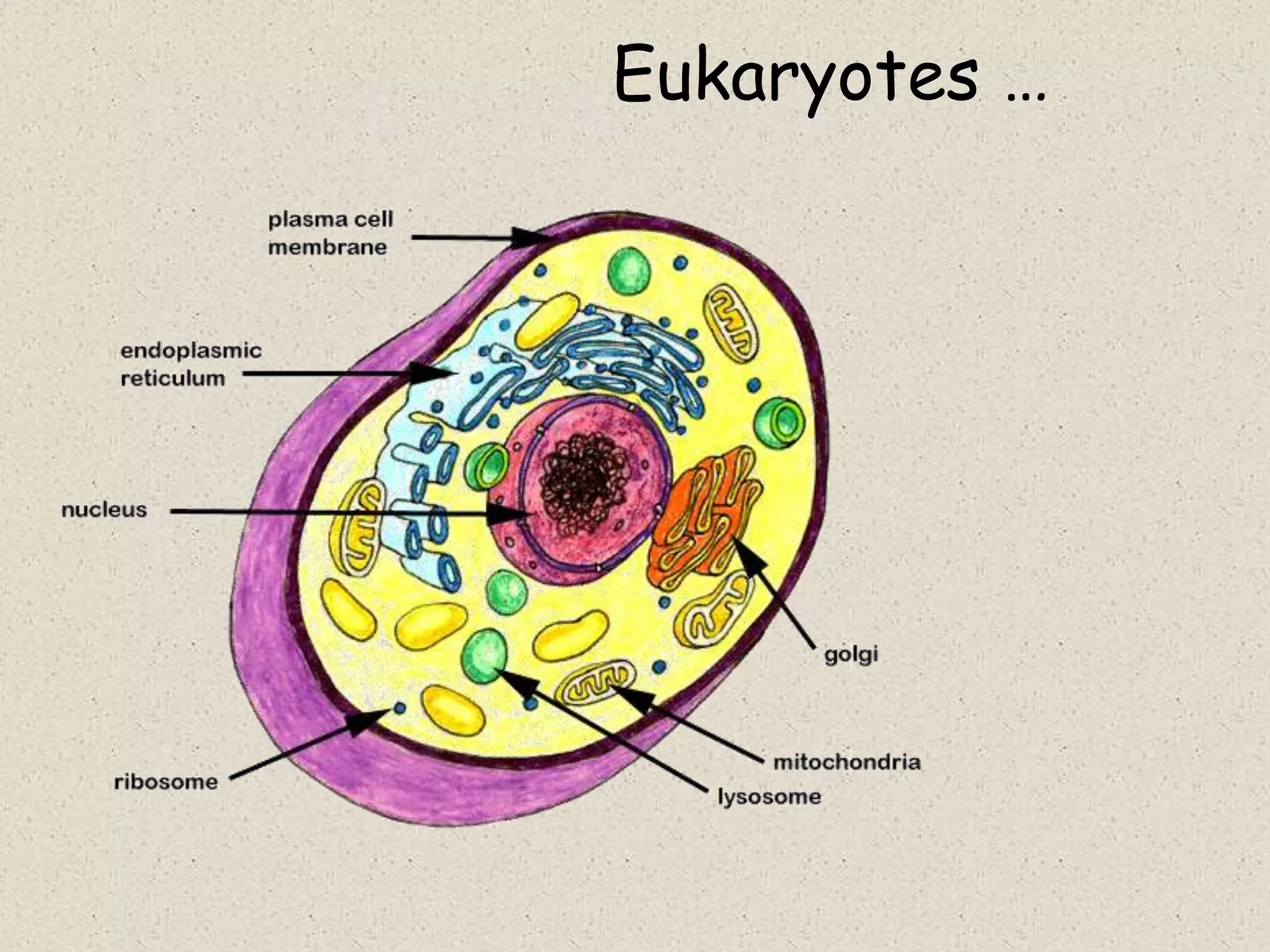
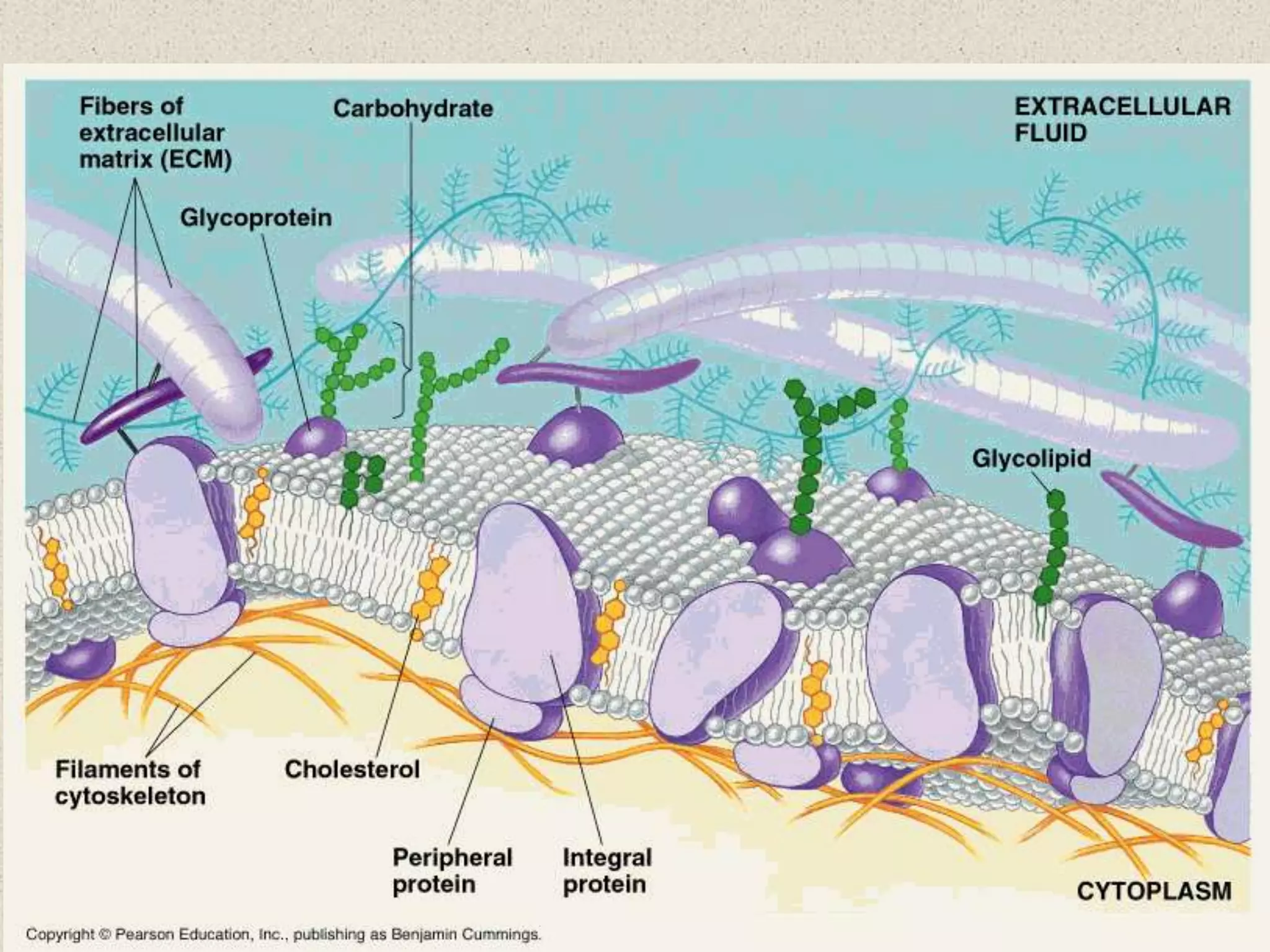
This document provides an overview of cells and cellular structures. It begins with an introduction to cells and explains that cells are the basic units of life. It then describes three types of microscopes used to view cells - light microscopes, transmission electron microscopes, and scanning electron microscopes - and notes one benefit of light microscopes. The document outlines the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and explains the importance of compartmentalization in eukaryotic cells. It provides descriptions and functions of major cellular structures and organelles found in plant and animal cells.