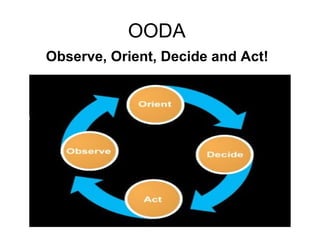
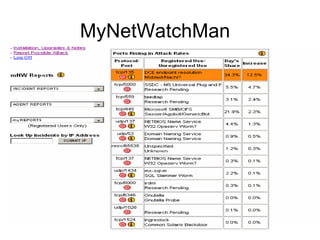
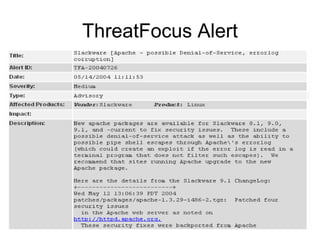
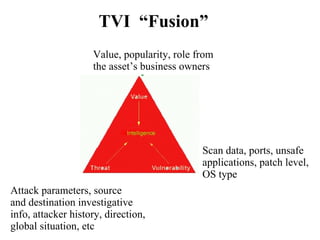
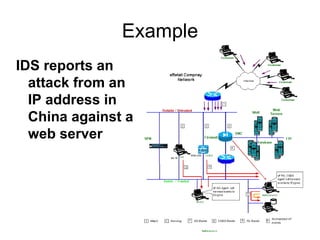
This document discusses threat and vulnerability intelligence (TVI), which is a process to collect information on threats and vulnerabilities, analyze their relevance to an organization, and determine the appropriate corrective actions. It defines threats as malicious factors and vulnerabilities as potential weaknesses. TVI aims to fuse threat and vulnerability information together and help organizations act on it. It discusses sources of threat and vulnerability data, both locally and globally, as well as existing technologies that can be used and enhanced for TVI purposes.