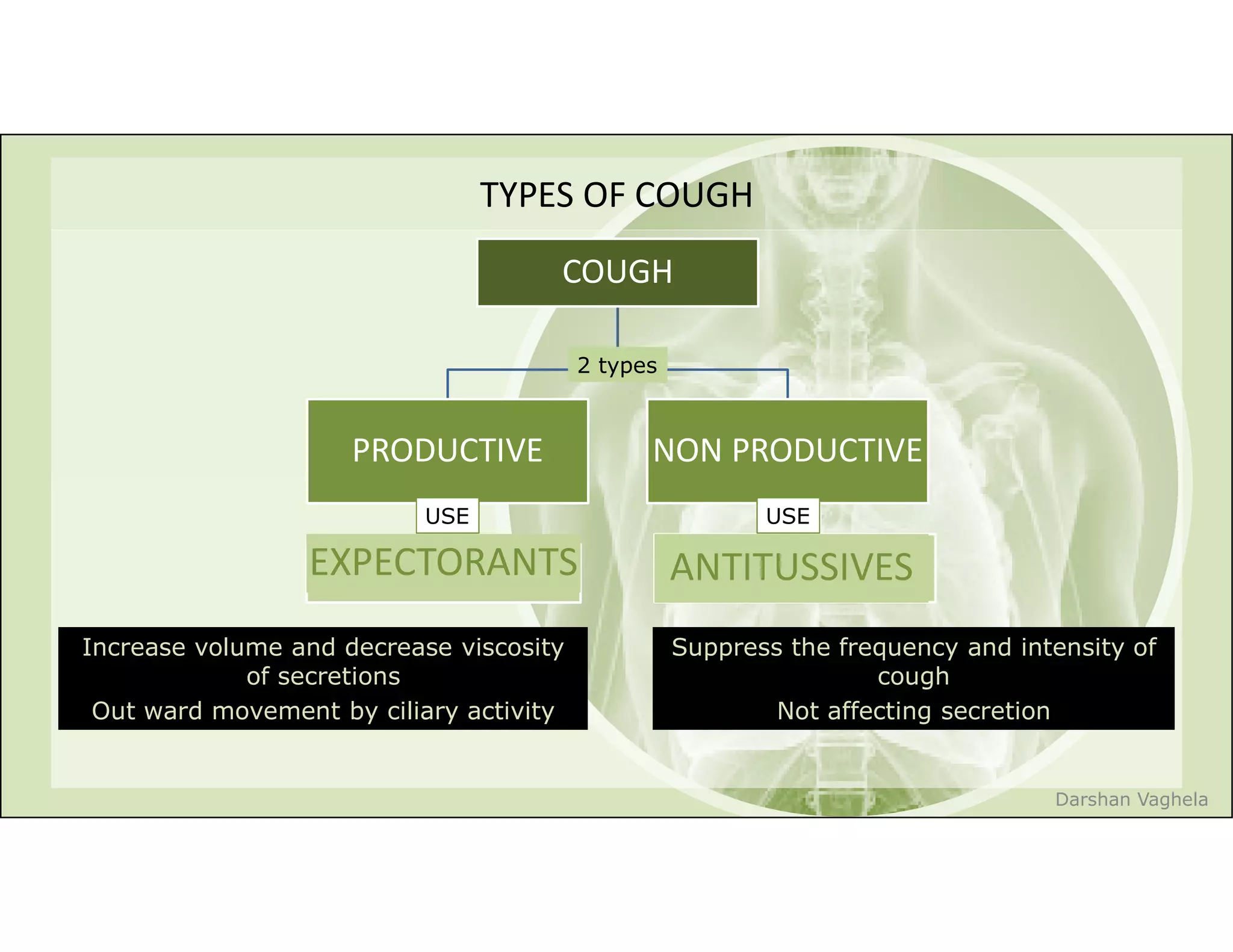
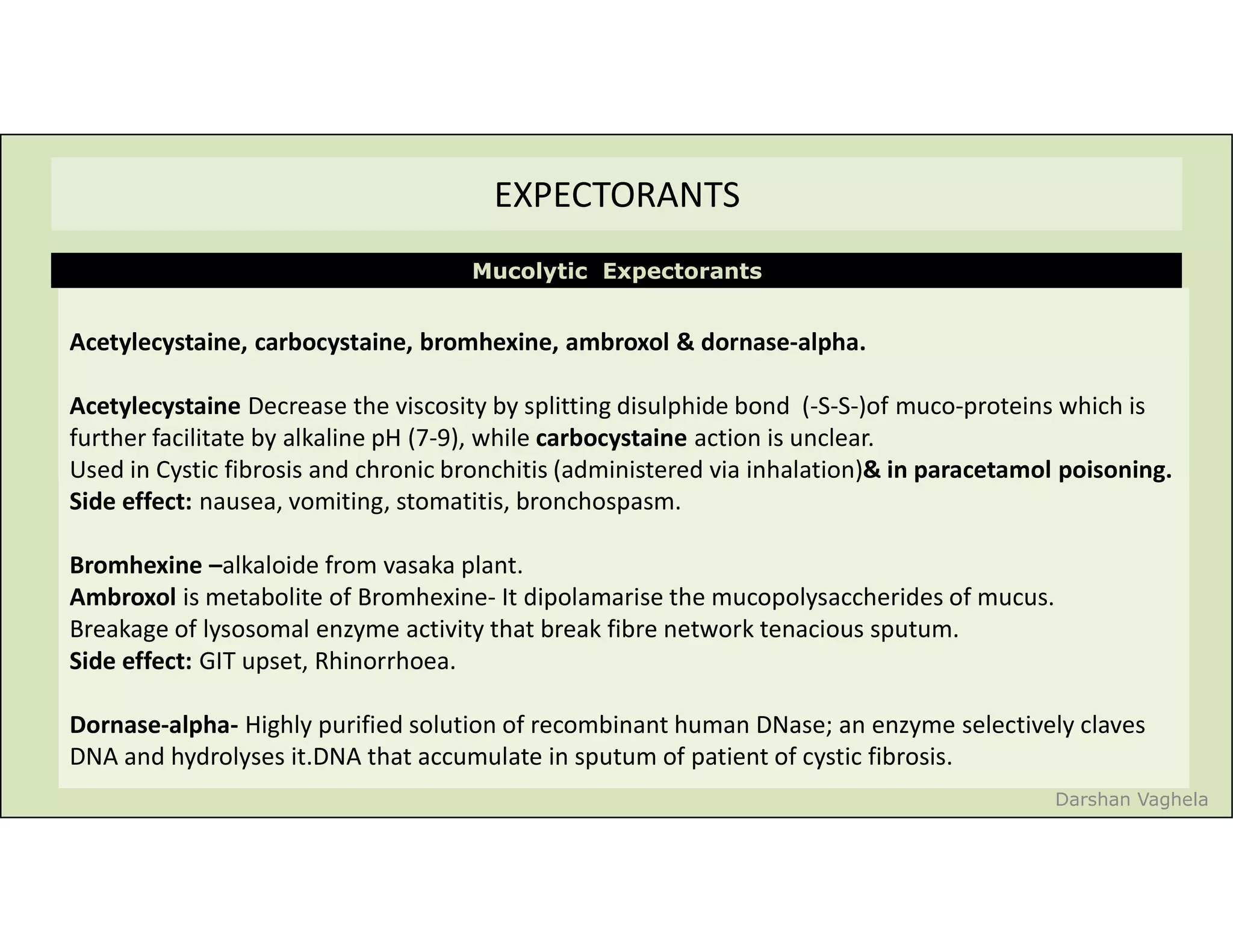
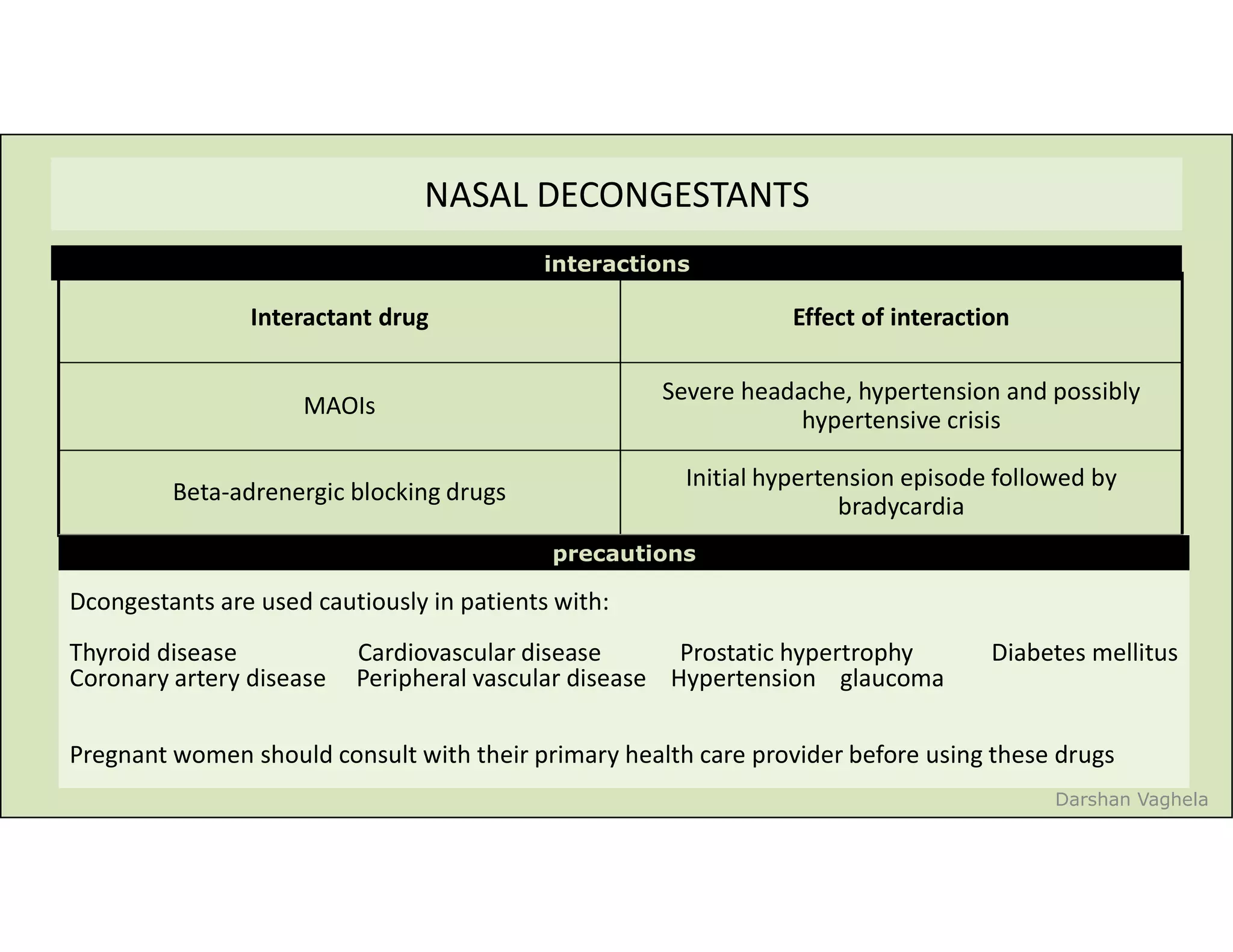
The document discusses respiratory pharmacology, focusing on types of cough, their treatment with expectorants and antitussives, and specific medications. It outlines the mechanisms of action, side effects, contraindications, and precautions for various antitussives and expectorants. Additionally, it covers nasal decongestants, their interactions, and contraindications in certain patient populations.