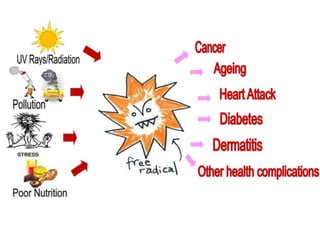
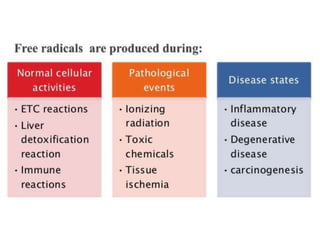
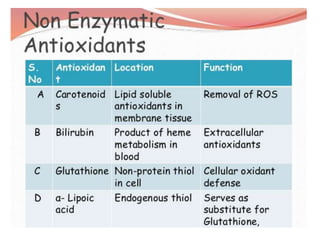
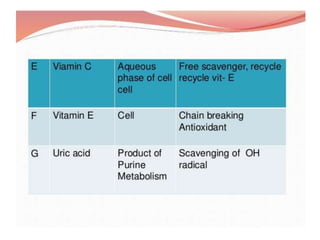
Antioxidants are compounds that can act as reducing agents and prevent oxidation reactions. They are used in pharmaceuticals to maintain easily oxidized substances in their reduced form. Oxidation causes damage to cells through free radicals but living organisms contain antioxidant systems like glutathione and vitamins C and E to prevent oxidative damage. Antioxidants prevent reactive oxygen species from being formed or remove them before they can harm cells. Hypophosphorous acid, sulfur dioxide, and sodium thiosulfate are official antioxidants used pharmaceutically to prevent oxidation.